Class Interface
See Also: Class FPStaticInterface, Class ViewExp, Class INode, Class INodeTab, Class CommandMode, Class Interval, Class Renderer, Class Modifier, Class Control, Class Atmospheric, Class Point3, Class Matrix3, Class ModContext, Class ReferenceTarget, Template Class Tab
class Interface : public FPStaticInterface
Description:
This class provides an interface for calling functions that are exported from the 3DStudio MAX executable. All the methods in this class are implemented by MAX itself.
Methods are provided for putting up many standard MAX dialogs, working with command modes, working with viewports, controlling the prompt, toolbar and status areas, and working with selection sets. There are also methods for creating objects and nodes in the scene, setting and getting the current time and animation ranges, working with the standard directories of MAX, and many more. See the Method Groups listed below for a breakdown of the various kinds of methods available.
Important Note for Finding Specific Methods:
To find documentation for a specific method choose the Help Topics button and the Index tab, then type:
methods, followed by the name of the method. Note the space after the comma -- this is required.
For example, enter
methods, ForceCompleteRedraw
This will jump directly to the Interface::ForceCompleteRedraw() method.
Note: When editing in the command panel, a developer gets passed an interface pointer during BeginEditParams(). This pointer is only valid before EndEditParams() is finished. A developer should not hang on to this pointer and call methods on it after EndEditParams() has returned.
Method Groups
These hyperlinks take you to the start of groups of related methods within the class.
Action Table and Menu Manager Methods
Ambient/Atmosphere/Background Access
Animation / Time / Playback Methods
Auto Backup Time Related Methods
Callback / Notification Registration
Command Panel and Rollup Page Methods
Deferred Loading Related Methods
Dialogs -- Methods to Display MAX Dialogs
Directory Access -- Plug-In / Bitmap Paths
Execute -- Generic Expansion Function
File Open / Merge / Save / Reset / Hold / Fetch
Fonts / Cursor Related Methods
Import / Export Related Methods
Keyboard Shortcut Related Methods
Material / Texmap Related Methods
Node Picking (Interactive Selection)
IObjCreate and IObjParam Pointer Casting
Renderer Access (also see Plug-In Renderer Access)
Right Click Menu Related Methods
Selection Sets (Nodes)Scene Access
Show End Result Related Methods
Sub-Object Selection Sets (Named)
Status Panel / Prompt Related Methods
Texmap / Material Related Methods
Time Configurations Key Steps Settings Access
Track Bar and Track View Related Methods
Transform Gizmo Related Methods
User Interface Controls and Properties
Viewport Access (Redrawing, etc)
Viewport Background Properties
Methods:
Animation / Time / Playback Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual TimeValue GetTime()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the current time, i.e. the frame slider position. See the Advanced Topics section on Time for an overview of time in MAX.
Prototype:
virtual void SetTime(TimeValue t, BOOL redraw=TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
Set the current time, updates the frame slider, and optionally redraws the viewports.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to set as current.
BOOL redraw=TRUE
If set to FALSE, the current time will be set to the specified time but the viewports will not be redrawn.
Prototype:
virtual Interval GetAnimRange()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the current setting of the animation interval. This can be used to get the total number of frames in the animation. Note: The values stored in the interval returned represent ticks not frames.
Prototype:
virtual void SetAnimRange(Interval range)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the animation interval. Note: The values passed in the interval are ticks not frames.
Parameters:
Interval range
Specifies the new animation range to set.
Prototype:
virtual void StartAnimPlayback(int selOnly=FALSE)=0;
Remarks:
Begins animation playback. The animation may be played for all objects, or just the selected ones.
Parameters:
int selOnly=FALSE
If TRUE only the selected objects are updated as the animation is played; otherwise all objects are.
Prototype:
virtual void EndAnimPlayback()=0;
Remarks:
Terminates the animation playback.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL IsAnimPlaying()=0;
Remarks:
Returns TRUE if the animation is currently playing; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void EnableAnimateButton(BOOL enable)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of the Animate button to enabled or disabled. When disabled the user cannot turn on Animate mode.
Note: Developers have additional functions available for controlling the state of the animate button. These functions are defined in \MAXSDK\INCLUDE\CONTROL.H. These functions can be used to determine if animating is on or off, or toggle it on and off without affecting the appearance of the Animate button in the user interface. In this way, a user will not be aware anything is happening. See List of Additional Controller Related Functions for documentation.
Parameters:
BOOL enable
Pass TRUE to enable the button; FALSE to disable it.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL IsAnimateEnabled()=0;
Remarks:
Returns TRUE if the Animate button is enabled; otherwise FALSE. See the note in the method above as well.
Prototype:
virtual void SetAnimateButtonState(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Turns the animate button (and animate mode) on or off.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE to turn on; FALSE to turn off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRealTimePlayback()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the state of the real-time animation playback toggle.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRealTimePlayback(BOOL realTime)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of the real-time animation playback toggle.
Parameters:
BOOL realTime
TRUE if frames should be dropped if necessary for the animation to play back in real time. FALSE specifies that every frame should be played.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetPlayActiveOnly()=0;
Remarks:
This method returns the flag controlling which viewports are updated when the animation is played.
Return Value:
TRUE if all the viewports are updated during play; FALSE if only the active viewport is updated.
Prototype:
virtual void SetPlayActiveOnly(BOOL playActive)=0;
Remarks:
This method sets the flag controlling which viewports are updated when the animation is played. This may be all the viewports, or just the active one.
Parameters:
BOOL playActive
If TRUE, only the active viewport is updated as the animation is played; otherwise all the viewports are updated.
Auto Backup Time Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual float GetAutoBackupTime()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns the auto backup interval in minutes.
Prototype:
virtual void SetAutoBackupTime(float minutes)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the auto backup time interval.
Parameters:
float minutes
The time to set in minutes.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL AutoBackupEnabled()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if auto backup mode is enabled; FALSE if it's disabled.
Prototype:
virtual void EnableAutoBackup(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Enables or Disables the auto backup system.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE to turn it on; FALSE to turn it off.
Action Table and Menu Manager Methods
Prototype:
virtual IActionManager* GetActionManager()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the Action Manager interface class. The action manager is used to manage ActionTables which plug-ins can use to export operations that can be tied to UI elements like keyboard shortcuts, menus and toolbars. See Class IActionManager.
Prototype:
virtual IMenuManager* GetMenuManager()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the manager for cusomizable menus. See Class IMenuManager.
Prototype:
virtual Matrix3 GetTransformAxis(INode *node,int subIndex,BOOL* local = NULL)=0;
Remarks:
An item that is doing sub-object hit testing gets to specify what their sub-object axes systems are. For example a mesh may have separate coordinate systems for every face or group of selected faces, while, for instance, a bend modifier has its own axes system for the gizmo. This method gets the axes system for a particular node. Each node may have several axes systems identified by an index.
See EDITMESH.CPP for an example of use.
Parameters:
INode *node
The node to get the axis coordinates system of.
int subIndex
The index of the axis system of the node.
BOOL* local = NULL
If 'local' is not NULL, it will be set to TRUE if the center of the axis is the pivot point of the node, FALSE otherwise.
Return Value:
The axis system of the node.
Prototype:
virtual int GetNumAxis()=0;
Remarks:
This returns the number of axis tripods in the scene. When transforming multiple sub-objects, in some cases each sub-object is transformed in a different space.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
NUMAXIS_ZERO
Nothing to transform.
NUMAXIS_ALL
Use only one axis.
NUMAXIS_INDIVIDUAL
Do all, one at a time.
Prototype:
virtual Matrix3 GetTransformAxis(INode *node, int subIndex, BOOL* local = NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns the axis which defines the space in which transforms should take place.
Parameters:
INode *node
The object the axis system should be based on.
int subIndex
The sub object which the axis system should be based on (the thing the user clicked on).
BOOL* local = NULL
If 'local' is not NULL, it will be set to TRUE if the center of the axis is the pivot point of the node, FALSE otherwise.
Return Value:
A matrix representing the axis system that transforms take place in.
Prototype:
virtual void LockAxisTripods(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method locks axis tripods so that they will not be updated.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE to lock; FALSE to unlock.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL AxisTripodLocked()=0;
Remarks:
This method returns TRUE if axis tripods are locked.
Bitmap / Texmap Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual void FreeSceneBitmaps()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method traverses the scene reference hierarchy, calling Animatable::FreeAllBitmaps() on every Animatable. This will free up all the memory used by bitmaps.
Prototype:
virtual void EnumAuxFiles(NameEnumCallback& nameEnum, DWORD flags)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method may be used to enumerate all the bitmap files in the scene. The flags allow control over which files are enumerated.
Parameters:
NameEnumCallback& nameEnum
The callback, called once for each bitmap. See Class NameEnumCallback.
DWORD flags
See List of EnumAuxFiles() Flags.
Prototype:
virtual void RenderTexmap(Texmap *tex, Bitmap *bm, float scale3d=1.0f, BOOL filter=FALSE, BOOL display=FALSE)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method may be called to render a texmap (or an entire texmap tree) to the specified bitmap.
Parameters:
Texmap *tex
The Texmap to render to a bitmap.
Bitmap *bm
A pointer to a bitmap to render to. This bitmap must be created at the resolution you wish to render to.
float scale3d=1.0f
This is a scale factor applied to 3D Texmaps. This is the scale of the surface in 3d space that is mapped to UV. This controls how much of the texture appears in the bitmap representation.
BOOL filter=FALSE
If TRUE the bitmap is filtered. It is quite a bit slower to rescale bitmaps with filtering on.
BOOL display=FALSE
If TRUE the resulting bitmap is displayed using the virtual frame buffer; otherwise it is not.
Prototype:
virtual bool CanImportBitmap(const TCHAR* filename)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method will check if the system can import the specified bitmap file.
Parameters:
const TCHAR* filename
The file name to check.
Return Value:
TRUE if the specified file is a bitmap file of a format that is supported by one of the bitmap reader plug-ins; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual bool CaptureSubObjectRegistration(bool OnOff, Class_ID cid)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method is used to lock and unlock subobject mode registrations and is primarily used by the FileLink wrapper classes acting as proxies to other classes in 3D Studio VIZ. When a class calls this method with OnOff set to TRUE, then other classes are prevented from registering new subobject modes. This continues until the original class "releases" by calling CaptureSubObjectModes(FALSE, myClassID). The second argument insures that only the class which does the capture can do the release. Note that this is used only by certain VIZ plugins.
Parameters:
bool OnOff
TRUE to prevent other classes from registering new subobject modes.
Class_ID cid
The class ID.
Return Value:
TRUE is successful, otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual bool DownloadUrl(HWND hwnd, const TCHAR* url, const TCHAR* filename, DWORD flags = 0)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method simplifies downloading files from any given URL and displays a floating progress dialog.
Parameters:
HWND hwnd
The window handle for owner window (required for the progress floating dialog).
const TCHAR* url
The string for the resource/file to download.
const TCHAR* filename
The target location and filename for the downloaded file.
DWORD flags = 0
Additional controls to the download behavior. Currently only one flag is supported, DOWNLOADDLG_NOPLACE, which hides an option in the progress dialog that allows the user to place (move) a dropped object immediately after being dropped.
Return Value:
TRUE if successful, otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual INode* GetImportCtxNode(void)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
On drag-and-drop, if the drop type is a file, the drop handler searches for an importer plugin that can handle the file (based on its extension). Some drop operations, such as bitmaps and material XML files, can or must be dropped on to an object in the scene.
Return Value:
The node that the operation is performed on, if one is "hit" at the drop location. It returns NULL if no nodes were found at the drop location.
Callback / Notification Registration
Related to callbacks is Structure NotifyInfo and its associated functions. Please see this topic for additional ways a developer can register a callback for events like the user performing a File/Reset or File/New, the system unit settings changing, etc.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterTimeChangeCallback(TimeChangeCallback *tc)=0;
Remarks:
Registers a callback object that will get called every time the user changes the MAX frame slider.
Parameters:
TimeChangeCallback *tc
Points to the callback object to register. See: Class TimeChangeCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void UnRegisterTimeChangeCallback(TimeChangeCallback *tc)=0;
Remarks:
This method un-registers the time change callback.
Parameters:
TimeChangeCallback *tc
Points to the callback object to un-register. See: Class TimeChangeCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterCommandModeChangedCallback(CommandModeChangedCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
Register a callback object that will get called when the user changes the command mode.
Parameters:
CommandModeChangedCallback *cb
Points to the callback object to register. See Class CommandModeChangedCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void UnRegisterCommandModeChangedCallback(CommandModeChangedCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
Un-registers the command mode change callback object.
Parameters:
CommandModeChangedCallback *cb
Points to the callback object to un-register. See Class CommandModeChangedCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterViewportDisplayCallback(BOOL preScene, ViewportDisplayCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Registers a ViewportDisplayCallback whose Display() method will be called to allow a plug-in to draw in the MAX viewports.
Parameters:
BOOL preScene
If TRUE the callback will be called before objects are rendered (typically, but not always); if FALSE the callback is called after the objects are rendered.
In some cases redrawing the viewports may take two passes; once to re-render the background plane and once to rerender the foreground plane. In this case the order of events would be:
Call pre callbacks
Render scene
Call post callbacks
Call pre callbacks
Render scene
Call post callbacks
The two calls to callbacks in the middle are neither pre nor post callbacks. However you could also look at this as two separate redraws.
ViewportDisplayCallback *cb
Points to the callback object. See Class ViewportDisplayCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void UnRegisterViewportDisplayCallback(BOOL preScene, ViewportDisplayCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Call this method to un-register the viewport display callback object.
Parameters:
BOOL preScene
If TRUE the callback will be called before object are rendered (typically, but not always); if FALSE the callback is called after the objects are rendered.
ViewportDisplayCallback *cb
Points to the callback object. See Class ViewportDisplayCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void NotifyViewportDisplayCallbackChanged(BOOL preScene, ViewportDisplayCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method is called to inform MAX that the viewport callback has changed. This is similar to when an object that is part of the reference hierarchy changes and it needs to call NotifyDependents() with the message REFMSG_CHANGE to inform the items that depend on it. In a sense a ViewportDisplayCallback is like an object in the scene in that it has a Display() method that is called. However, the callback is not actually an object that is part of the reference hierarchy so it cannot send a REFMSG_CHANGE message when it changes. So this method provides the equivalent functionality. If the callback changes this method needs to be called.
To understand why this is needed consider that if a plug-in called RedrawViews() five times in a row, the viewports may be redrawn the first time (if something has changed), but the next four calls won't do anything. This is because MAX maintains some flags that indicate if things have changed or not and these flags are reset on the first redraw to indicate that everything is up to date. Therefore, when a ViewportDisplayCallback changes, it needs to call this method to let MAX know that changes have been made and the viewports indeed need to be redrawn the next time RedrawViews() is called.
Parameters:
BOOL preScene
If TRUE the callback will be called before objects are rendered (typically, but not always); if FALSE the callback is called after the objects are rendered.
ViewportDisplayCallback *cb
Points to the callback object. See Class ViewportDisplayCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterExitMAXCallback(ExitMAXCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Registers a ExitMAXCallback whose Exit() method will be called when MAX is about to exit. The return value from the callback allows the plug-in to decide if MAX exits or not.
Parameters:
ExitMAXCallback *cb
Points to the callback object. See Class ExitMAXCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void UnRegisterExitMAXCallback(ExitMAXCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Un-registers the exit callback so it's no longer called.
Parameters:
ExitMAXCallback *cb
Points to the callback object. See Class ExitMAXCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterAxisChangeCallback(AxisChangeCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
Registers a callback object that will get called any time the user changes the reference coordinate system by:
Changing the transform coordinate system drop-down menu.
Changing the state of the transform center fly-off.
Changing X, Y, Z, XY, YZ, ZX constraint buttons/fly-off.
Using an accelerator or anything else that changes the above.
Parameters:
AxisChangeCallback *cb
Points to the callback to register. See AxisChangeCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void UnRegisterAxisChangeCallback(AxisChangeCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
Un-registers the axis change callback.
Parameters:
AxisChangeCallback *cb
Points to the callback to un-register. See AxisChangeCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterRedrawViewsCallback(RedrawViewsCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
Registers a call back object that gets called every time the viewports are redrawn. The proc() method is called after the views are finished redrawing.
Parameters:
RedrawViewsCallback *cb
Points to the callback object whose proc() method is called when the viewports are redrawn. See Class RedrawViewsCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void UnRegisterRedrawViewsCallback(RedrawViewsCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
Un-registers the viewport redraw callback.
Parameters:
RedrawViewsCallback *cb
Points to the callback object to un-register. See Class RedrawViewsCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterSelectFilterCallback(SelectFilterCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Registers a call back object that gets called to filter the selection of nodes.
Parameters:
SelectFilterCallback *cb
Points to the callback object to register. See Class SelectFilterCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void UnRegisterSelectFilterCallback(SelectFilterCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Un-registers the select filter callback.
Parameters:
SelectFilterCallback *cb
Points to the callback object to un-register. See Class SelectFilterCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterDisplayFilterCallback(DisplayFilterCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Registers a call back object that gets called to filter the display of nodes.
Parameters:
DisplayFilterCallback *cb
Points to the callback object to register. See Class DisplayFilterCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void UnRegisterDisplayFilterCallback(DisplayFilterCallback *cb)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Un-registers the display filter callback.
Parameters:
DisplayFilterCallback *cb
Points to the callback object to un-register. See Class DisplayFilterCallback.
Prototype:
virtual PickModeCallback* GetCurPickMode()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
If a Pick Mode is on top of the command stack, then this function will return the PickModeCallback. If the Pick Mode is not on top of the command stack the it returns NULL.
Prototype:
virtual INode *CreateObjectNode( Object *obj )=0;
Remarks:
Creates a new node in the scene with the given object. Normally a developer will use the standard creation methods for procedural objects and this method is not used. However if the developer wants to handle the creation process on their own they may need to use this method. See Also: Object Creation Methods.
Parameters:
Object *obj
Pointer to the Object to create.
Return Value:
Pointer to the node created.
Prototype:
virtual void *CreateInstance(SClass_ID superID, Class_ID classID)=0;
Remarks:
Creates an instance of a registered class. This will call Create() on the class descriptor.
Parameters:
SClass_ID superID
The super class ID of the item to create an instance of.
Class_ID classID
The class ID of the item to create an instance of. See Class Class_ID.
Return Value:
Pointer to the created instance.
Also Note:
There is a global method that duplicates the functionality of this class method to let you create an instance of any registered class wherever you are (without the interface pointer):
void *CreateInstance(SClass_ID superID, Class_ID classID);
Prototype:
virtual void NonMouseCreate(Matrix3 tm)=0;
Remarks:
This creates a new object/node without going through the usual create mouse proc sequence. The matrix is relative to the construction plane. This must be called during the creation phase of an object. For example, the procedural sphere uses it when the user clicks on the 'Create' button after they type in the parameters for the sphere. See Object Creation Methods.
Parameters:
Matrix3 tm
The transformation matrix relative to the construction plane.
Prototype:
virtual void NonMouseCreateFinish(Matrix3 tm)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method is presently only used in the Line object. It's used for repositioning the pivot point of the object at the end of the creation process. You simply pass it the new matrix, and the creation manager sets the TM for the node being created to the given TM * the construction plane TM.
Parameters:
Matrix3 tm
The transformation matrix relative to the construction plane for the node.
Prototype:
virtual void StopCreating()=0;
Remarks:
When a plug-in object implements its own ClassDesc::BeginCreate() / ClassDesc::EndCreate() it can cause EndCreate() to be called by calling this method. See Object Creation Methods.
Prototype:
virtual int BindToTarget(INode *laNode, INode *targNode)=0;
Remarks:
This method binds a node to a target using a lookat controller.
Parameters:
INode *laNode
Pointer to the node to assign the lookat controller to.
INode *targNode
Pointer to the target node.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if the node was bound; otherwise FALSE.
Sample Code:
This method is used in \MAXSDK\SAMPLES\OBJECTS\CAMERA.CPP.
For more information on CommandModes, see the Advanced Topics section Command Modes and Mouse Procs.
Prototype:
virtual void PushCommandMode(CommandMode *m)=0;
Remarks:
This method pushes the specified command mode on the stack. Typically this is used by developers handling their own creation using ClassDesc::BeginCreate(). See Class ClassDesc for more details.
Note: This method works as documented but a developer may not want to use it. The problem is that other modes can be pushed on the stack (such as viewport transformation modes) and it becomes complicated to track when it is OK to pop your mode. See the methods below for alternatives (such as SetCommandMode).
Parameters:
CommandMode *m
A pointer to the command mode to push.
Prototype:
virtual void SetCommandMode(CommandMode *m)=0;
Remarks:
This method sets the top of the stack to the specified command mode. A developer should call DeleteMode() to delete their command mode when done using it.
Parameters:
CommandMode *m
The command mode to set.
Prototype:
virtual void PopCommandMode()=0;
Remarks:
Pops the command mode off the top of the stack.
Prototype:
virtual CommandMode* GetCommandMode()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the current mode on the top of the stack.
Prototype:
virtual int GetCommandStackSize();
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns the number of command modes in the command mode stack.
Prototype:
virtual CommandMode* GetCommandStackEntry(int entry);
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the command mode at the specified position in the command mode stack. A developer may use this to determine if their command mode is in the stack.
Parameters:
int entry
The index into the command mode stack of the entry to get. Pass 0 to get the current command mode.
Prototype:
virtual void SetStdCommandMode(int cid)=0;
Remarks:
This is the typical method called by the developer to handle mouse interaction. It allows the developer to set the command mode to one of the standard command modes. For example: CID_OBJMOVE, CID_OBJROTATE, CID_OBJSCALE, CID_OBJUSCALE, CID_OBJSQUASH, CID_OBJSELECT, etc.
Parameters:
int cid
The index of the command mode to set. See List of Standard Command Modes to review the full list.
Prototype:
virtual void PushStdCommandMode(int cid)=0;
Remarks:
Allows the developer to push one of the standard command modes on the command stack. For example: CID_OBJMOVE, CID_OBJROTATE, CID_OBJSCALE, CID_OBJUSCALE, CID_OBJSQUASH, CID_OBJSELECT, etc.
Parameters:
int cid
The index of the command mode to set. See List of Standard Command Modes to review the full list.
Prototype:
virtual void RemoveMode(CommandMode *m)=0;
Remarks:
Removes the specified command mode from the stack. This method pops items off the command mode stack up to and including the specified mode. The top item in the stack is then set as the active command mode. As usual, ExitMode() is called on the specified mode before it is popped and EnterMode() is called on the newly active mode.
Parameters:
CommandMode *m
Points to the command mode to remove.
Prototype:
virtual void DeleteMode(CommandMode *m)=0;
Remarks:
If the developer sets or pushes a command mode, this method should be called when the developer is done with the mode to ensure that it is no longer anywhere in the stack. If the mode is already deleted this method does nothing.
Note: It is normal for a developer to set the 'Select and Move' command mode to be the active one if their mode was at the top of the stack and is being deleted. For instance:
ip->SetStdCommandMode(CID_OBJMOVE);
ip->DeleteMode(&myCMode);
Parameters:
CommandMode *m
The command mode to delete.
Command Panel and Rollup Page methods
Prototype:
virtual HWND AddRollupPage(HINSTANCE hInst, TCHAR *dlgTemplate, DLGPROC dlgProc, TCHAR *title, LPARAM param=0, DWORD flags=0, int category = ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD)=0;
Remarks:
This method is used to add a rollup page to the command panel. It returns the window handle of the rollup page.
Parameters:
HINSTANCE hInst
The DLL instance handle of the plug-in.
TCHAR *dlgTemplate
The dialog template for the rollup page.
DLGPROC dlgProc
The dialog proc to handle the messages sent to the rollup page.
TCHAR *title
The title displayed in the title bar of the rollup page.
LPARAM param=0
Any specific data to pass along may be stored here. This may be later retrieved using the GetWindowLong() call from the Windows API if it was set in the window using SetWindowLong().
For example, at the beginning of the dialog proc do something like:
BOOL CALLBACK MyDlgProc(
HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) {
MyUtil *u = (MyUtil *)GetWindowLong(hWnd, GWL_USERDATA);
if (!u && message != WM_INITDIALOG ) return FALSE;
. . .
Then inside the code block handling the WM_INITDIALOG message do something like:
switch (message) {
case WM_INITDIALOG:
u = (MyUtil *)lParam;
SetWindowLong(hWnd, GWL_USERDATA, (LONG)u);
. . .
Then later in the dialog you can access the object passed in -- in the case above an instance of MyUtil (using u->).
DWORD flags=0
The following flag value may be used:
APPENDROLL_CLOSED
Starts the page in the rolled up (closed) state.
int category = ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD
The category parameter provides flexibility with regard to where a particular rollup should be displayed in the UI. RollupPanels with lower category fields will be displayed before RollupPanels with higher category fields. For RollupPanels with equal category value the one that was added first will be displayed first. Allthough it is possible to pass any int value as category there exist currently 5 different category defines: ROLLUP_CAT_SYSTEM, ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD, and ROLLUP_CAT_CUSTATTRIB.
When using ROLLUP_SAVECAT, the rollup page will make the provided category sticky, meaning it will not read the category from the RollupOrder.cfg file, but rather save the category field that was passed as argument in the CatRegistry and in the RollupOrder.cfg file.
The method will take the category of the replaced rollup in case the flags argument contains ROLLUP_USEREPLACEDCAT. This is mainly done, so that this system works with param maps as well.
Sample Code:
hBendParams = ip->AddRollupPage(
hInstance,
MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_BEND_ROLLUP),
BendParamDialogProc,
_T("Parameters"),
(LPARAM)this );
Return Value:
The window handle of the rollup page.
Prototype:
virtual HWND AddRollupPage(HINSTANCE hInst, DLGTEMPLATE *dlgTemplate, DLGPROC dlgProc, TCHAR *title, LPARAM param=0, DWORD flags=0, int category = ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method is used to add a rollup page to the command panel. It returns the window handle of the rollup page. This method is currently not being used.
Parameters:
HINSTANCE hInst
The DLL instance handle of the plug-in.
DLGTEMPLATE *dlgTemplate
The dialog template for the rollup page.
DLGPROC dlgProc
The dialog proc to handle the messages sent to the rollup page.
TCHAR *title
The title displayed in the title bar of the rollup page.
LPARAM param=0
Any specific data to pass along may be stored here. This may be later retrieved using the GetWindowLong() call from the Windows API if it was set in the window using SetWindowLong().
DWORD flags=0
The following flag value may be used:
APPENDROLL_CLOSED
Starts the page in the rolled up (closed) state.
int category = ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD
The category parameter provides flexibility with regard to where a particular rollup should be displayed in the UI. RollupPanels with lower category fields will be displayed before RollupPanels with higher category fields. For RollupPanels with equal category value the one that was added first will be displayed first. Allthough it is possible to pass any int value as category there exist currently 5 different category defines: ROLLUP_CAT_SYSTEM, ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD, and ROLLUP_CAT_CUSTATTRIB.
When using ROLLUP_SAVECAT, the rollup page will make the provided category sticky, meaning it will not read the category from the RollupOrder.cfg file, but rather save the category field that was passed as argument in the CatRegistry and in the RollupOrder.cfg file.
The method will take the category of the replaced rollup in case the flags argument contains ROLLUP_USEREPLACEDCAT. This is mainly done, so that this system works with param maps as well.
Return Value:
The window handle of the rollup page.
Prototype:
virtual void DeleteRollupPage(HWND hRollup)=0;
Remarks:
Removes a rollup page and destroys it.
Parameters:
HWND hRollup
The window handle of the rollup window. This is the handle returned from AddRollupPage().
Prototype:
virtual HWND ReplaceRollupPage(HWND hOldRollup, HINSTANCE hInst, TCHAR *dlgTemplate, DLGPROC dlgProc, TCHAR *title, LPARAM param=0,DWORD flags=0, int category = ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This replaces an existing rollup with another one and (deletes the original).
Parameters:
HWND hOldRollup
The window handle of the old rollup.
HINSTANCE hInst
The DLL instance handle of the plug-in.
TCHAR *dlgTemplate
The dialog template for the rollup page.
DLGPROC dlgProc
The dialog proc to handle the messages sent to the rollup page.
TCHAR *title
The title displayed in the title bar of the rollup page.
LPARAM param=0
Any specific data to pass along may be stored here.
DWORD flags=0
The following flag value may be used:
APPENDROLL_CLOSED
Starts the page in the rolled up (closed) state.
int category = ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD
The category parameter provides flexibility with regard to where a particular rollup should be displayed in the UI. RollupPanels with lower category fields will be displayed before RollupPanels with higher category fields. For RollupPanels with equal category value the one that was added first will be displayed first. Allthough it is possible to pass any int value as category there exist currently 5 different category defines: ROLLUP_CAT_SYSTEM, ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD, and ROLLUP_CAT_CUSTATTRIB.
When using ROLLUP_SAVECAT, the rollup page will make the provided category sticky, meaning it will not read the category from the RollupOrder.cfg file, but rather save the category field that was passed as argument in the CatRegistry and in the RollupOrder.cfg file.
The method will take the category of the replaced rollup in case the flags argument contains ROLLUP_USEREPLACEDCAT. This is mainly done, so that this system works with param maps as well.
Return Value:
The window handle of the rollup.
Prototype:
virtual HWND ReplaceRollupPage(HWND hOldRollup, HINSTANCE hInst, TCHAR *dlgTemplate, DLGPROC dlgProc, TCHAR *title, LPARAM param=0,DWORD flags=0, int category = ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This replaces an existing rollup with another one and (deletes the original). This method is currently not being used.
Parameters:
HWND hOldRollup
The window handle of the old rollup.
HINSTANCE hInst
The DLL instance handle of the plug-in.
DLGTEMPLATE *dlgTemplate
The dialog template for the rollup page.
DLGPROC dlgProc
The dialog proc to handle the messages sent to the rollup page.
TCHAR *title
The title displayed in the title bar of the rollup page.
LPARAM param=0
Any specific data to pass along may be stored here.
DWORD flags=0
The following flag value may be used:
APPENDROLL_CLOSED
Starts the page in the rolled up (closed) state.
int category = ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD
The category parameter provides flexibility with regard to where a particular rollup should be displayed in the UI. RollupPanels with lower category fields will be displayed before RollupPanels with higher category fields. For RollupPanels with equal category value the one that was added first will be displayed first. Allthough it is possible to pass any int value as category there exist currently 5 different category defines: ROLLUP_CAT_SYSTEM, ROLLUP_CAT_STANDARD, and ROLLUP_CAT_CUSTATTRIB.
When using ROLLUP_SAVECAT, the rollup page will make the provided category sticky, meaning it will not read the category from the RollupOrder.cfg file, but rather save the category field that was passed as argument in the CatRegistry and in the RollupOrder.cfg file.
The method will take the category of the replaced rollup in case the flags argument contains ROLLUP_USEREPLACEDCAT. This is mainly done, so that this system works with param maps as well.
Return Value:
The window handle of the rollup.
Prototype:
virtual IRollupWindow *GetCommandPanelRollup()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method returns a rollup window interface to the command panel rollup. This interface provides methods for showing and hiding rollups, adding and removing rollup pages, etc. Note: This interface does not need to be released with ReleaseIRollup() as MAX takes care of this when it shuts down.
See Class IRollupWindow.
Prototype:
virtual void RollupMouseMessage(HWND hDlg, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam )=0;
Remarks:
This method allows hand cursor scrolling in the command panel when the user clicks and drags the mouse in an unused area of the dialog. When the user mouse-es down in dead area of the command panel, the plug-in should pass mouse messages to this function which will pass them on to the rollup.
Note: This method is obsolete in MAX 2.0 and later. These messages no longer need to be passed along as this is handled internally.
Parameters:
HWND hDlg
The window handle of the dialog.
UINT message
The message sent to the dialog proc.
WPARAM wParam
Passed in to the dialog proc. Pass along to this method.
LPARAM lParam
Passed in to the dialog proc. Pass along to this method.
Sample Code:
case WM_LBUTTONDOWN: case WM_LBUTTONUP: case WM_MOUSEMOVE:
ip->RollupMouseMessage(hDlg,message,wParam,lParam);
Prototype:
virtual int GetCommandPanelTaskMode()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns a value to indicate which brach of the command panel is currently active.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
TASK_MODE_CREATE
TASK_MODE_MODIFY
TASK_MODE_HIERARCHY
TASK_MODE_MOTION
TASK_MODE_DISPLAY
TASK_MODE_UTILITY
Prototype:
virtual void SetCommandPanelTaskMode(int mode)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method sets the brach of the command panel that is currently active.
Parameters:
int mode
One of the following values:
TASK_MODE_CREATE
TASK_MODE_MODIFY
TASK_MODE_HIERARCHY
TASK_MODE_MOTION
TASK_MODE_DISPLAY
TASK_MODE_UTILITY
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterDeleteUser(EventUser *user)=0;
Remarks:
Registers a callback invoked when the user presses the Delete Key. This allows the developer to override the default processing of the Delete Key.
Parameters:
EventUser *user
Pointer to an instance of the EventUser class.
Sample Code:
See \MAXSDK\SAMPLES\MODIFIERS\EDITSPL.CPP.
Prototype:
virtual void UnRegisterDeleteUser(EventUser *user)=0;
Remarks:
Un-registers a Delete Key callback.
Parameters:
EventUser *user
Pointer to an instance of the EventUser class.
Dialogs -- Methods to Display MAX dialogs
This section describes methods to put up many of the standard dialog boxes used by MAX. Some dialogs are accessed outside of this class. For the Arc Rotate dialog box see Class ArcballDialog. For the modal or modeless color selector dialog see Class ColorPicker. For a Win32 MessageBox() like function that supports 'Hold' and 'Don't show this dialog again' items see List of Miscellaneous Utility Functions.
Prototype:
virtual void PutMtlToMtlEditor(MtlBase *mb , int slot=-1)=0;
Remarks:
Puts the specified material into the material editor. The material is put to the specified slot, or if -1 is passed, the following dialog is presented which allows the user to choose a sample slot for the material.
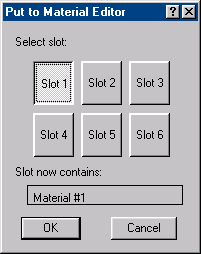
Parameters:
MtlBase *mb
The material to put to the material editor.
int slot=-1
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
The Materials Editor slot number (a value in the range 0 to 23). If a slot number is specified, then this method will replace that material in the Materials Editor without user interaction. If -1 is passed (the default) then the function brings up the put dialog.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL TrackViewPickDlg(HWND hParent, TrackViewPick *res, TrackViewFilter *filter=NULL, DWORD flags=0)=0;
Remarks:
This method brings up the track view pick dialog. This dialog appears below:
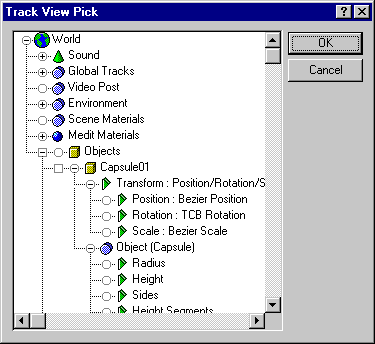
Parameters:
HWND hParent
The handle of the parent window.
TrackViewPick *res
The item chosen by the user. See Class TrackViewPick
TrackViewFilter *filter=NULL
The call back object to filter selection in the track view. See Class TrackViewFilter.
DWORD flags=0
Currently not used.
Return Value:
TRUE if the user selected OK to exit the dialog; otherwise FALSE.
Sample Code:
This code brings up the Track View Pick Dialog and filters the input to MAX's controllers. After the controller is selected GetValue() is called on it.
class MyTVFilter : public TrackViewFilter {
BOOL proc(Animatable *anim, Animatable *client,int subNum) {
Control *c = (Control*)anim->GetInterface(I_CONTROL);
return (c) ? TRUE : FALSE;
}
};
void DoTest() {
TrackViewPick res;
MyTVFilter tvf;
BOOL okay = IP->TrackViewPickDlg(IP->GetMAXHWnd(), &res, &tvf);
if (!okay) return;
Control *c = (Control *)res.anim;
SClass_ID sid = c->SuperClassID();
GetSetMethod method = CTRL_ABSOLUTE;
switch(sid) {
case CTRL_FLOAT_CLASS_ID:
float r;
Interval ivalid;
c->GetValue(IP->GetTime(), &r, ivalid, method);
...
Prototype:
virtual BOOL TrackViewPickMultiDlg(HWND hParent, Tab<TrackViewPick> *res, TrackViewFilter *filter=NULL,DWORD flags=0)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This methods brings up a dialog that allows one to select multiple tracks. This method works much like the TrackViewPickDlg method above except it is passed a pointer to a table of a TrackViewPick items instead.
Parameters:
HWND hParent
The handle of the parent window.
Tab<TrackViewPick> *res
This is a table (See Template Class Tab) of items chosen by the user. See Class TrackViewPick
TrackViewFilter *filter=NULL
The call back object to filter selection in the track view. See Class TrackViewFilter.
DWORD flags=0
Currently not used.
Prototype:
virtual int DoExclusionListDialog(ExclList *nl, BOOL doShadows=TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
This brings up the standard Exclude / Include dialog box used for light exclusion / inclusion lists. This dialog appears below:
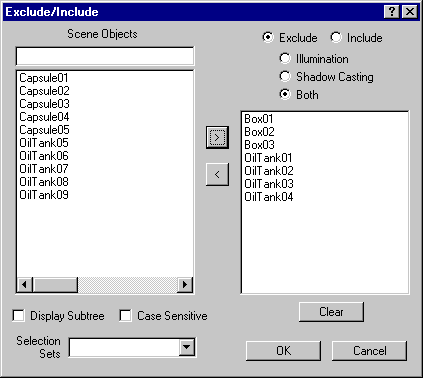
Parameters:
ExclList *nl
If the user selects OK, this is the list of names chosen by the user. See Class ExclList.
BOOL doShadows=TRUE
The shadows switch.
Return Value:
Nonzero if the user selected OK to exit the dialog; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual void ConvertNameTabToExclList(const NameTab *nt, ExclList *excList)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method will convert a NameTab to an ExclList (the new format for Exclusion lists).
Parameters:
const NameTab *nt
A pointer to the name table.
ExclList *excList
A pointer to the resulting exclusion list.
Prototype:
virtual MtlBase *DoMaterialBrowseDlg(HWND hParent,DWORD flags,BOOL &newMat,BOOL &cancel)=0;
Remarks:
This method brings up the Material / Map Browser dialog box. This dialog appears below:
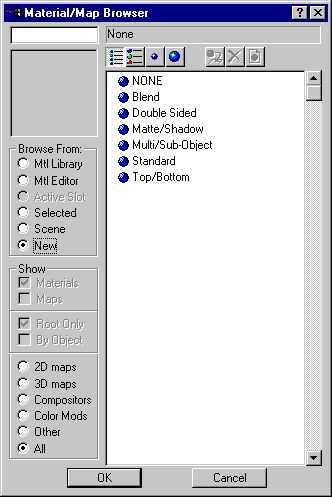
Parameters:
HWND hParent
The parent window handle.
DWORD flags
See List of Material Browser Flags.
BOOL &newMat
TRUE if the user has selected a new item; otherwise FALSE. If TRUE it is safe to modify this item. If FALSE the item may be an instance and a developer should not modify this as other materials may be using this same item.
BOOL &cancel
TRUE if the user canceled the dialog; otherwise FALSE.
Return Value:
If cancel is FALSE, the item chosen by the user is returned. See Class MtlBase.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL DoHitByNameDialog(HitByNameDlgCallback *hbncb=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
Implemented by the Plug-In.
This method is called to put up the standard MAX Hit By Name dialog. This dialog appears below:
If the callback is NULL this method does a standard select by name. The nodes choosen by the user are selected if the user selects 'Select' from the dialog to exit. Use Interface::GetSelNodeCount() and GetSelNode(i) to retrieve the results.
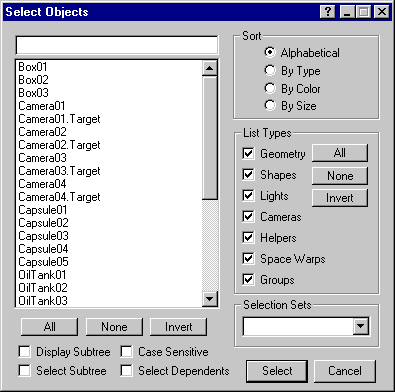
Parameters:
HitByNameDlgCallback *hbncb=NULL
Points to the callback object. See Class HitByNameDlgCallback. Developers should delete this callback when done.
Return Value:
TRUE if the user selects 'Select' from the dialog; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL NodeColorPicker(HWND hWnd,DWORD &col)=0;
Remarks:
This method brings up the standard MAX object color picker dialog. This dialog appears below:
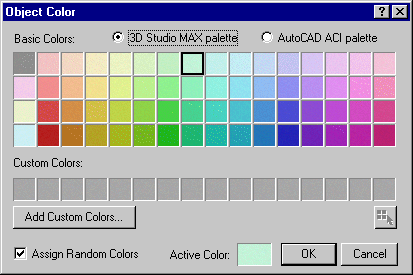
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
The parent window handle.
DWORD &col
If the user picks a color then this will be set to the chosen color. This is stored in a 32 bit format, with the high order 8 bits as 0's, the next 8 bits as the Blue amount, the next 8 bits as the Green amount, and the low order 8 bits as the Red amount (0x00BBGGRR). See COLORREF - DWORD Color Format.
Return Value:
TRUE if the user picks a color and FALSE if the user cancels the dialog.
Prototype:
virtual void ChooseDirectory(HWND hWnd, TCHAR *title, TCHAR *dir, TCHAR *desc=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This methods puts up the Choose Directory dialog box to allow the user to select a directory. The choosen directory including the drive and path is stored in dir. This dialog appears below:
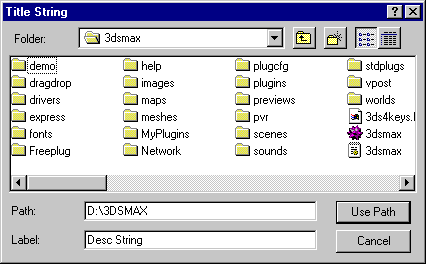
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
The parent window handle.
TCHAR *title
The title in the dialog box.
TCHAR *dir
The choosen directory is stored here. This points to an empty string on cancel.
TCHAR *desc=NULL
The string to go into the Label field of the dialog. This string may be changed by the user and is returned here.
Prototype:
virtual int ConfigureBitmapPaths()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method puts up the dialog to let the user configure the bitmap loading paths. This dialog appears below:
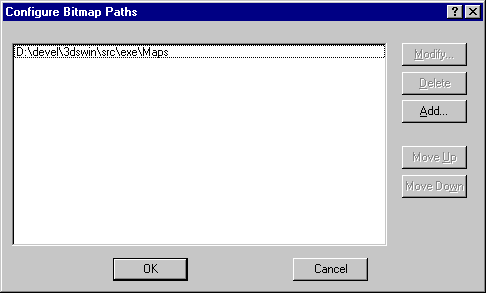
Return Value:
Nonzero on user selecting OK, zero on Cancel.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL DoSpaceArrayDialog(SpaceArrayCallback *sacb=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Puts up the space array dialog. If the callback is NULL it just does the standard space array tool.
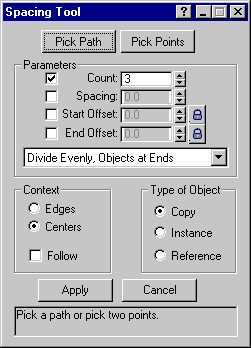
Parameters:
SpaceArrayCallback *sacb=NULL
The callback. See Class SpaceArrayCallback.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if the user OKs the dialog, otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void RAMPlayer(HWND hWndParent, TCHAR* szChanA=NULL, TCHAR* szChanB=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Brings up the RAMPlayer dialog and optionally loads one, or both channels with the supplied files.
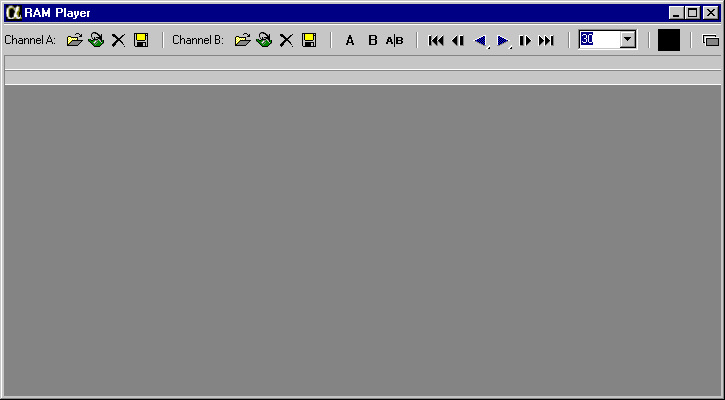
Parameters:
HWND hWndParent
The parent window handle.
TCHAR* szChanA=NULL
The file to load for channel A (for example, _T("movie.avi")). If NULL is passed no file is loaded into the channel.
TCHAR* szChanB=NULL
The file to load for channel B. If NULL is passed no file is loaded into the channel.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterDlgWnd(HWND hDlg)=0;
Remarks:
Registers a dialog window so IsDialogMessage() gets called for it. This is not required if you add rollup pages to the command panel as this is done automatically, however if you create a floating, modeless dialog you must call this method.
Important Note: ALL modeless dialogs in MAX must be registered to the application window with this method so that it, and any sub dialogs, will behave as they should.
Parameters:
HWND hDlg
The window handle of the dialog.
Prototype:
virtual int UnRegisterDlgWnd(HWND hDlg)=0;
Remarks:
Un-registers a dialog window so IsDialogMessage() is no longer called for it.
Parameters:
HWND hDlg
The window handle of the dialog.
Return Value:
Nonzero if successful; otherwise 0.
Directory Access -- Plug-In and Bitmap Paths
Prototype:
virtual TCHAR *GetDir(int which)=0;
Remarks:
Returns the pathname of a directory used by 3ds max.
Parameters:
int which
One of the following directories. See List of Directory Names.
Return Value:
The pathname of the directory.
Prototype:
virtual int GetPlugInEntryCount()=0;
Remarks:
This is the number of entries in PLUGIN.INI. PLUGIN.INI contains a list of descriptions and directories used by plug-in DLLs. See Also: Plug-In Directory Search Mechanism.
Return Value:
The number of entries in PLUGIN.INI.
Prototype:
virtual TCHAR *GetPlugInDesc(int i)=0;
Remarks:
Returns the 'i-th' description string from PLUGIN.INI. See Also: Plug-In Directory Search Mechanism.
Parameters:
int i
Specifies which description to return.
Return Value:
The 'i-th' description string from PLUGIN.INI.
Prototype:
virtual TCHAR *GetPlugInDir(int i)=0;
Remarks:
Returns the pathname string for the 'i-th' plug-in directory from PLUGIN.INI. See Also: Plug-In Directory Search Mechanism.
Parameters:
int i
Specifies which directory to return.
Return Value:
The 'i-th' pathname string from PLUGIN.INI.
Prototype:
virtual DllDir& GetDllDir()=0;
Remarks:
Returns a reference to the central DLL directory. See Class DllDir.
Prototype:
virtual DllDir *GetDllDirectory()=0;
Remarks:
Returns a pointer to the central DLL directory. See Class DllDir.
The following methods allow a developer to write to the error log file created in each network server's directory. These three methods allow more detailed information to be recorded than the single line error message that is returned to the network "master" when a render fails. If there is any place in your code where an Alert is put up that might be encountered during rendering, you can print the information out to the error log instead.
Prototype:
virtual LogSys *Log()=0;
Remarks:
Returns a pointer which may be used for calling methods to write information to the system log. See Class LogSys for details.
Prototype:
virtual Texmap *GetEnvironmentMap()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the current environment map.
Prototype:
virtual void SetEnvironmentMap(Texmap *map)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the current environment map to the specified map. See \MAXSDK\SAMPLES\UTILITIES\UTILTEST.CPP for sample code.
Parameters:
Texmap *map
The map to set.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetUseEnvironmentMap()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the 'Use Map' checkbox is checked in the Environment / Background dialog; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void SetUseEnvironmentMap(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the state of the 'Use Map' checkbox in the Environment / Background dialog.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for checked; FALSE for unchecked.
Prototype:
virtual Point3 GetAmbient(TimeValue t,Interval &valid)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Retrieves the color of the ambient light at the time passed and updates the validity interval passed to reflect the validity of the ambient light.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to retrieve the ambient light color.
Interval &valid
The validity interval to update.
Return Value:
The color as a Point3.
Prototype:
virtual void SetAmbient(TimeValue t, Point3 col)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the color of the ambient light in the scene to the color passed at the specified time.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to set the color.
Point3 col
The new color for the ambient light.
Prototype:
virtual Control *GetAmbientController()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Retrieves a pointer to the controller use to animate the ambient light.
Prototype:
virtual void SetAmbientController(Control *c)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the controller used for handling the animation of the ambient light.
Parameters:
Control *c
The controller to set.
Prototype:
virtual Point3 GetLightTint(TimeValue t,Interval &valid)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns the rendering environment global lighting tint color at the specified time and updates the validity interval passed to reflect the validity of the tint color controller.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time at which to return the color.
Interval &valid
The validity interval that is updated.
Prototype:
virtual void SetLightTint(TimeValue t, Point3 col)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the rendering environment global lighting tint color at the specified time to the color passed.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time at which to set the color.
Point3 col
The color to set.
Prototype:
virtual Control *GetLightTintController()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the controller use to animate the tint color.
Prototype:
virtual void SetLightTintController(Control *c)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the controller use to animate the tint color.
Parameters:
Control *c
Points to the controller to set.
Prototype:
virtual float GetLightLevel(TimeValue t,Interval &valid)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns the rendering environment global lighting level at the specified time and updates the validity interval passed to reflect the validity of the lighting level controller.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time at which to return the level.
Interval &valid
The validity interval that is updated.
Prototype:
virtual void SetLightLevel(TimeValue t, float lev)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the rendering environment global lighting level at the specified time.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time at which to set the lighting level.
float lev
The level to set.
Prototype:
virtual Control *GetLightLevelController()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the controller use to animate the lighting level.
Prototype:
virtual void SetLightLevelController(Control *c)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the controller use to animate the lighting level.
Parameters:
Control *c
Points to the controller to set.
Prototype:
virtual int NumAtmospheric()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns the number of atmospheric effects currently assigned.
Prototype:
virtual Atmospheric *GetAtmospheric(int i)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the 'i-th' atmospheric effect.
Parameters:
int i
Specifies which atmospheric effect to retrieve.
Prototype:
virtual void SetAtmospheric(int i,Atmospheric *a)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the 'i-th' atmospheric effect.
Parameters:
int i
Specifies which effect to set.
Atmospheric *a
A pointer to the atmospheric effect.
Prototype:
virtual void AddAtmosphere(Atmospheric *atmos)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Adds the specified atmospheric effect to the list of effects.
Parameters:
Atmospheric *a
A pointer to the atmospheric effect to add.
Prototype:
virtual void DeleteAtmosphere(int i)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Deletes the specified atmospheric effect.
Parameters:
int i
The index of the atmospheric effect to delete.
Prototype:
virtual void EditAtmosphere(Atmospheric *a, INode *gizmo=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method selects the specified atmosphere's gizmo and displays the parameters for it (if any).
Parameters:
Atmospheric *a
Points to the Atmospheric plug-in. See Class Atmospheric.
INode *gizmo=NULL
Points to the gizmo node associated with the plug-in.
Prototype:
virtual int NumEffects()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns the number of Render Effects currently assigned.
Prototype:
virtual Effect *GetEffect(int i)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the 'i-th' Render Effect. See Class Effect.
Parameters:
int i
The zero based index of the effect to return.
Prototype:
virtual void SetEffect(int i, Effect *e)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets the specified Render Effect to the one passed.
Parameters:
int i
The zero based index of the effect to set.
Effect *e
Points to the Renderer Effect to set.
Prototype:
virtual void AddEffect(Effect *eff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Adds the specified Renderer Effect to the existing list of effects.
Parameters:
Effect *eff
Points to the render effect to add. See Class Effect.
Prototype:
virtual void DeleteEffect(int i)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Deletes the specified Renderer Effect.
Parameters:
int i
The zero based index of the effect to delete.
Prototype:
virtual void EditEffect(Effect *e, INode *gizmo=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method selects the specified gizmo and displays the parameters for it (if any).
Parameters:
Effect *e
Points to the Effect plug-in. See Class Effect.
INode *gizmo=NULL
Points to the gizmo node associated with the effect.
Prototype:
virtual Point3 GetBackGround(TimeValue t,Interval &valid)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Retrieves the background color at the specified time and updates the validity interval passed to reflect the validity of the background color.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to retrieve the color.
Interval &valid
The validity interval to update.
Prototype:
virtual void SetBackGround(TimeValue t,Point3 col)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the background color to the specified color at the specified time.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to set the color.
Point3 col
The color to set.
Prototype:
virtual Control *GetBackGroundController()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the controller animating the background color.
Prototype:
virtual void SetBackGroundController(Control *c)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the controller used for animating the background color.
Parameters:
Control *c
Specifies which controller to set.
Prototype:
virtual void ExecuteMAXCommand(int id)=0;
Remarks:
This method may be used to execute a MAX command. These are the same commands that may be assigned using the MAX Customize/Preferences.../Keyboard Tab key assignment system.
For MAX version 1.1 or later, this method may also be used to set various aspects of the preview display. The id to pass for these options is shown below:
ExecuteMAXCommand(MAXCOM_API_PVW_GRID_OFF)
This turns off the preview grid display.
ExecuteMAXCommand(MAXCOM_API_PVW_GRID_ON)
This turns on the preview grid display.
ExecuteMAXCommand(MAXCOM_API_PVW_SMOOTH_MODE)
This sets the preview rendering mode to "smooth".
ExecuteMAXCommand(MAXCOM_API_PVW_FACET_MODE)
This sets the preview rendering mode to "facet".
ExecuteMAXCommand(MAXCOM_API_PVW_WIRE_MODE)
This sets the preview rendering mode to "wireframe".
Note: In MAX 2.0 and later there is an alternate (better) way to do this. See the method:
virtual void CreatePreview(PreviewParams *pvp=NULL)=0;
Parameters:
int id
The command to execute. See List of MAX Command IDs.
Execute -- General API Expansion Function
Prototype:
virtual INT_PTR Execute(int cmd, ULONG_PTR arg1=0, ULONG_PTR arg2=0, ULONG_PTR arg3=0, ULONG_PTR arg4=0, ULONG_PTR arg5=0, ULONG_PTR arg6=0)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This is a general purpose function that allows the API to be extended in the future. The MAX development team can assign new cmd numbers and continue to add functionality to this class without having to 'break' the API.
Note: In R4 the return value changed from int to INT_PTR
New in R5.1 An additional Command was added to allow the setting of certain directories such as Plugins. It looks like this:
Execute(I_EXEC_SET_DIR, (ULONG_PTR)(int) which, ULONG_PTR)(TCHAR *)dir)
where 'which' designates the particular Max directory to be changed (like the corresponding argument of Interface::GetDir()), and 'dir' is the path as a string.
Parameters:
int cmd
The index of the command to execute. See List of Interface::Execute Command Options.
ULONG arg1=0
Optional argument 1. See the documentation where the cmd option is discussed for more details on these parameters.
ULONG arg2=0
Optional argument 2.
ULONG arg3=0
Optional argument 3.
ULONG arg4=0
This parameter is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Optional argument 4.
ULONG arg5=0
This parameter is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Optional argument 5.
ULONG arg6=0
This parameter is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Optional argument 6.
Return Value:
An INT_PTR return value. See the documentation where the cmd option is discussed for more details on the meaning of this value.
Prototype:
virtual void SetExtendedDisplayMode(int flags)=0;
Remarks:
This method is used internally to set the extended display mode.
Parameters:
int flags
See List of Extended Display Modes.
Prototype:
virtual int GetExtendedDisplayMode()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the extended display mode flags. This method provides a mechanism to retrieve some additional information about an object that is more dependent on MAX than on the particular object. For example, when a spotlight is selected, it can use this method to detect that it is the only item selected, and display its cone. It checks this using and extended display mode EXT_DISP_ONLY_SELECTED. See List of Extended Display Modes.
Prototype:
virtual TSTR &GetCurFileName()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the name of the current MAX file (but not the path). For example, if the currently loaded file is "D:\3DSMAX\SCENES\Expgears.max" this method returns " Expgears.max".
Prototype:
virtual TSTR &GetCurFilePath()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the file and path of the current MAX file. For example, if the currently loaded file is "D:\3DSMAX\SCENES\Expgears.max" this method returns "D:\3DSMAX\SCENES\Expgears.max ".
Prototype:
virtual TCHAR *GetMatLibFileName()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the current material library file name.
File Open/Merge/Save/Reset/Hold/Fetch Methods
For file IO using the MAX import / export mechanism see the section: Import / Export Related Methods.
Prototype:
virtual bool IsMaxFile(const TCHAR* filename)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns true if the specified file is a valid MAX file; otherwise false.
Parameters:
const TCHAR* filename
The name of the file to check.
Prototype:
virtual bool IsInternetCachedFile(const TCHAR* filename)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns true if the specified file is an internet cached file; otherwise false.
Parameters:
const TCHAR* filename
The name of the file to check.
Prototype:
virtual void SetMAXFileOpenDlg(MAXFileOpenDialog* dlg)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method allows a custom file open dialog to be registered.
Parameters:
MAXFileOpenDialog* dlg
Points to the file open dialog object to use. See Class MAXFileOpenDialog.
Prototype:
virtual void SetMAXFileSaveDlg(MAXFileSaveDialog* dlg)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method allows a custom file save dialog to be registered.
Parameters:
MAXFileSaveDialog* dlg
Points to the file save dialog object to use. See Class MAXFileSaveDialog.
Prototype:
virtual void FileOpenMatLib(HWND hWnd)=0;
Remarks:
This method brings up the File Open dialog box and allows the user to select a material library to load.
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
The parent window handle.
Prototype:
virtual void FileSaveMatLib(HWND hWnd)=0;
Remarks:
If the current material library has been saved previously (has been named) this method saves the material library to the same file. Otherwise it brings up the standard Save File As dialog box to allow the user to save the current material library.
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
The parent window handle.
Prototype:
virtual void FileSaveAsMatLib(HWND hWnd)=0;
Remarks:
Brings up the standard Save File As dialog box to allow the user to save the current material library.
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
The parent window handle.
Prototype:
virtual void LoadDefaultMatLib()=0;
Remarks:
This method loads the default material library 3DSMAX.MAT (if this file exists).
Prototype:
virtual int LoadFromFile(const TCHAR *name, BOOL refresh=TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
Loads the specified MAX file. A developer should normally specify a complete path name. This method does not bring up a file dialog.
Parameters:
const TCHAR *name
The MAX file to load.
BOOL refresh=TRUE
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Set this to FALSE to prevent the viewports from automatically being refreshed.
Return Value:
Nonzero if the file was loaded; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual int SaveToFile(const TCHAR *fname)=0;
Remarks:
Saves the current scene to the specified MAX file. This method does not bring up a file dialog.
Parameters:
const TCHAR *name
The MAX file to save.
Return Value:
Nonzero if the library was saved; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual void FileSaveSelected(TCHAR *fname)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Saves the selected nodes to the specified file.
Parameters:
TCHAR *fname
The MAX file to save.
Prototype:
virtual void FileSaveNodes(INodeTab* nodes, TCHAR *fname)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Saves the specified nodes to the specified file.
Parameters:
INodeTab* nodes
Points to the table of nodes to save. See Class INodeTab.
TCHAR *fname
The MAX file to save.
Prototype:
virtual int LoadMaterialLib(const TCHAR *name, MtlBaseLib *lib=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
Loads the specified material library. This method does not bring up a file dialog.
Parameters:
const TCHAR *name
The material library to load.
MtlBaseLib *lib=NULL
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Points to the material library to load into. If NULL the library is loaded into the current material library. See Class MtlBaseLib.
Note: You need to call MtlBaseLib::DeleteAll() on the library during a MAX reset operation. This will remove all its references to the materials and set its count to zero.
Return Value:
Nonzero if the library was loaded; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual int SaveMaterialLib(const TCHAR *name, MtlBaseLib *lib=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
Saves the specified material library to the specified file. This method does not bring up a file dialog.
Parameters:
const TCHAR *name
The material library to save.
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Points to the material library to save from. If NULL the library is saved from the current material library. See Class MtlBaseLib.
Return Value:
Nonzero if the library was saved; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual int MergeFromFile(const TCHAR *name, BOOL mergeAll=FALSE, BOOL selMerged=FALSE, BOOL refresh=TRUE, int dupAction = MERGE_DUPS_PROMPT, NameTab* mrgList=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
Merges the specified MAX file into the current scene. In MAX 2.0 and later additional parameters allow automatic viewport updates to be optionally be turned off, cases of duplicate objects being merged may be handled, a table of names of the merged objects may be generated, and only specific named objects from the file may be merged.
Parameters:
const TCHAR *name
The MAX file to merge.
BOOL mergeAll=FALSE
If TRUE all the items in the file are merged; otherwise the selector dialog appears allowing the user to choose.
selMerged=FALSE
If TRUE the nodes are selected when they are merged.
BOOL refresh=TRUE
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Set this to FALSE to prevent the viewports from automatically being refreshed.
int dupAction = MERGE_DUPS_PROMPT
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Determines what to do when duplicate named objects are encountered during the merge. One of the following values specifies what to do:
MERGE_DUPS_PROMPT
Prompt the user for what to do when duplicates are encountered.
MERGE_DUPS_MERGE
Merge new objects, but keep original objects when duplicates are encountered.
MERGE_DUPS_SKIP
Skip any duplicates encountered (don't merge them).
MERGE_DUPS_DELOLD
Delete the old objects and merge the new ones when duplicates are encountered.
MERGE_LIST_NAMES
Specifies that the name table mrgList below should be filled in with the names of the merged objects.
NameTab* mrgList=NULL
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
When you specify a pointer to a NameTab for this parameter, and don't set dupAction to MERGE_LIST_NAMES, then this method will merge the nodes whose names are listed in the mrgList.
If dupAction==MERGE_LIST_NAMES, (and mergeAll==TRUE, and mrgList != NULL) then this method puts a list of the nodes in the file into mrgList, and simply returns (no merging is done).
See Class NameTab.
Return Value:
Nonzero if the file was merged; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual void FileOpen()=0;
Remarks:
This brings up the standard MAX file open dialog and allows the user to load a new scene.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL FileSave()=0;
Remarks:
This saves the current file. If the file has not been saved yet (and is thus unnamed) this brings up the standard MAX file Save As dialog box and allows the user to choose a name.
Return Value:
TRUE if successful, otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL CheckForSave()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method can be used to write out a .MAX file if needed. First it ends animation if it's in progress. Next it determines whether a save operation is required (change marked in scene, or undo operations present).
Return Value:
If the save is not required, it returns TRUE; otherwise, it puts up a dialog box asking if the user wants to save. If the user picks No, it returns TRUE. If the user picks Cancel it returns FALSE. If the user picks Yes then the method proceeds as for FileSave() above.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL FileSaveAs()=0;
Remarks:
This brings up the standard MAX file saveas dialog box and allows the user to save the current scene to a new file.
Return Value:
TRUE if successful, otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void FileSaveSelected()=0;
Remarks:
This brings up the standard MAX file save selected dialog box and allows the user to save the selected items from the current scene.
Prototype:
virtual void FileReset(BOOL noPrompt=FALSE)=0;
Remarks:
This resets MAX to its startup condition after a confirmation prompt. This performs the same operation as choosing File / Reset from the MAX menus.
Parameters:
BOOL noPrompt=FALSE
If TRUE the confirmation prompt is not presented.
Prototype:
virtual void FileMerge()=0;
Remarks:
This allows the user to merge another MAX file with the current scene. This performs the same operation as choosing File / Merge from the MAX menus.
Prototype:
virtual void FileHold()=0;
Remarks:
This saves the current state of the scene to a temporary hold buffer (same as Edit / Hold). This state may later be restored using FileFetch() or (Edit / Fetch from MAX).
Prototype:
virtual void FileFetch()=0;
Remarks:
This restores the current state of the scene from the temporary hold buffer created using FileHold() (or from the MAX menu command Edit / Hold).
File Import / Export Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual BOOL FileImport()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method simply brings up the 'Select File to Import' dialog just as if the user picked this option from the File / Import... pulldown menu.
Return Value:
TRUE if the file was imported successfully; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL FileExport()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method simply brings up the 'Select File to Export' dialog just as if the user picked this option from the File / Export... pulldown menu.
Return Value:
TRUE if the export file was written successfully; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL ImportFromFile(const TCHAR *name, BOOL suppressPrompts=FALSE, Class_ID *importerID=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method allows the import of the specified file by any of the supported import formats. This is done by specifying a full filename thus bypassing the file browser. If suppressPrompts is set to TRUE, the import mechanism will not display any prompts requiring user action.
Note: Developers of Import plug-ins need to support the suppressPrompts mechanism for this to work properly. Developers of such plug-ins should see the Class SceneImport for details.
Parameters:
const TCHAR *name
The full file name (including extension -- which identifies the importer used) of the input file.
BOOL suppressPrompts=FALSE
If TRUE the default choices in the import plug-in are used and no options dialogs are presented. If FALSE any options dialogs provided by the importer are presented to the user.
Class_ID *importerID=NULL
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
The parameter specifies the Class_ID of the import module to use. This is for those cases where more than one import module uses the same file extension. Omitting this class ID operates in the pre-R3 mode, i.e. the first importer found is used.
Return Value:
TRUE if the export file was written successfully; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL ExportToFile(const TCHAR *name, BOOL suppressPrompts=FALSE, DWORD options, Class_ID *exporterID=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method allows the export of the current MAX file to any of the supported export formats. This is done by specifying a full filename thus bypassing the file browser. If suppressPrompts is set to TRUE, the export mechanism will not display any prompts requiring user action.
Note: Developers of Export plug-ins need to support the suppressPrompts mechanism for this to work properly. Developers of such plug-ins should see the Class SceneExport for details.
Parameters:
const TCHAR *name
The full file name (including extension -- which identifies the exporter used) of the output file.
BOOL suppressPrompts=FALSE
If TRUE the default choices in the export plug-in are used and no options dialogs are presented. If FALSE any options dialogs provided by the exporter are presented to the user.
DWORD options
This option is available in release 4.0 and later only.
There is currently one option; SCENE_EXPORT_SELECTED which allows you to export only selected nodes.
Class_ID *exporterID=NULL
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
The parameter specifies the Class_ID of the export module to use. This is for those cases where more than one export module uses the same file extension. Omitting this class ID operates in the pre-R3 mode, i.e. the first exporter found is used.
Return Value:
TRUE if the export file was written successfully; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual bool CanImportFile(const TCHAR* filename)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method will check is the specified file can be imported.
Parameters:
const TCHAR* filename
The file name to check.
Return Value:
TRUE if the specified file can be imported by one of the import plug-ins; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetImportZoomExtents()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This returns the state of the system zoom extents flag. Note that individual SceneImport plug-ins can override this in their ZoomExtents() method. See Class SceneImport.
Return Value:
TRUE indicates that zoom extents will occur after imports, FALSE indicates that no zoom extents.
Prototype:
virtual void SetImportZoomExtents(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Sets the state of the system zoom extents flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE indicates that zoom extents will occur after imports, FALSE indicates that no zoom extents.
Fonts / Cursor Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual HFONT GetAppHFont()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the handle of the font used by MAX. The default font is the same one returned from GetAppHFont(). So if a developer makes a dialog in the rollup page the correct font will be used automatically.
Prototype:
virtual HCURSOR GetSysCursor( int id )=0;
Remarks:
This method returns the cursor handle for the standard MAX cursors. Use SetCursor() from the Windows API to set the cursor.
Parameters:
int id
One of the following values:
SYSCUR_MOVE, SYSCUR_ROTATE, SYSCUR_USCALE, SYSCUR_NUSCALE,
SYSCUR_SQUASH, SYSCUR_SELECT, SYSCUR_DEFARROW.
Return Value:
The handle of the cursor.
Prototype:
virtual void SetCrossHairCur(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is reserved for future use.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetCrossHairCur()=0;
Remarks:
This method is reserved for future use.
Prototype:
virtual float GetGridSpacing()=0;
Remarks:
This method returns the grid spacing value that the user specifies in the Views / Grid and Snap Settings dialog in the Home Grid tab under Grid Spacing.
Prototype:
virtual int GetGridMajorLines()=0;
Remarks:
This method returns the value that the user specifies in the Views / Grid and Snap Settings dialog in the Home Grid tab under Major Lines every Nth.
Prototype:
virtual void SetActiveGrid(INode *node)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the given node as the active grid object. This is used with grid helper objects to allow them to take effect. This method may also be used to activate the home grid.
Note: This API is not working in the SDK prior to version 2.5.
Parameters:
INode *node
The node to set as the active grid object. To activate the home grid pass NULL.
Prototype:
virtual INode *GetActiveGrid()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns the active grid node or NULL if the home grid is in use.
Prototype:
virtual void AddGridToScene(INode *node)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method is not operative in MAX (only in 3D Studio VIZ).
Hide By Category Flags
Prototype:
virtual DWORD GetHideByCategoryFlags()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the state of the hide by category flags.
Return Value:
One or more of the following values:
HIDE_OBJECTS
HIDE_SHAPES
HIDE_LIGHTS
HIDE_CAMERAS
HIDE_HELPERS
HIDE_WSMS
HIDE_SYSTEMS
HIDE_ALL
HIDE_NONE
Prototype:
virtual void SetHideByCategoryFlags(DWORD f)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of the hide by category flags.
Parameters:
DWORD f
One or more of the following values:
HIDE_OBJECTS
HIDE_SHAPES
HIDE_LIGHTS
HIDE_CAMERAS
HIDE_HELPERS
HIDE_WSMS
HIDE_SYSTEMS
HIDE_ALL
HIDE_NONE
See the Advanced Topics section Keyboard Accelerators and Dialog Messages for more details. Also see the Keyboard Shortcut System topic for details of the system used in release 3.0 and later.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterAccelTable(HWND hWnd, HACCEL hAccel)=0;
Remarks:
Registers a keyboard accelerator table.
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
The window handle.
HACCEL hAccel
The handle of the accelerator table (from the Windows API). See the Windows API for more details on accelerator tables.
Prototype:
virtual int UnRegisterAccelTable(HWND hWnd, HACCEL hAccel)=0;
Remarks:
Un-registers a keyboard accelerator table.
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
The window handle.
HACCEL hAccel
The handle of the accelerator table (from the Windows API). See the Windows API for more details on accelerator tables.
Return Value:
Nonzero if successful; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetPluginKeysEnabled()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Note that this method has been removed in release 4.0 and later.
In the MAX UI there is a icon button for toggling between the MAX system keyboard accelerators and those registered by the plug-in. This icon has a tooltip 'Plug-in Keyboard Shortcut Toggle'.
Return Value:
TRUE if the state is set such that the plug-in accelerators are enabled and FALSE if the system accelerators are enabled.
Prototype:
virtual void SetPluginKeysEnabled(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Note that this method has been removed in release 4.0 and later.
In the MAX UI there is a icon button for toggling between the MAX system keyboard accelerators and those registered by plug-ins. This method may be used to set the state such that the plug-in accelerators are enabled or disabled.
Note: Normally the user should decide which accelerators are enabled. The user will probably find it disconcerting to have a plug-in change the state of this button. Therefore developers should simply register their accelerators and let the user toggle them on and off.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE to enable plug-in accelerators; FALSE to enable system accelerators.
Keyboard Shortcut Table Related Methods
The keyboard shortcut system used prior to release 4 of MAX has been replaced by a more comprehensive system. See the Advanced Topics section UI Customization for details.
Prototype:
virtual float GetLightConeConstraint()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the light cone constraint angle (in radians). This is the hotspot / falloff separation angle.
Prototype:
virtual void AddLightToScene(INode *node)=0;
Remarks:
Adds a light to the scene and registers the light with the viewports.
Parameters:
INode *node
The light to add.
Prototype:
virtual void AddSFXRollupPage(ULONG flags=0)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method should be called in an light's BeginEditParams() method, after adding rollups to the modify panel: it puts up a rollup containing a list of all Atmospherics and Effects that use the current selected node as a "gizmo".
Parameters:
ULONG flags=0
These are reserved for future use.
Prototype:
virtual void DeleteSFXRollupPage()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This is called in a light's EndEditParams() when removing rollups.
Prototype:
virtual void RefreshSFXRollupPage()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
An Atmospheric or Rendering Effect calls this when it adds or removes a "gizmo" reference. This is called to refresh the Special Effects rollup. The Atmospherics and Rendering Effects may also use the REFMSG_SFX_CHANGE message, though calling this method would have the same effect.
Prototype:
virtual MtlBaseLib& GetMaterialLibrary()=0;
Remarks:
This method provides access to the currently loaded material library.
Return Value:
See Class MtlBaseLib.
Prototype:
MtlBaseLib* GetSceneMtls();
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns a list of all the materials used in the scene.
Return Value:
See Class MtlBaseLib.
Prototype:
MtlBase* GetMtlSlot(int slot);
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the material in the specified slot in the Materials Editor.
Parameters:
int slot
The number of the slot in the Materials Editor (a value in the range 0 to 23).
Prototype:
virtual BOOL OkMtlForScene(MtlBase *m)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Before assigning material to scene, call this to avoid duplicate names.
Return Value:
TRUE if it is okay to assign the material; FALSE if not.
Prototype:
virtual void AssignNewName(Mtl *m)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Modifies the name of the material to make it unique. The name is of the form "Material #1" where the number is incremented as required to make ensure it's unique.
Parameters:
Mtl *m
The material whose name is modified.
Prototype:
virtual void AssignNewName(Texmap *m)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Modifies the name of the texture to make it unique. . The name is of the form "Map #1" where the number is incremented as required to make ensure it's unique.
Parameters:
Texmap *m
The texmap whose name is modified.
Prototype:
void ActivateTexture(Texmap *tx, Mtl *mtl, int subNum=-1);
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
The method activates the texture map in the viewports.
Note: In the MAX 2.0 SDK a bug prevents this function from being used -- it results in a link error. This is fixed in the 2.5 SDK.
Parameters:
Texmap *tx
Points to the texmap to activate.
Mtl *mtl
The top level material containing the texture map.
int subNum=-1
If mtl above is a Multi-material, this specifies which sub-branch of the material contains tx.
Prototype:
void DeActivateTexture(Texmap *tx, Mtl *mtl, int subNum=-1);
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
The method deactivates the texture map in the viewports.
Note: In the MAX 2.0 SDK a bug prevents this function from being used -- it results in a link error. This is fixed in the 2.5 SDK.
Parameters:
Texmap *tx
Points to the texmap to deactivate.
Mtl *mtl
The top level material containing the texture map.
int subNum=-1
If mtl above it a Multi-material, this specifies which sub-branch of the material contains tx.
Prototype:
virtual void UpdateMtlEditorBrackets()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method makes sure the Materials Editor slots correctly reflect which materials are used in the scene, which are used by selected objects, etc. This is used internally for the drag-and-drop of materials to nodes -- there is no reason why a plug-in developer should need to call it.
Prototype:
virtual void ConvertMtl(TimeValue t, Material &gm, Mtl *mtl, BOOL doTex, int subNum, float vis, BOOL &needDecal, INode *node, BitArray *needTex, GraphicsWindow *gw)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This function converts a material (class Mtl) to a viewport material (class Material).
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to convert the material.
Material &gm
The viewport material (output). See Class Material.
Mtl *mtl
The material to convert (input). See Class Mtl.
BOOL doTex
Determines whether or not to include textures. TRUE for yes; FALSE for no.
int subNum
If the input material mtl is a sub-material then pass its subnum; otherwise pass 0.
float vis
The visibility value in the range of 0.0 (completely transparent) to 1.0 (fully opaque) for the viewport representation.
BOOL &needDecal
Pass TRUE if the texture needs decal mapping; otherwise FALSE.
INode *node
Points to the node that the material is assigned to. See Class INode.
BitArray *needTex
A BitArray that returns which map channels are needed. The BitArray is enlarged if needed. See Class BitArray.
GraphicsWindow *gw
The GraphicsWindow to do the conversion for. See Class GraphicsWindow.
Prototype:
virtual void GetModContexts(ModContextList& list, INodeTab& nodes)=0;
Remarks:
A modifier may be applied to several objects in the scene. This method retrieves a list of all the ModContexts for the modifier at the current place in the modifier stack. It also gets a list of the nodes the modifier is applied to. For example a modifier may store data into the local data portion of the ModContext for each object affected by the modifier. In order to get at this data it needs to get each ModContext.
Note: this method returns only the ModContext of the currently selected objects, even if the modifier is applied to several objects.
Parameters:
ModContextList& list
A reference to the list of ModContexts. See ModContextList.
INodeTab& nodes
A reference to the table of each of the nodes. See INodeTab.
Prototype:
virtual BaseObject* GetCurEditObject()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the object (or modifier) that is currently being edited in the modifier panel. See Class BaseObject.
Prototype:
virtual INode *GroupNodes(INodeTab *nodes=NULL,TSTR *name=NULL,BOOL selGroup=TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
Combines the specified nodes into a MAX group.
Parameters:
INodeTab *nodes=NULL
The table of nodes to combine into a MAX group. If NULL is passed, the current selection set is used.
TSTR *name=NULL
The name of the group to create. If the name is NULL, a dialog box will prompt the user to select a name.
BOOL selGroup=TRUE
If TRUE, the group of nodes will be selected after the operation is completed.
Return Value:
A pointer to the group of nodes created.
Prototype:
virtual void UngroupNodes(INodeTab *nodes=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
Un-groups the specified nodes.
Parameters:
INodeTab *nodes=NULL
The table of nodes to un-group. If NULL is passed, the current selection set is used.
Prototype:
virtual void ExplodeNodes(INodeTab *nodes=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
Explodes the grouped nodes. This completely un-groups nested groups.
Parameters:
INodeTab *nodes=NULL
The table of nodes to explode. If NULL is passed, the current selection set is used.
Prototype:
virtual void OpenGroup(INodeTab *nodes=NULL,BOOL clearSel=TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
Opens the grouped nodes. Items in an opened group may be edited individually.
Parameters:
INodeTab *nodes=NULL
The table of nodes comprising a group that will be opened. If NULL is passed, the current selection set is used.
BOOL selGroup=TRUE
If TRUE, the group of nodes will be selected after the operation is completed.
Prototype:
virtual void CloseGroup(INodeTab *nodes=NULL,BOOL selGroup=TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
Closes the specified group of nodes. Items in a closed group cannot be edited individually.
Parameters:
INodeTab *nodes=NULL
The table of nodes to close. If NULL is passed, the current selection set is used.
BOOL selGroup=TRUE
If TRUE, the group of nodes will be selected after the operation is completed.
Prototype:
virtual void MakeNameUnique(TSTR &name)=0;
Remarks:
Given a name, this method will modify it to ensure it is unique. It does this by appending a two digit number to the end of the name, or incrementing the existing number, until the name created is unique. Important Note: See NewNameMaker() below for a much faster version of this method when creating many nodes whose names must be unique.
Parameters:
TSTR &name
The name to make unique.
Prototype:
virtual NameMaker* NewNameMaker(BOOL initFromScene = TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
Returns a class used for efficiently creating unique names. To use, do the following:
NameMaker *nm = interface->NewNameMaker();
for(;;) {
...
nm->MakeUniqueName(nodename);
...
}
delete nm;
Parameters:
BOOL initFromScene = TRUE
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
If FALSE then the name maker is not seeded with the names of the objects in the current scene.
Return Value:
See Class NameMaker for details.
Prototype:
virtual INode *GetINodeByName(const TCHAR *name)=0;
Remarks:
This method may be called to retrieve the INode pointer for the node with the given name.
Parameters:
const TCHAR *name
The name of the node to find.
Prototype:
virtual INode *GetINodeByHandle(ULONG handle)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the node whose handle is specified. In 3dsmax version 4.0 and later each node is assigned a unique handle.
Parameters:
ULONG handle
The handle of the node to find.
Prototype:
virtual void DeleteNode(INode *node, BOOL redraw=TRUE, BOOL overrideSlaves=FALSE)=0;
Remarks:
This deletes the specified node from the scene and handles setting up for an undo.
In order to be able to undo this deletion properly the undo system must be in a holding state. A developer can do this by calling theHold.Begin() before calling DeleteNode() and calling theHold.Accept() after. For example, to delete the first node in the current selection set, you could use the following code:
theHold.Begin();
ip->DeleteNode(ip->GetSelNode(0));
theHold.Accept(_T("Delete"));
The string used in the Accept() method is what appears to the user in the Undo menu choice.
Note that the object reference of the node is deleted as well if the only item referencing that object is the node. This is because when the node is deleted, it first deletes all its references. Whenever a reference is deleted, if the item is the last reference, then the system deletes the item as well.
Parameters:
INode *node
The node to delete.
BOOL redraw=TRUE
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
If FALSE the viewports will not be redrawn after the node is deleted. This allows several nodes to be deleted at once without the viewports having to be redrawn after each one.
BOOL overrideSlaves=FALSE
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
If TRUE then this method will delete nodes whose TM controllers implement the Control::PreventNodeDeletion() method to return TRUE. If a TM controller implements that method then normally DeleteNode() won't work on the nodes associated with that controller. However if this parameter is TRUE then these nodes still can be deleted. This allows a master controller to easily delete slaves nodes if it needs to.
Prototype:
virtual INode *GetRootNode()=0;
Remarks:
Returns a pointer to the root node. From the root node one can retrieve the children (using INode::NumberOfChildren(), and INode::GetChildNode(i)). This allows a developer enumerated the scene by enumerating the node tree.
Prototype:
virtual void NodeInvalidateRect( INode *node )=0;
Remarks:
This invalidates the rectangle in the viewports that the node occupies. Rectangles flagged as invalid will be updated on the next screen redraw.
Parameters:
INode *node
Specifies the node whose rectangle is invalidated.
Prototype:
virtual void SetNodeTMRelConstPlane(INode *node, Matrix3& mat)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the nodes transform relative to the current construction plane. This may be used during creating so you can set the position of the node in terms of the construction plane and not in world units.
Parameters:
INode *node
The node whose transform will be set.
Matrix3& mat
The transformation matrix.
Prototype:
virtual int GetSelNodeCount()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the number of nodes in the selection set.
Prototype:
virtual INode *GetSelNode(int i)=0;
Remarks:
Selection sets are handled as a virtual array and accessed using an index starting at 0. This method returns a pointer to the 'i-th' node in the current selection set. See also: GetSelNodeCount().
Parameters:
int i
Index of the node in the selection set.
Return Value:
Pointer to the 'i-th' node in the selection set.
Prototype:
virtual void GetSelectionWorldBox(TimeValue t,Box3 &box)=0;
Remarks:
This method retrieves the world space bounding box of the current selection set.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to retrieve the bounding box.
Box3 &box
The bounding box is returned here.
Prototype:
virtual void SelectNode(INode *node, int clearSel = 1)=0;
Remarks:
This selects the specified node, either adding it to the current selection set, or creating a new selection set with the node.
Note: A developer should call theHold.Begin() before this method and theHold.Accept() after this call. Otherwise, MAX may crash if the user selects undo after this call has been issued. See the sample code below. Also see Undo / Redo for more details on this system.
Parameters:
INode *node
The node to select.
int clearSel = 1
If zero, the node is added to the current selection set. If nonzero, the node replaces the selection set.
Sample Code:
theHold.Begin();
ip->SelectNode(node);
TSTR undostr; undostr.printf("Select");
theHold.Accept(undostr);
Prototype:
virtual void DeSelectNode(INode *node)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method unselects the specified node.
Parameters:
INode *node
The node to deselect.
Prototype:
virtual void SelectNodeTab(INodeTab &nodes,BOOL sel,BOOL redraw=TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method may be used to select or deselect a group of nodes all at once and optionally redraw the viewports when done.
Parameters:
INodeTab &nodes
The Table of nodes to select or deselect.
BOOL sel
If TRUE the nodes are selected; otherwise they are deselected.
BOOL redraw=TRUE
If TRUE the viewports are redrawn when done; otherwise they are not.
Prototype:
virtual void ClearNodeSelection(BOOL redraw=TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method may be used to clear the current selection set and optionally redraw the viewports.
Parameters:
BOOL redraw=TRUE
If TRUE the viewports are redrawn when done; otherwise they are not.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL SelectionFrozen()=0;
Remarks:
In MAX the space bar freezes the selection set. This keeps the selection set from being inadvertently changed. This method access the status of the selection set frozen state.
Return Value:
TRUE if the selection set is frozen; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void FreezeSelection()=0;
Remarks:
Toggles the selection set to the frozen state.
Prototype:
virtual void ThawSelection()=0;
Remarks:
Toggles the selection set to the thawed state.
Prototype:
virtual bool CloneNodes(INodeTab& nodes, Point3& offset, bool expandHierarchies = true, CloneType cloneType = NODE_COPY, INodeTab* resultSource = NULL, INodeTab* resultTarget = NULL) = 0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method allows you to clone nodes and node hierarchies.
Parameters:
INodeTab& nodes
The node table containing the nodes you wish to clone.
Point3& offset
The position offset you wish to apply to the cloned nodes.
bool expandHierarchies = true
This determines if children will be cloned in hierarchies.
CloneType cloneType = NODE_COPY
The type of cloning you wish to do, which is one of the following; NODE_COPY, NODE_INSTANCE or NODE_REFERENCE.
INodeTab* resultSource = NULL
This node table will be filled in with the original nodes to be cloned. The reason for this is that there can be dependencies between nodes that cause other nodes to be added to the list. For example light/camera targets, nodes part of systems, belonging to groups or expanded hierarchies etc.
INodeTab* resultTarget = NULL
This node table will be filled in with the new cloned nodes. There is a one to one relationship between the nodes in the resultSource and the resultTraget.
Return Value:
TRUE if the nodes were cloned successfully, otherwise FALSE. Note that with R4.0 the return value will always be TRUE since no actual error checking is undertaken.
Node Picking (interactive selection in the scene)
Prototype:
virtual INode *PickNode(HWND hWnd,IPoint2 pt,PickNodeCallback *filt=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method hit tests the screen position for nodes and returns an INode pointer if one is hit, NULL otherwise.
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
Handle of the window to check.
IPoint2 pt
Point to check in screen coordinates.
PickNodeCallback *filt=NULL
This callback may be used to filter nodes from being picked. See Class PickNodeCallback.
Return Value:
INode pointer of node that was hit; NULL if no node was found.
Prototype:
virtual void BoxPickNode(ViewExp *vpt,IPoint2 *pt,BOOL crossing,PickNodeCallback *filt=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method performs a node level hit test on the specified rectangular region. Use either the ViewExp::GetClosestHit() or ViewExp::GetHit() method to access the result.
Parameters:
ViewExp *vpt
The viewport to perform the hit testing.
IPoint2 *pt
These points specify the box region to hit test. The first point in the array is the lower left. The second point is the upper right.
BOOL crossing
If TRUE Crossing selection is used; otherwise Window seleciton is used.
PickNodeCallback *filt=NULL
This callback may be used to filter nodes from being picked. See Class PickNodeCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void CirclePickNode(ViewExp *vpt,IPoint2 *pt,BOOL crossing,PickNodeCallback *filt=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method performs a node level hit test on the specified circular region. Use either the ViewExp::GetClosestHit() or ViewExp::GetHit(int i) method to access the result.
Parameters:
ViewExp *vpt
The viewport to perform the hit testing.
IPoint2 *pt
These points specify the circular region to hit test. The first point in the array is the center. The second point is a point on the radius.
BOOL crossing
If TRUE Crossing selection is used; otherwise Window seleciton is used.
PickNodeCallback *filt=NULL
This callback may be used to filter nodes from being picked. See Class PickNodeCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void FencePickNode(ViewExp *vpt,IPoint2 *pt,BOOL crossing,PickNodeCallback *filt=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method performs a node level hit test on the specified arbitrary polygonal region. Use either the ViewExp::GetClosestHit() or ViewExp::GetHit() method to access the result.
Parameters:
ViewExp *vpt
The viewport to perform the hit testing.
IPoint2 *pt
These points specify the fence region to hit test. It is assumed the last point is connected to the first point to close the region. The fence knows when it's out of points when it hits a point that has negative x and y values. So, the initializer IPoint2(-1, -1) added to the bottom of this IPoint2 list signals the end.
BOOL crossing
If TRUE Crossing selection is used; otherwise Window seleciton is used.
PickNodeCallback *filt=NULL
This callback may be used to filter nodes from being picked. See Class PickNodeCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void SetPickMode(PickModeCallback *pc)=0;
Remarks:
This will set the command mode to a standard pick mode. The callback implements hit testing and a method that is called when the user actually picks an item. Note that this method, if called a second time, will cancel the pick mode and put the user into 'Select and Move' mode. This can be used to handle the case where a user clicks on a user interface control a second time to cancel to picking.
Sample code using this API is available in \MAXSDK\SAMPLES\OBJECTS\MORPHOBJ.CPP. A utility plug-in that uses this API is \MAXSDK\SAMPLES\UTILITIES\ASCIIOUT.CPP.
Parameters:
PickModeCallback *pc
A pointer to an instance of the class PickModeCallback.
Prototype:
virtual void ClearPickMode()=0;
Remarks:
This method is called to make sure there are no pick modes in the command stack.
Prototype:
virtual void FlashNodes(INodeTab *nodes)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method is used to 'flash' a group of nodes. This is usually used as a confirmation of some operation (for example as an indication of the completion of a pick node operation.) The nodes are briefly erased and then redrawn in the viewport to flash them.
Parameters:
INodeTab *nodes
Pointer to the table of nodes to 'flash'.
Sample Code:
INodeTab flash;
INode *node;
for (int i=0; i<ip->GetSelNodeCount(); i++) {
node = ip->GetSelNode(i);
flash.Append(1,&node,10);
}
ip->FlashNodes(&flash);
IObjCreate and IObjParam Pointer Casting
Prototype:
virtual IObjCreate *GetIObjCreate()=0;
Remarks:
Returns this interface pointer cast as a IObjCreate pointer.
Prototype:
virtual IObjParam *GetIObjParam()=0;
Remarks:
Returns this interface pointer cast as a IObjParam pointer.
Prototype:
virtual IOsnapManager *GetOsnapManager()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns an interface pointer to the object snap manager. See Class IOsnapManager. Also see the Advanced Topics section on Snapping.
Prototype:
virtual MouseManager *GetMouseManager()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This is used internally by the Osnap Manager. Plug-Ins don't need to use this method.
Prototype:
virtual void InvalidateOsnapdraw()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This is used internally to invalidate the osnap drawing mechanism. Plug-Ins don't need to use this method.
Prototype:
virtual void CreatePreview(PreviewParams *pvp=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is used to render a preview image (or animation) from the currently active viewport using the real-time (viewport) renderer.
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Parameters:
PreviewParams *pvp=NULL
This class defines the way the preview is generated (via its data members). If this is passed as NULL the parameters from the preview rendering dialog box are used. See Class PreviewParams.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL ProgressStart(TCHAR *title, BOOL dispBar, LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE fn, LPVOID arg)=0;
Remarks:
This method puts up a progress bar in the status panel. The function fn is then called and is passed the argument arg. This function fn does the processing work of the plug-in. See the sample code below.
Note: It is not possible to use the progress bar APIs in the create or modify branches of the command panel. In the create or modify branch of the command panel, EndEditParams() gets called from this method. This is because most of MAX is "shut down" during a progress operation. For example, it is not appropriate for users to be moving objects during an IK calculation, or changing the camera lens while a preview is being created (all these operations use the ProgressStart() API). It is for this same reason that the Transform Type-in, Medit, Track View and Video Post windows are hidden during a progress operation. Since EndEditParams() is called, the Interface pointer a plug-in maintains is no longer valid after the operation is started. This method is useful for Utility plug-ins, and Import/Export plug-ins however.
Parameters:
TCHAR *title
The title string for the progress bar to let the user know what is happening.
BOOL dispBar
If FALSE the progress bar is not displayed; if TRUE the progress bar is displayed.
LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE fn
This is a pointer to a function that returns a DWORD and takes a single argument. When ProgressStart() is called, this function is called with the argument arg passed. This function should be declared as follows:
DWORD WINAPI fn(LPVOID arg)
LPVOID arg
This is the argument to the function fn.
Return Value:
TRUE means the progress mode was entered successfully. FALSE means that there was a problem. Currently the return value is always TRUE. When compiled for multi-threading (which is turned off in the 1.0 build), FALSE is returned if the new thread could not be created.
Sample Code:
This code demonstrates the use of the ProgressStart(), ProgressEnd() GetCancel() and SetCancel() APIs. There are two ways to use the APIs. One is to use a dummy function for fn in ProgressStart(). Then just call ProgressUpdate() from whatever function you want to do the processing. The other way is to use fn to do the processing.
In this version, the fn function passed to ProgressStart() performs the work.
DWORD WINAPI fn(LPVOID arg) {
int i, percent;
Interface *ip = theUtility.ip;
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
percent = i/10;
ip->ProgressUpdate(percent);
if (ip->GetCancel()) {
switch(MessageBox(ip->GetMAXHWnd(), _T("Really Cancel"),
_T("Question"), MB_ICONQUESTION | MB_YESNO)) {
case IDYES:
return(0);
case IDNO:
ip->SetCancel(FALSE);
}
}
}
return(0);
}
void Utility::Test1() {
Interface *ip = theUtility.ip;
LPVOID arg;
ip->ProgressStart(_T("Title String"), TRUE, fn, arg);
ip->ProgressEnd();
}
In this version, the fn function passed to ProgressStart() is a dummy function, and the processing is done outside it.
DWORD WINAPI fn(LPVOID arg) {
return(0);
}
void Utility::Test1() {
int i, percent, retval;
Interface *ip = theUtility.ip;
LPVOID arg;
ip->ProgressStart(_T("Title String"), TRUE, fn, arg);
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
percent = i/10;
ip->ProgressUpdate(percent);
if (ip->GetCancel()) {
retval = MessageBox(ip->GetMAXHWnd(), _T("Really Cancel"),
_T("Question"), MB_ICONQUESTION | MB_YESNO);
if (retval == IDYES)
break;
else if (retval == IDNO)
ip->SetCancel(FALSE);
}
}
ip->ProgressEnd();
}
Prototype:
virtual void ProgressUpdate(int pct, BOOL showPct = TRUE, TCHAR *title = NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method updates the progress bar. As the function fn passed in ProcessStart() above is working it should periodically call this method to report its progress.
Parameters:
int pct
The percentage complete (0 to 99). This is what causes the progress bar to move.
BOOL showPct = TRUE
If TRUE, then the title parameter is ignored, and a percent is displayed to the right of the progress bar. If FALSE, then the title parameter is displayed next to the progress bar. This is for operations that are discrete -- the title might change from "extruding" to "capping" to "welding" for example. Note that currently the Cancel button is not shown if showPct is set to FALSE, however the ESC key may be used to cancel.
TCHAR *title = NULL
If showPct is FALSE, this string is displayed next to the progress bar.
Prototype:
virtual void ProgressEnd()=0;
Remarks:
This method removes the progress bar and frees the memory that was allocated internally to handle the processing.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetCancel()=0;
Remarks:
This method returns the progress bar cancel button status. Also see SetCancel() below.
Return Value:
TRUE if the user pressed the cancel button; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void SetCancel(BOOL sw)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the canceled status returned from GetCancel(). This may be used if you want to give the user a confirmation dialog box asking if they really want to cancel. For example, when a MAX user creates an preview animation this API is used. If the user presses cancel, the preview code reads this via GetCancel(). Then a confirmation dialog is displayed asking the user if they indeed want to cancel. If the user selects that they don't want to cancel, this method is called passing FALSE. This sets the class variable that is returned by GetCancel(). The cancel request is ignored and processing continues.
Note that this will not cancel unless you implement code to process GetCancel(). It merely sets the state returned from GetCancel().
Parameters:
BOOL sw
TRUE to set the cancel flag; FALSE to clear the cancel flag.
The following APIs provide a simplistic method to call the renderer and render frames (to gain more control over the renderer, see the methods after these first three). The renderer just uses the current user specified parameters. Note that the renderer uses the width, height, and aspect of the specified bitmap so the caller can control the size of the rendered image rendered. Also Note: These methods drive the renderer and not video post.
Prototype:
virtual int OpenCurRenderer(INode *camNode,ViewExp *view,RendType t = RENDTYPE_NORMAL, int w=0, int h=0)=0;
Remarks:
This method is called to open the current renderer. It must be opened before frames can be rendered. Either camNode or view must be non-NULL, but not both. Remember to close the renderer when you are done (using CloseCurRenderer()).
Parameters:
INode *camNode
A pointer to the camera node to render, or NULL if a viewport should be rendered.
ViewExp *view
A pointer to the view to render, or NULL if the camera should be rendered.
RendType t = RENDTYPE_NORMAL
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This provides an optional way to specify the view when opening the renderer. This specifies the type of render. See List of Render Types.
int w=0
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This specifies the width of the rendering.
int h=0
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This specifies the height of the rendering.
Return Value:
Nonzero indicates success; failure is zero.
Prototype:
virtual int OpenCurRenderer(ViewParams *vpar,RendType t = RENDTYPE_NORMAL, int w=0, int h=0)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method is called to open the current renderer. It provides an optional way to specify the view when opening.
Parameters:
ViewParams *vpar
This class describes the properties of a view that is being rendered. See Class ViewParams.
RendType t = RENDTYPE_NORMAL
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This provides an optional way to specify the view when opening the renderer. This specifies the type of render. See List of Render Types.
int w=0
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This specifies the width of the rendering.
int h=0
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This specifies the height of the rendering.
Return Value:
Nonzero indicates success; failure is 0.
Prototype:
virtual void CloseCurRenderer()=0;
Remarks:
This method is called to close the renderer. The renderer must be closed when you are finished with it.
Prototype:
virtual int CurRendererRenderFrame(TimeValue t,Bitmap *bm,RendProgressCallback *prog=NULL, float frameDur = 1.0f , ViewParams *vp=NULL, RECT *regionRect = NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is called to render a frame to the given bitmap. The renderer uses the width, height, and aspect ratio of the specified bitmap to control the size of the rendered image.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to render the image.
Bitmap *bm
The bitmap to render to. This bitmap defines the size and aspect ratio of the render. See Class Bitmap.
RendProgressCallback *prog=NULL
The RendProgressCallback is an optional callback. See Class RendProgressCallback.
float frameDur = 1.0f
This parameter should always be set to 1.0.
ViewParams *vp=NULL
This parameter allows you to specify a different view transformation on each render call. For instance, you can render a given scene at a given time from many different viewpoints, without calling Render::Open() for each one.
RECT *regionRect = NULL
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This value, if passed, defines the region to be rendererd. This only works for RENDTYPE_REGION and RENDTYPE_REGIONCROP.
Return Value:
The result of the render - Nonzero if success; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual IScanRenderer *CreateDefaultScanlineRenderer()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method creates a default scanline renderer. This renderer must be deleted by calling IScanRenderer::DeleteThis().
Return Value:
A pointer to a new IScanRenderer object.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL DisplayActiveCameraViewWithMultiPassEffect() = 0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method will draw the active view (if it is a camera view with a multi-pass effect enabled) with that effect active.
Return Value:
TRUE if the active view is a camera view with a multi-pass effect enabled, FALSE otherwise.
Below is a set of functions parallel to those above to work with any Renderer instance.
Prototype:
virtual int OpenRenderer(Renderer *pRenderer, INode *camNode,ViewExp *view, RendType type = RENDTYPE_NORMAL, int w=0, int h=0)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method is called to open the specified renderer. It must be opened before frames can be rendered. Either camNode or view must be non-NULL, but not both. Remember to close the renderer when you are done (using CloseRenderer()).
Parameters:
Renderer *pRenderer
Points to the renderer to open.
INode *camNode
A pointer to the camera node to render, or NULL if a viewport should be rendered.
ViewExp *view
A pointer to the view to render, or NULL if the camera should be rendered.
RendType type = RENDTYPE_NORMAL
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This provides an optional way to specify the view when opening the renderer. This specifies the type of render. See List of Render Types.
int w=0
This specifies the width of the rendering.
int h=0
This specifies the height of the rendering.
Return Value:
Nonzero indicates success; failure is zero.
Prototype:
virtual int OpenRenderer(Renderer *pRenderer, ViewParams *vpar, RendType type = RENDTYPE_NORMAL, int w=0, int h=0)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method is called to open the specified renderer. It provides an optional way to specify the view when opening.
Parameters:
Renderer *pRenderer
Points to the renderer to do the rendering.
ViewParams *vpar
This class describes the properties of a view that is being rendered. See Class ViewParams.
RendType type = RENDTYPE_NORMAL
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This provides an optional way to specify the view when opening the renderer. This specifies the type of render. See List of Render Types.
int w=0
This specifies the width of the rendering.
int h=0
This specifies the height of the rendering.
Return Value:
Nonzero indicates success; failure is 0.
Prototype:
virtual int RendererRenderFrame(Renderer *pRenderer, TimeValue t, Bitmap *bm, RendProgressCallback *prog=NULL, float frameDur = 1.0f, ViewParams *vp=NULL, RECT *regionRect = NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method is called to render a frame with the specified renderer to the given bitmap. The renderer uses the width, height, and aspect ratio of the specified bitmap to control the size of the rendered image.
Parameters:
Renderer *pRenderer
Points to the renderer which will do the rendering.
TimeValue t
The time to render the image.
Bitmap *bm
The bitmap to render to. This bitmap defines the size and aspect ratio of the render. See Class Bitmap.
RendProgressCallback *prog=NULL
The RendProgressCallback is an optional callback. See Class RendProgressCallback.
float frameDur = 1.0f
This parameter should always be set to 1.0.
ViewParams *vp=NULL
This parameter allows you to specify a different view transformation on each render call. For instance, you can render a given scene at a given time from many different viewpoints, without calling Render::Open() for each one.
RECT *regionRect = NULL
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This value, if passed, defines the region to be rendererd. This only works for RENDTYPE_REGION and RENDTYPE_REGIONCROP.
Return Value:
The result of the render - Nonzero if success; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual void CloseRenderer(Renderer *pRenderer)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Closes the specified renderer.
Parameters:
Renderer *pRenderer
Points to the renderer to close.
To get more control over the renderer, the renderer can be called directly. The following methods give access to the current renderer and the user's current rendering settings. Note: These methods drive the renderer and not video post.
Prototype:
virtual Renderer *GetCurrentRenderer()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves a pointer to the renderer currently set as the active renderer. This will be either the production rederer or the draft renderer depending upon which is active. A developer can determine which renderer this is by calling the ClassID() method of the renderer.
Return Value:
A pointer to the renderer.
Prototype:
virtual Renderer *GetProductionRenderer()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Retrieves a pointer to the renderer currently set as the production renderer. A developer can determine which renderer this is by calling the ClassID() method of the renderer.
Return Value:
A pointer to the renderer.
Prototype:
virtual Renderer *GetDraftRenderer()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Retrieves a pointer to the renderer currently set as the draft renderer. A developer can determine which renderer this is by calling the ClassID() method of the renderer.
Return Value:
A pointer to the renderer.
Prototype:
virtual Renderer *GetRenderer(RenderSettingID renderSettingID)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer to the specified renderer.
Parameters:
RenderSettingID renderSettingID
One of these values: See List of Render Setting IDs
Return Value:
A pointer to the renderer.
Prototype:
virtual void AssignCurRenderer(Renderer *rend)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Assigns the renderer passed for use as either the draft renderer or the production renderer depending upon which is active.
Parameters:
Renderer *rend
The renderer to assign.
Prototype:
virtual void AssignProductionRenderer(Renderer *rend)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Assigns the renderer passed as the production renderer.
Parameters:
Renderer *rend
The renderer to assign.
Prototype:
virtual void AssignDraftRenderer(Renderer *rend)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Assigns the renderer passed as the draft renderer.
Parameters:
Renderer *rend
The renderer to assign.
Prototype:
virtual void AssignRenderer(RenderSettingID renderSettingID, Renderer *rend)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Assigns the renderer passed as one of the standard MAX rendering options (Production, Draft, etc).
Parameters:
RenderSettingID renderSettingID
One of these values: See List of Render Setting IDs
Renderer *rend
Points to the renderer to assign.
Prototype:
virtual void SetUseDraftRenderer(BOOL b)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Specifies which renderer is active -- draft or production. Pass TRUE to use the draft renderer and FALSE to get the production renderer.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetUseDraftRenderer()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Determines which renderer is active -- draft or production.
Return Value:
TRUE for the draft renderer and FALSE for the production renderer.
Prototype:
virtual void ChangeRenderSetting(RenderSettingID renderSettingID)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Sets the specified renderer as active.
Parameters:
RenderSettingID renderSettingID
One of these values: See List of Render Setting IDs.
Prototype:
virtual RenderSettingID GetCurrentRenderSetting()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns a value which indicates which renderer is current. See List of Render Setting IDs.
Prototype:
virtual IRenderElementMgr *GetCurRenderElementMgr()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method returns a pointer to the current render elements manager interface.
Prototype:
virtual IRenderElementMgr *GetRenderElementMgr(RenderSettingID renderSettingID)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method returns a pointer to the production or draft render element manager -- passing in renderSettingID = RS_IReshade will return NULL.
Parameters:
RenderSettingID renderSettingID
One of these values: See List of Render Setting IDs.
Prototype:
virtual void SetupRendParams(RendParams &rp, ViewExp *vpt, RendType t = RENDTYPE_NORMAL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is called to fill in a RendParams structure that can be passed to the renderer with the user's current rendering settings. This is whatever was last used, or the default settings.
In MAX 1.x note the following (this needs not be done in MAX 2.0 or later): In order to open a renderer using this method to setup the RendParams class the following code should be used:
RendParams rp;
SetupRendParams(rp, �);
rp.atmos = NULL;
rp.envMap = NULL;
As shown above, this method does not automatically set the values for envMap and atmos. You must do this manually if you are using the RendParams object to initialize the renderer. Then you can call Renderer::Open(�, rp, �). In MAX 2.0 and later, atmos and envMap are properly initialized without the above code.
Parameters:
RendParams &rp
This is the class instance whose data is filled in. See Class RendParams.
ViewExp *vpt
This pointer only needs to be passed in if the RendType is RENDTYPE_REGION or RENDTYPE_BLOWUP. In these cases it will set up the RendParams regxmin, regxmax, regymin, regymax from values stored in the viewport. See Class ViewExp.
RendType t = RENDTYPE_NORMAL
See List of Render Types.
Prototype:
virtual void GetViewParamsFromNode(INode* vnode, ViewParams& vp, TimeValue t)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method fills in the specified ViewParams structure based on type of node passed (camera or light). It can be used when instantiating a renderer and calling Open(), Render(), and Close() directly on it.
Parameters:
INode* vnode
Points to the node to initialize from.
ViewParams& vp
The ViewParams structure to initalize.
TimeValue t
The time at which to initialize the structure.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL CheckForRenderAbort()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method may be called during a rendering to check if user has cancelled the render.
Return Value:
TRUE if user has cancelled; otherwise FALSE. If not rendering the method returns FALSE.
These methods give access to the individual user specified render parameters. These are either parameters that the user specifies in the render dialog or the renderer page of the preferences dialog.
Prototype:
virtual int GetRendTimeType()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the type of time range to be rendered.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
REND_TIMESINGLE
A single frame.
REND_TIMESEGMENT
The active time segment.
REND_TIMERANGE
The user specified range.
REND_TIMEPICKUP
The user specified frame pickup string (for example "1,3,5-12").
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendTimeType(int type)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the type of time range rendered.
Parameters:
int type
One of the following values:
REND_TIMESINGLE
A single frame.
REND_TIMESEGMENT
The active time segment.
REND_TIMERANGE
The user specified range.
REND_TIMEPICKUP
The user specified frame pickup string (for example "1,3,5-12").
Prototype:
virtual TimeValue GetRendStart()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's start time setting.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendStart(TimeValue start)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's start time setting.
Parameters:
TimeValue start
The time to begin rendering.
Prototype:
virtual TimeValue GetRendEnd()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's end time setting.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendEnd(TimeValue end)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's end time setting.
Parameters:
TimeValue end
The time to end rendering.
Prototype:
virtual int GetRendNThFrame()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the renderer's 'n-th' frame setting.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendNThFrame(int n)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's 'n-th' frame setting.
Parameters:
int n
The n-th frame setting.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendShowVFB()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the state of the renderer's show virtual frame buffer flag. Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendShowVFB(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of the renderer's show virtual frame buffer flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE is on; FALSE is off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendSaveFile()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the state of the renderer's save file flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendSaveFile(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of the renderer's save file flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE is on; FALSE is off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendUseDevice()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the state of the renderer's use device flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendUseDevice(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of the renderer's use device flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE is on; FALSE is off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendUseNet()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the state of the renderer's use net flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendUseNet(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of the renderer's use net flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE is on; FALSE is off.
Prototype:
virtual BitmapInfo& GetRendFileBI()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the rendering file BitmapInfo. This class describes the output file. See Class BitmapInfo.
Prototype:
virtual BitmapInfo& GetRendDeviceBI()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the rendering device BitmapInfo. This class describes the output device. See Class BitmapInfo.
Prototype:
virtual int GetRendWidth()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the rendering output width in pixels.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendWidth(int w)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the rendering output width.
Parameters:
int w
The width in pixels.
Prototype:
virtual int GetRendHeight()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the rendering output height in pixels.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendHeight(int h)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the rendering output height.
Parameters:
int h
The height in pixels.
Prototype:
virtual float GetRendApect()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's pixel aspect ratio setting. Note for MAX 1.2: To get the 'Image Aspect Ratio' setting use:
float aspectRatio =
((float) ip->GetRendWidth())/((float) ip->GetRendHeight());
In MAX 2.0 or later GetRendImageAspect() may be used:
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendAspect(float a)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's pixel aspect ratio setting.
Parameters:
float a
The pixel aspect ratio to set.
Prototype:
virtual float GetRendImageAspect()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Return Value:
Returns the image aspect ratio.
Prototype:
virtual float GetRendApertureWidth()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Return Value:
Returns the aperture width in millimeters (mm).
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendApertureWidth(float aw)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the aperture width.
Parameters:
float aw
The width to set in millimeters (mm).
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendFieldRender()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's field render flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendFieldRender(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's field render flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendColorCheck()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's color check flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendColorCheck(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's color check flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendSuperBlack()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's super black flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendSuperBlack(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's super black flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendHidden()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's render hidden objects flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendHidden(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's render hidden objects flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendForce2Side()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's force two-sided flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendForce2Side(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's force two-sided flag. TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendAtmosphere()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's uses atmospheric effects flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendAtmosphere(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets if the renderer uses atmospheric effects.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendEffects()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if Rendering Effects will be used; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendEffects(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets if Rendering Effects will be used.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE to use (on); FALSE to not use (off).
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendDisplacement()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if rendering displacements is enabled; otherwise FALSE.
Note: Developers should use the flags parameter of the View class which is passed into GetRenderMesh() to determine if Displacement Mapping is being used because the values may not the same (for instance when rendering in the Materials Editor). See Class View.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendDisplacement(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets if rendering displacements are enabled.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual TSTR& GetRendPickFramesString()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the string holding the frames the user wants to render. For example "1,3,5-12".
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendDitherTrue()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's dither true color flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendDitherTrue(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's dither true color flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendDither256()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's dither 256 color flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendDither256(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's dither 256 color flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendMultiThread()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the renderer's multi-threaded flag.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendMultiThread(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the renderer's multi-threaded flag.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetRendNThSerial()=0;
Remarks:
This retrieves the output file sequencing nth serial numbering setting.
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendNThSerial(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This sets the output file sequencing nth serial numbering setting.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual int GetRendVidCorrectMethod()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the video color check method.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
0 is FLAG
1 is SCALE_LUMA
2 is SCALE_SAT
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendVidCorrectMethod(int m)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the video color check method.
Parameters:
int m
One of the following values:
0 is FLAG
1 is SCALE_LUMA
2 is SCALE_SAT
Prototype:
virtual int GetRendFieldOrder()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the rendering field order.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
0 is Even
1 is Odd
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendFieldOrder(int fo)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the rendering field order to even or odd.
Parameters:
int fo
One of the following values:
0 sets Even
1 sets Odd
Prototype:
virtual int GetRendNTSC_PAL()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the video color check NTSC or PAL setting.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
0 is NTSC
1 is PAL
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendNTSC_PAL(int np)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the video color check NTSC or PAL setting.
Parameters:
int np
One of the following values:
0 sets NTSC
1 sets PAL
Prototype:
virtual int GetRendSuperBlackThresh()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the super black threshold setting.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendSuperBlackThresh(int sb)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the super black threshold setting.
Parameters:
int sb
The super black threshold.
Prototype:
virtual int GetRendFileNumberBase()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns the File Number Base in the 'Common Parameters' rollup of the Render Scene dialog.
Prototype:
virtual void SetRendFileNumberBase(int n)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets the File Number Base in the 'Common Parameters' rollup of the Render Scene dialog.
Parameters:
int n
The number to set.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetSkipRenderedFrames()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the skip existing rendered frames state is on; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void SetSkipRenderedFrames(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets the skip existing rendered frames state to on or off.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Right Click Menu Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual RightClickMenuManager* GetRightClickMenuManager()=0;
Remarks:
Using this pointer a developer can add to the menu that pops ups when the user clicks the right mouse button. Example code is available in: \MAXSDK\SAMPLES\MODIFIERS\EDITSPL.CPP. See Also: Class RightClickMenuManager.
Return Value:
A pointer to the RightClickMenuManager.
Rollup Page Related Methods
See Command Panel -- Rollup Page Methods.
See Also: Sub-Object Selection Sets (Named)
Prototype:
virtual void ClearCurNamedSelSet()=0;
Remarks:
This method clears the current edit field of the named selection set drop down.
Prototype:
virtual void SetCurNamedSelSet(TCHAR *setName)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the edit field of the named selection set drop down to the set whose name is passed.
Parameters:
TCHAR *setName
The name of the selection set to make current.
Prototype:
virtual void NamedSelSetListChanged()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Calling this method tells the system that the named sub-object selection sets have changed and that the drop down needs to be rebuilt. This will cause BaseObject::SetupNamedSelDropDown() to be called on the current item being edited. This is often called inside restore objects that undo changes to the selection set. This causes the system to check if the current item being edited is in sub-object selection mode, and if so, will cause SetupNamedSelDropDown() to be called. Note that restore objects can be invoked at any time and the user may not be in sub-object selection mode (for instance they might be in the Display panel). Restore objects however can simply call this method and the system will figure out if the drop down needs to be updated.
Prototype:
virtual int GetNumNamedSelSets()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns the number of named selection sets at the object level.
Prototype:
virtual TCHAR *GetNamedSelSetName(int setNum)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns the name of the named selection set whose index is passed.
Parameters:
int setNum
The index of the named selection set.
Prototype:
virtual int GetNamedSelSetItemCount(int setNum)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns the number of items in the named selection set whose index is passed.
Parameters:
int setNum
The index of the named selection set.
Prototype:
virtual INode *GetNamedSelSetItem(int setNum,int i)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method may be used to retrieve the INode pointer of the 'i-th' item in the named selection set whose index is passed.
Parameters:
int setNum
The index of the selection set whose 'i-th' INode pointer is returned.
int i
The index into the selection set.
Prototype:
virtual void AddNewNamedSelSet(INodeTab &nodes, TSTR &name)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Adds a new named selection set to those already available in the drop down list in the MAX toolbar.
Parameters:
INodeTab &nodes
The table of nodes making up the selection set.
TSTR &name
The name for the set.
Prototype:
virtual void RemoveNamedSelSet(TSTR &name)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Removes the specified named selection set those already available in the drop down list in the MAX toolbar.
Parameters:
TSTR &name
The name for the set to remove.
Prototype:
virtual ReferenceTarget *GetScenePointer()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns a pointer for direct access to the scene. This is primarily used for hanging AppData off the entire scene as opposed to a certain Animatable.
Show End Result Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual void EnableShowEndResult(BOOL enabled)=0;
Remarks:
This method is called if a modifier wants to temporarily disable any modifiers following it. For example the edit mesh modifier does not let you edit a mesh while other modifiers later in the pipeline are affecting the result so it calls this method to disable the others temporarily.
Parameters:
BOOL enabled
TRUE is enabled; FALSE is disabled.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetShowEndResult()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the Show End Result button is on (pressed); otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void SetShowEndResult(BOOL show)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets the on/off (pressed/unpressed) state of the Show End Result button. Note that calling this method generates a redraw.
Parameters:
BOOL show
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL InSlaveMode()=0;
Remarks:
Returns TRUE if MAX is operating in network rendering mode and FALSE if operating in normal interactive mode. This method returns the same value as Interface::IsNetServer().
Prototype:
virtual BOOL IsNetServer()=0;
Remarks:
Returns TRUE if MAX is operating in network rendering mode and FALSE if operating in normal interactive mode. This method returns the same value as Interface::InSlaveMode().
Prototype:
virtual void SetNetServer()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method is for internal use only. Calling this method will not (alone) set MAX in "Server" mode. Developers should not call this method.
Prototype:
virtual int InitSnapInfo(SnapInfo *info)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only (previously available as a global function).
Initialized the SnapInfo structure passed with the current snap settings.
Parameters:
SnapInfo *info
Points to the SnapInfo structure to initialize. See Structure SnapInfo.
Return Value:
Returns nonzero if snap is on; zero if off.
Prototype:
virtual float SnapAngle(float angleIn, BOOL fastSnap=TRUE, BOOL forceSnap=FALSE)=0;
Remarks:
Normally, with angle snap off, interactive rotation of a node uses a rate of 1/2 degree per pixel. With angle snap on, the angles are snapped to the nearest MAX angle snap value.
This method may be used when interactive rotation is taking place with the mouse to snap the angle passed to the nearest MAX angle snap value. In this method, the input value/output value snap correspondence is accelerated as the angle grows. This prevents the user from having to move the mouse too much with larger angle values. This is why this method does not return a linear relationship between the input angle and the snapped output angle.
Note that when angle snap is off, this method just returns the input value unaltered.
Note for R3: This method formerly was set up with a single parameter, the angle to be snapped. If the angle snap toggle was on, snapping occurred. If not, it did nothing. There were two problems with this:
1) A multiplier was applied to the angle input, giving faster interactive results in object rotations, etc. This had a negative effect if you just wanted your input angle snapped to the nearest snap angle.
2) It only snapped if the angle snap toggle was on. Sometimes, you might want to snap something to the angle snap value even if the master toggle was off.
To remedy these shortcomings, the method has had two parameters added (fastSnap and forceSnap).
Parameters:
float angleIn
Angle to snap in radians.
BOOL fastSnap=TRUE
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
If TRUE the snapping multiplier is used; if FALSE it is not.
BOOL forceSnap=FALSE
This parameter is available in release 3.0 and later only.
If TRUE snapping is used even if the master angle snap toggle is off.
Return Value:
Angle snapped to the nearest angle snap setting (considering acceleration if specified), in radians, to be used for interactive rotation.
Prototype:
virtual float SnapPercent(float percentIn)=0;
Remarks:
Given a value in the range 0.0 (0%) to 1.0 (100%) this method snaps the value using the current percentage snap.
Parameters:
float percentIn
The value to snap.
Return Value:
The snapped value where 0.0 = 0% and 1.0 = 100%.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetSnapState()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the snap toggle state.
Return Value:
TRUE if snap is on; FALSE if snap is off.
Prototype:
virtual int GetSnapMode()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the current snap type.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
SNAPMODE_RELATIVE
SNAPMODE_ABSOLUTE
Prototype:
virtual BOOL SetSnapMode(int mode)=0;
Remarks:
Set the current snap mode. Note that setting the mode to SNAPMODE_ABSOLUTE will fail if the reference coordinate system is not in set to Screen.
Parameters:
int mode
One of the following values:
SNAPMODE_RELATIVE
SNAPMODE_ABSOLUTE
Return Value:
Returns TRUE if succeeded; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual SoundObj *GetSoundObject()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the current sound object. See the sample code in \MAXSDK\SAMPLES\UTILITIES\UTILTEST.CPP.
See Also: Class SoundObj, Class IWaveSound.
Prototype:
virtual void SetSoundObject(SoundObj *snd)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the current sound object to the one specified. See Class SoundObj.
Parameters:
SoundObj *snd
The sound object to set as current.
Prototype:
virtual void RegisterSubObjectTypes(const TCHAR **types, int count, int startIndex=0)=0;
Remarks:
This method registers the sub-object types for a given plug-in object type. See the Advanced Topics section on sub-object selection for more details.
Parameters:
const TCHAR **types
Array of strings listing the sub object levels. The order the strings appear in the array sets the indices used for the sub-object levels. Level 0 is always object level, the first string corresponds to level 1, and the second string corresponds to level 2, etc. In the sample code below, "Center" is level 1 and "Gizmo" is level 2.
int count
The number of strings in the array.
int startIndex=0
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Specifies which string to display initially in the sub-object type combo box. This is needed because the NURBS object computes its sub-object list dynamically, and sometimes it add a new sub-object level while already in a sub-object level. The default value of zero replicates the original behavior.
Sample Code:
const TCHAR *ptype[] = { _T("Center"), _T("Gizmo") };
ip->RegisterSubObjectTypes(ptype, 2);
Prototype:
virtual int GetSubObjectLevel()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the state of the sub object drop-down.
Return Value:
0 is object level and >= 1 refers to the levels registered by the object using RegisterSubObjectTypes(). The value refers to the order the item appeared in the list. 1 is the first item, 2 is the second, etc.
Prototype:
virtual void SetSubObjectLevel(int level, BOOL force = FALSE)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the sub-object drop down. This will cause the object being edited to receive a notification that the current sub-object level has changed (via BaseObject::ActivateSubobjSel()).
Parameters:
int level
The level registered by the object using RegisterSubObjectTypes(). 0 indicates object level. Values greater than 1 refer to the order the items appeared in the list.
BOOL force = FALSE
If this parameter is TRUE, this method will set the level even if the current level is the same as the level requested. This is to support objects that change sub-object levels on the fly, for instance NURBS.
Prototype:
virtual int GetNumSubObjectLevels()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method returns the number of sub object levels that the currently edited object (or modifier) has. Like the other sub-object related methods in this class, this method will only return a valid answer if the modifier panel is displayed.
Prototype:
virtual void EnableSubObjectSelection(BOOL enable)=0;
Remarks:
This method enables or disables sub-object selection. Note that it will already be disabled if there are no subobject levels registered. In this case, this method has no effect.
Parameters:
BOOL enable
TRUE to enable sub-object selection; FALSE to disable.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL IsSubObjectSelectionEnabled()=0;
Remarks:
This method returns the state that is modified by EnableSubObjectSelection(). That is, it does not actually return the state of the button, but indicates the disabled state as set by EnableSubObjectSelection().
Return Value:
TRUE if the sub-object button has been disabled by EnableSubObjectSelection(); otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void PipeSelLevelChanged()=0;
Remarks:
Plug-ins call this method to notify the system that the selection level in the pipeline has changed. The selection level flows up the pipeline so if you change the selection level you affect things later in the pipeline. For example an edit modifier that changes the sub-object level from vertex to object level must call this method after making the change to notify the system. Note that it is only called for modifiers whose sub-object levels propagate up the pipeline. For example, when entering a sub-object level within the Bend modifier, PipeSelLevelChanged() is not called.
This method should be called from within ActivateSubobjSel() to notify the system that a selection level has changed in the pipeline. Note that calling this method from within ModifyObject() is no good since it involves re-evaluating the pipeline, which will call ModifyObject(), which will the call PipeSelLevelChanged() again, etc.
Prototype:
virtual void GetPipelineSubObjLevel(DWORDTab &levels)=0;
Remarks:
Gets the sub-object selection level at the point in the pipeline just before the current place in the history.
Parameters:
DWORDTab &levels
The sub-object level. This value depends on the object. The only level defined is level 0, which means 'object' level selection.
Prototype:
virtual int SubObHitTest(TimeValue t, int type, int crossing, int flags, IPoint2 *p, ViewExp *vpt)=0;
Remarks:
This method may be called to perform a sub-object hit test. You may access the number of hits using: vpt->NumSubObjHits(); See Class ViewExp for a list of the other methods that may be used to examine the results.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time of the hit testing.
int type
The hit test type. See List of Hit Test Types.
int crossing
Nonzero for crossing selection; 0 for normal (window).
int flags
The flags for hit testing. See List of Hit Test Flags.
IPoint2 *p
Point to check in screen coordinates.
ViewExp *vpt
An interface pointer that may be used to call methods associated with the viewports.
Return Value:
Nonzero if the item was hit; otherwise 0.
Sub-Object Selection Sets (Named)
Prototype:
virtual void AppendSubObjectNamedSelSet(const TCHAR *set)=0;
Remarks:
A modifier may call this method to add sub-object named selection sets to the named selection set drop down list in the MAX toolbar. This should be done whenever the selection level changes (in the Modifiers BaseObject::ActivateSubobjSel() method). See Class BaseObject for additional methods associated with sub-object named selection sets.
Parameters:
const TCHAR *set
The named selection set to add to the list.
Prototype:
virtual void ClearSubObjectNamedSelSets()=0;
Remarks:
This method clears the named sub-object selection sets from the drop down.
Status Panel / Prompt Related Methods
Generally prompts are set by the command mode and these are the methods used. The developer may use the DisplayTempPrompt() method below to temporarily display a prompt to the user independent of a command mode.
Prototype:
virtual void PushPrompt( TCHAR *s )=0;
Remarks:
Pushes a prompt to display on the prompt stack.
Parameters:
TCHAR *s
The string to display.
Prototype:
virtual void PopPrompt()=0;
Remarks:
Pops a displayed string off the prompt stack. The previous prompt will be restored.
Prototype:
virtual void ReplacePrompt( TCHAR *s )=0;
Remarks:
Replaces the string on the top of the prompt stack.
Parameters:
TCHAR *s
The string to display.
Prototype:
virtual void DisplayTempPrompt( TCHAR *s, int msec=1000)=0;
Remarks:
Displays the string passed for the duration passed. After the time elapses, the string is popped from the stack. This may be used to put up a temporary error message for example.
Parameters:
TCHAR *s
The string to display temporarily.
int msec=1000
The duration in milliseconds to display the string.
Prototype:
virtual void RemoveTempPrompt()=0;
Remarks:
Removes the temporary prompt immediately.
Prototype:
virtual void DisableStatusXYZ()=0;
Remarks:
Disables mouse tracking and display of coordinates to the X, Y, Z status boxes. Typically a plug-in would disable mouse tracking on mouse down and enable it on mouse up.
Prototype:
virtual void EnableStatusXYZ()=0;
Remarks:
Enables mouse tracking and display of coordinates to the X, Y, Z status boxes. Typically a plug-in would disable mouse tracking on mouse down and enable it on mouse up.
Prototype:
virtual void SetStatusXYZ(Point3 xyz,int type)=0;
Remarks:
Displays the point passed using the format passed in the X, Y, Z status boxes.
Parameters:
Point3 xyz
The point to be displayed.
int type
The format of the point:
STATUS_UNIVERSE
Current system units.
STATUS_SCALE
0=0%, 1=100%.
STATUS_ANGLE
Degrees.
STATUS_OTHER
Straight floating point value.
Prototype:
virtual void SetStatusXYZ(AngAxis aa)=0;
Remarks:
This method will convert the specified angle axis for status display.
Parameters:
AngAxis aa
The angle axis to convert and display.
Track Bar and Track View Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual ITrackViewNode *GetTrackViewRootNode()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method returns a pointer to the Track View Root Node. See Class ITrackViewNode.
Prototype:
virtual ITreeView* CreateTreeViewChild(ReferenceTarget* root, HWND hParent, DWORD style=0, ULONG id=0, int open=OPENTV_SPECIAL)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method will creates a plain treeview window (no title,borders,etc.) as a child window of the given window. To destroy the window, delete the ITreeView pointer.
Parameters:
ReferenceTarget* root
Points to the root node of the hierarchy to display in the Track View.
HWND hParent
The window handle of the parent for the dialog.
DWORD style=0
The style flags;
TVSTYLE_MAXIMIZEBUT
Provide a maximize button.
TVSTYLE_INVIEWPORT
Display in the viewport.
TVSTYLE_NAMEABLE
The treeview is namable.
TVSTYLE_INMOTIONPAN
Used in the motion panel.
ULONG id=0
The ID of the treeview window.
int open=OPENTV_SPECIAL
One of the following values:
OPENTV_NEW
Open a new treeview.
OPENTV_SPECIAL
Open a special treeview.
OPENTV_LAST
Open the last treeview.
Prototype:
virtual ITrackBar* GetTrackBar()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method returns an instance of the ITrackBar class. This class may be used to manipulate the track bar. See Class ITrackBar.
Time Configuration Key Steps Settings Access
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetKeyStepsSelOnly()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Selected Objects Only check box is on; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void SetKeyStepsSelOnly(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Selected Objects Only check box to on or off.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetKeyStepsUseTrans()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Use Current Transform check box is on; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void SetKeyStepsUseTrans(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Use Current Transform check box to on or off.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetKeyStepsPos()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Position check box is on; otherwise FALSE. This value is only meaningful if Use Current Transform is off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetKeyStepsPos(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Position check box is to on or off.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetKeyStepsRot()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Rotation check box is on; otherwise FALSE. This value is only meaningful if Use Current Transform is off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetKeyStepsRot(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Rotation check box is to on or off.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetKeyStepsScale()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Scale check box is on; otherwise FALSE. This value is only meaningful if Use Current Transform is off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetKeyStepsScale(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Sets the Time Configuration / Key Steps / Scale check box is to on or off.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetKeyStepsUseTrackBar()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns the state of the Time Configuration dialog 'Key Steps / Use TrackBar' checkbox. TRUE if checked; FALSE if unchecked.
Prototype:
virtual void SetKeyStepsUseTrackBar(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets the state of the Time Configuration dialog 'Key Steps / Use TrackBar' checkbox.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
User Interface Controls and Properties
Prototype:
virtual void SetFlyOffTime(int msecs)=0;
Remarks:
This sets the custom control flyoff time to the value passed. This is the number of milliseconds the user must hold down on a flyoff button before the flyoff is activated.
Parameters:
int msecs
The number of milliseconds the user must hold down on the button before the flyoff is activated.
Prototype:
virtual int GetFlyOffTime()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the number of milliseconds the user must hold down on a flyoff button before the flyoff is activated.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetCrossing()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the state of the 'crossing' preference for hit testing.
Return Value:
TRUE if crossing selection is on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetToolButtonState(int button, BOOL state )=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of one of the transform tool buttons.
Parameters:
int button
The transform tool buttons:
MOVE_BUTTON
ROTATE_BUTTON
NUSCALE_BUTTON
USCALE_BUTTON
SQUASH_BUTTON
SELECT_BUTTON
BOOL state
TRUE indicates pressed, FALSE is not pressed.
Prototype:
virtual int GetAxisConstraints()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the state of the axis constraints flyoff.
Return Value:
One of the following axis constraints:
AXIS_XY
AXIS_ZX
AXIS_YZ
AXIS_X
AXIS_Y
AXIS_Z
Prototype:
virtual void SetAxisConstraints(int c)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of the axis constraints flyoff.
Parameters:
int c
The axis constraint to set. You may pass one of the following:
AXIS_XY
AXIS_ZX
AXIS_YZ
AXIS_X
AXIS_Y
AXIS_Z
Prototype:
virtual void EnableAxisConstraints(int c, BOOL enabled)=0;
Remarks:
Enables or disables the specified axis constraint.
Parameters:
int c
The axis constraint. You may pass one of the following:
AXIS_XY
AXIS_ZX
AXIS_YZ
AXIS_X
AXIS_Y
AXIS_Z
BOOL enabled
TRUE to enable; FALSE to disable.
Prototype:
virtual void PushAxisConstraints(int c)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Pushes the specified axis constraint. This push/pop mechanism is used so that the appropriate axis mode can be restored after the Transform Gizmo has been used. The Gizmo itself calls this Push method is response to the HitTest with certain flags.
Parameters:
int c
The axis constraint. You may pass one of the following:
AXIS_XY
AXIS_ZX
AXIS_YZ
AXIS_X
AXIS_Y
AXIS_Z
Prototype:
virtual void PopAxisConstraints()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Pops the active constraint. After the Transform Gizmo pushes a constraint a selection processor pops it back again after the manipulators are deactivated.
Prototype:
virtual int GetCoordCenter()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the state of the coordinate system center.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
ORIGIN_LOCAL
Object's pivot.
ORIGIN_SELECTION
Center of selection set (or center of individual object for local or parent space).
ORIGIN_SYSTEM
Center of the reference coordinate system.
Prototype:
virtual void SetCoordCenter(int c)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the state of the coordinate system center.
Parameters:
int c
One of the following values (from MAXAPI.H).
ORIGIN_LOCAL
Object's pivot.
ORIGIN_SELECTION
Center of selection set (or center of individual object for local or parent space).
ORIGIN_SYSTEM
Center of the reference coordinate system.
Prototype:
virtual void EnableCoordCenter(BOOL enabled)=0;
Remarks:
Enables or disables the coordinates system center.
Parameters:
BOOL enabled
TRUE to enable; FALSE to disable.
Prototype:
virtual int GetRefCoordSys()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the reference coordinate system setting.
Return Value:
One of the following reference coordinate systems:
COORDS_HYBRID
COORDS_SCREEN
COORDS_WORLD
COORDS_PARENT
COORDS_LOCAL
COORDS_OBJECT
Prototype:
virtual void SetRefCoordSys(int c)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the reference coordinate system used.
Parameters:
int c
Reference coordinate system:
COORDS_HYBRID
COORDS_SCREEN
COORDS_WORLD
COORDS_PARENT
COORDS_LOCAL
COORDS_OBJECT
Prototype:
virtual void EnableRefCoordSys(BOOL enabled)=0;
Remarks:
Enables or disables the reference coordinates system.
Parameters:
BOOL enabled
TRUE to enable; FALSE to disable.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetPlaybackLoop()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method returns the state of the "loop" checkbox in the time configuration panel. Note that the loop control is only active when "real time" is selected.
Return Value:
TRUE if loop is on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetPlaybackLoop(BOOL loop)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method allows you to set the state of the "loop" checkbox in the time configuration panel. Note that the loop control is only active when "real time" is selected.
Parameters:
BOOL loop
TRUE to set the loop to on; FALSE to set it off.
Prototype:
virtual INode *GetINodeFromRenderID(UWORD id)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method returns the node pointer from the id in the BMM_CHAN_NODE_RENDER_ID G-Buffer channel. The renderer will set the RenderID of all rendered nodes, and will set all non-rendered nodes to 0xffff. See List of Image Channels.
Parameters:
UWORD id
The id from the G Buffer channel.
Prototype:
virtual int GetSelectFilter()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method returns your current selected select filter in the toolbar.
Prototype:
virtual void SetSelectFilter(int c)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method allows you to set the current selected select filter in the toolbar.
Parameters:
int c
The index of the filter you wish to set.
Prototype:
virtual int GetNumberSelectFilters()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method returns the number of select filters in the drop down list.
Prototype:
virtual TCHAR* GetSelectFilterName(int index)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method returns the name that appears in the interface for the specified filter.
Parameters:
int index
The index of the filter.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetDisplayFilter(int index) = 0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method returns the state of a display filter.
Parameters:
int index
The index of the display filter that you want to check.
Prototype:
virtual void SetDisplayFilter(int index, BOOL on) = 0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method allows you to set the state of a display filter.
Parameters:
int index
The index of the display filter you wish to set.
BOOL on
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual int GetNumberDisplayFilters() = 0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method returns the number of display filters in the display panel.
Prototype:
virtual TCHAR* GetDisplayFilterName(int index)=0;;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method returns the name of the specified filter.
Parameters:
int index
The index of the filter.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL DisplayFilterIsNodeVisible(int index, int sid, Class_ID cid, INode *node) = 0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method checks the display filter at index, and sees if the node, class id, and super class id fail the filter check or not.
Parameters:
int index
The index of the filter
int sid
The super class id
Class_ID cid
The class ID
INode *node
The node to check.
Return Value:
TRUE if visible, otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void RedrawViews(TimeValue t, DWORD vpFlags=REDRAW_NORMAL, ReferenceTarget *change=NULL)=0;
Remarks:
This method may be called to cause the viewports to be redrawn.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time at which to redraw the viewports.
DWORD vpFlags=REDRAW_NORMAL
You may specify one of the following:
REDRAW_BEGIN
Call this before you redraw.
REDRAW_INTERACTIVE
This allows the view quality to degrade to maintain interactively.
REDRAW_END
If during interactive redraw the state degraded, this will redraw the views in the undegraded state.
REDRAW_NORMAL
This redraws the views in the undegraded state.
ReferenceTarget *change=NULL
This parameter is not used - always let it default to NULL.
Example:
ip->RedrawViews(ip->GetTime(),REDRAW_BEGIN);
// More code ...
ip->RedrawViews(ip->GetTime(),REDRAW_INTERACTIVE);
// More code ...
ip->RedrawViews(ip->GetTime(),REDRAW_END);
Prototype:
virtual void ForceCompleteRedraw(BOOL doDisabled=TRUE)=0;
Remarks:
Calling this method will cause all the viewports to be completely redrawn. Note: This method literally forces everything (every object, every screen rectangle, every view) to be marked invalid and then the whole scene is regenerated. (The individual object pipeline caches are not flushed, however.) So this routine is guaranteed to be slow.
Parameters:
BOOL doDisabled=TRUE
This parameter is available in release 2.0 and later only.
If TRUE disabled viewports are redrawn; otherwise they are not.
Prototype:
virtual void DisableSceneRedraw()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This turns the scene redraw off (disables it). Scene redraw should be disabled in any renderer's Open() method, and re-enabled in the renderer's Close() method. All calls to DisableSceneRedraw()/Enable SceneRedraw() should be in pairs, since an internal counter is used to actually do the redraw enable/disable action.
Prototype:
virtual void EnableSceneRedraw()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This turns the scene redraw on (enables it). Scene redraw should be disabled in any renderer's Open() method, and re-enabled in the renderer's Close() method. All calls to DisableSceneRedraw()/Enable SceneRedraw() should be in pairs, since an internal counter is used to actually do the redraw enable/disable action.
Prototype:
virtual int IsSceneRedrawDisabled()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
Returns nonzero if the redraw is disabled; zero if enabled.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL SetActiveViewport( HWND hwnd )=0;
Remarks:
This allows you to specify the active viewport.
Parameters:
HWND hwnd
The handle of the window to activate.
Return Value:
TRUE if the viewport was not previously active; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual ViewExp *GetActiveViewport()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the ViewExp pointer of the active MAX viewport. Remember to release the ViewExp pointer with Interface::ReleaseViewport().
Prototype:
virtual ViewExp *GetViewport( HWND hwnd )=0;
Remarks:
This method gets a viewport interface given a window handle.
Parameters:
HWND hwnd
The window handle of the viewport.
Prototype:
virtual void ReleaseViewport( ViewExp *vpt )=0;
Remarks:
When the developer is done with the viewport interface acquired via GetViewport() or GetActiveViewport() they should call this method to release it.
Parameters:
ViewExp *vpt
The viewport interface to release.
Prototype:
virtual int GetViewportLayout()=0;
Remarks:
This method may be called to retrieve a value that describes the configuration of the MAX viewports.
Return Value:
The viewport layout configuration. The list below uses the following syntax:
# is the total number of viewports.
V = vertical split
H = horizontal split
L/R = left/right placement
T/B = top/bottom placement
One of the following values. Note: The bottom nibble (4-bits) is the total number of views. You may use the constant VP_NUM_VIEWS_MASK to mask off the 4 bits that contains the total number of viewports.
VP_LAYOUT_1
VP_LAYOUT_2V
VP_LAYOUT_2H
VP_LAYOUT_2HT
VP_LAYOUT_2HB
VP_LAYOUT_3VL
VP_LAYOUT_3VR
VP_LAYOUT_3HT
VP_LAYOUT_3HB
VP_LAYOUT_4
VP_LAYOUT_4VL
VP_LAYOUT_4VR
VP_LAYOUT_4HT
VP_LAYOUT_4HB
VP_LAYOUT_1C
Prototype:
virtual void SetViewportLayout(int layout)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets the viewport configuration layout.
Parameters:
int layout
The layout to use. See the return values of GetViewportLayout() above.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL IsViewportMaxed()=0;
Remarks:
Returns TRUE if the current viewport is full screen; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void SetViewportMax(BOOL max)=0;
Remarks:
This method will maximize (set to a single full screen view) or minimize the current viewport.
Parameters:
BOOL max
If TRUE the viewport is maximized; otherwise it is minimized.
Prototype:
virtual void ViewportZoomExtents(BOOL doAll, BOOL skipPersp=FALSE)=0;
Remarks:
This method performs a zoom extents on the viewport(s). This fills the viewport(s) with the objects of the scene.
Parameters:
BOOL doAll
If TRUE all the viewports are zoomed to their extents; otherwise just the current viewport is.
BOOL skipPersp=FALSE
If TRUE perspective viewports are not altered; otherwise these views are zoomed to their extents as well.
Prototype:
virtual int IsCPEdgeOnInView()=0;
Remarks:
This method returns nonzero if the construction plane is 'head on' in the current viewport. For example if the construction plane was XY and you were looking from the Front view, this method would return nonzero. This is used for example during object creation because this process doesn't work very well when the view is 'head on'.
Return Value:
Nonzero if the construction plane is 'head on' in the current viewport; otherwise 0.
For use with extended views: - make the extended viewport active (set on mouse click, for example) -put up the view type popup menu (put up on right-click, for example)
Prototype:
virtual void MakeExtendedViewportActive(HWND hWnd)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method is used with Extended Viewports (see Class ViewWindow). It is called when the extended viewport needs to become active. It should be called whenever the user clicks in the non-3D window (so as to deactivate the current 3D window, and redirect commands like the Min/Max toggle to the non-3D viewport window).
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
The handle of the window which to made active.
Prototype:
virtual void PutUpViewMenu(HWND hWnd, POINT pt)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method is used with Extended Viewports (see Class ViewWindow). It is called to put up the view type popup menu (for example the right-click menu). It should be called when the user right-clicks in a dead region of the non-3D window. This brings up the view selection menu so that the user can choose to replace the current window with a 3D or other non-3D window without having to go to the Views | Viewport Config dialog directly.
Parameters:
HWND hWnd
The handle of the window the menu is to appear in.
POINT pt
The point at which the menu is put up.
Sample Code:
case WM_RBUTTONDOWN:
pt.x = LOWORD(l);
pt.y = HIWORD(l);
GetCOREInterface()->PutUpViewMenu(h, pt);
Prototype:
virtual BOOL RegisterViewWindow(ViewWindow *vw)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method allows you to register a window that can appear in a viewport.
Parameters:
ViewWindow *vw
The pointer to the view window to register.
Return Value:
TRUE if successful, otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL UnRegisterViewWindow(ViewWindow *vw)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method allows you to unregister a window that can appear in a viewport.
Parameters:
ViewWindow *vw
The pointer to the view window to unregister.
Return Value:
TRUE if successful, otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual void ZoomToBounds(BOOL doAll, Box3 box)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method allows you to zoom the current or selected viewport to a bounding region.
Parameters:
BOOL doAll
This flag determines whether only the selected or all viewports get zoomed. TRUE for all, FALSE for selected only.
Box3 box
The bounding region to zoom to.
Viewport Background Properties
Prototype:
virtual void SetViewportBGColor(const Point3 &color)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the viewport background color to the specified color.
Parameters:
const Point3 &color
The color to set.
Prototype:
virtual Point3 GetViewportBGColor()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the viewport background color.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL setBkgImageName(TCHAR *name)=0;
Remarks:
This method is used to specify the background image used.
Parameters:
TCHAR *name
The name of the background image.
Return Value:
TRUE if the image was set; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual TCHAR *getBkgImageName()=0;
Remarks:
This method is used to retrieve the name of the background image used. The pointer returned from this method does not need to be freed.
Prototype:
virtual void setBkgImageAspect(int t)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the background image aspect ratio. This may match the viewport, the bitmap, or the rendering output aspect ratio.
Parameters:
int t
One of the following values:
VIEWPORT_BKG_ASPECT_VIEW
VIEWPORT_BKG_ASPECT_BITMAP
VIEWPORT_BKG_ASPECT_OUTPUT
Prototype:
virtual int getBkgImageAspect()=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the background image aspect ratio. This will be the viewport, the bitmap, or the rendering output aspect ratio.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
VIEWPORT_BKG_ASPECT_VIEW
VIEWPORT_BKG_ASPECT_BITMAP
VIEWPORT_BKG_ASPECT_OUTPUT
Prototype:
virtual void setBkgImageAnimate(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method sets if the background image is animated in the viewports. If TRUE the image updates to reflect the current frame. If FALSE the image remains static regardless of time.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE to enable viewport background image animation; FALSE to disable it.
Prototype:
virtual int getBkgImageAnimate()=0;
Remarks:
This method determines if the background image is set to update with the current frame in the viewports.
Prototype:
virtual void setBkgFrameRange(int start, int end, int step=1)=0;
Remarks:
This method establishes the range of frames used for an animated background.
Parameters:
int start
The start frame number.
int end
The end frame number.
int step=1
The frame increment.
Prototype:
virtual int getBkgFrameRangeVal(int which)=0;
Remarks:
This method retrieves either the start or end frame number.
Parameters:
int which
One of the following values:
VIEWPORT_BKG_START
VIEWPORT_BKG_END
Prototype:
virtual void setBkgORType(int which, int type)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the background Out of Range Type. This may be the start or end ORT.
Parameters:
int which
One of the following values:
0 : Sets the Start Processing ORT.
1 : Sets the End Processing ORT.
int type
One of the following values:
VIEWPORT_BKG_BLANK
VIEWPORT_BKG_HOLD
VIEWPORT_BKG_LOOP
Prototype:
virtual int getBkgORType(int which)=0;
Remarks:
Retrieves the background Out of Range Type. This may be the start or end ORT.
Parameters:
int which
One of the following values:
0 : Gets the Start Processing ORT.
1 : Gets the End Processing ORT.
Return Value:
One of the following values:
VIEWPORT_BKG_BLANK
VIEWPORT_BKG_HOLD
VIEWPORT_BKG_LOOP
Prototype:
virtual void setBkgStartTime(TimeValue t)=0;
Remarks:
This sets the "Start at" parameter from the Views / Background Image... dialog.
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to start.
Prototype:
virtual TimeValue getBkgStartTime()=0;
Remarks:
This returns the "Start at" parameter from the Views / Background Image... dialog.
Prototype:
virtual void setBkgSyncFrame(int f)=0;
Remarks:
Sets the background "Sync Start to Frame" setting.
Parameters:
int f
The frame number.
Prototype:
virtual int getBkgSyncFrame()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the background "Sync Start to Frame" setting.
Prototype:
virtual int getBkgFrameNum(TimeValue t)=0;
Remarks:
This method will convert the TimeValue passed to a frame number based on the background image settings (ORTs, start/end times, sync frame, etc.).
Parameters:
TimeValue t
The time to convert.
Return Value:
The frame number corresponding to the time passed.
Prototype:
virtual HWND GetMAXHWnd()=0;
Remarks:
Returns the window handle of MAX.
Prototype:
virtual void TranslateAndDispatchMAXMessage(MSG &msg)=0;
Remarks:
If a plug-in needs to do a PeekMessage() and wants to actually remove the message from the queue, it can use this method to have the message translated and dispatched.
Parameters:
MSG &msg
The message from PeekMessage().
Prototype:
virtual BOOL CheckMAXMessages()=0;
Remarks:
This will go into a PeekMessage() loop until there are no more messages left. This is a way a plug-in can relieve control to the system.
There may be certain circumstances where a plug-in wants to give control back to MAX. For example a plug-in may put up a progress bar with a cancel button during a lengthy operation. However the cancel button would not receive any messages if the user was clicking on it because no messages are being dispatched.
This method will relieve control and let any messages that are in the queue get processed. If there are no messages it will return right away. This provides a way for a plug-in to yield control.
Note: A developer must be prepared to handle a lot of different conditions if this is done. For example the user could click on the delete key and delete the object that was being processed. EndEditParams() could be called on the plug-in. So in EndEditParams() there must be some logic to signal the other lengthy process that EndEditParams() was called.
Return Value:
If this method returns FALSE then the user is attempting to quit MAX and the caller should return.
Prototype:
virtual void RescaleWorldUnits(float f, BOOL selected)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 2.0 and later only.
This method is used to rescale the world units of the entire scene, or optionally the current selection set.
Parameters:
float f
The scale factor to apply to the scene.
BOOL selected
TRUE to scale selected objects only; otherwise the entire scene is scaled.
Transform Gizmo Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetUseTransformGizmo()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns the state of the Transform Tools / Gizmo toggle.
Return Value:
TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetUseTransformGizmo(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method enables or disables the use of Transform Gizmos.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetTransformGizmoRestoreAxis(BOOL bOnOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method sets whether the TransformGizmo should restore the axis constraint when released, or if the axis constraint is permanently changed. The value is saved in the 3DSMAX.INI file for later sessions.
Parameters:
BOOL bOnOff
Enable or disable the restoration of the axis constraint.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetTransformGizmoRestoreAxis()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Indicates if the TransformGizmo will restore the axis constraint when released. Returns TRUE if it will; FALSE if it won't.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetConstantAxisRestriction()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns the state of the Transform Tools / Constant Axis toggle.
Return Value:
TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void SetConstantAxisRestriction(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets the state of the Transform Tools / Constant Axis toggle.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual int HitTestTransformGizmo(IPoint2 *p, ViewExp *vpt, int axisFlags) = 0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method is used to hittest gizmos for sub-objects.
Parameters:
IPoint2 *p
Point to check in screen coordinates.
ViewExp *vpt
An interface pointer that may be used to call methods associated with the viewports.
int axisFlags
One or more of the following values:
HIT_TRANSFORMGIZMO
This flag is passed in on a MOUSE_FREEMOVE message so that the axis is hit tested and it hightlights if it is hit, but it doesn't actually switch the transform mode.
HIT_SWITCH_GIZMO
In case of a MOUSE_POINT, this flag is used, and if the axis is hit, the 'hit' transform mode will be pushed on the transform mode stack.
Return Value:
Nonzero if the item was hit; otherwise 0.
Prototype:
virtual int AddClass(ClassDesc *cd)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method is used to dynamically add a plug-in class. This method will update the control panel in the Create or Modify branches dynamically.
Parameters:
ClassDesc *cd
Points to the Class Descriptor to add. See Class ClassDesc.
Return Value:
Returns -1 if the superclass was unknown, 0 if the class already exists, or 1 if the class was added successfully.
Prototype:
virtual int DeleteClass(ClassDesc *cd)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method is used to dynamically delete a plug-in class. This method will update the control panel in the Create or Modify branches dynamically.
Parameters:
ClassDesc *cd
Points to the Class Descriptor to add. See Class ClassDesc.
Return Value:
Returns -1 if the superclass was unknown, 0 if the class does not exist, or 1 if the class was deleted successfully.
The following methods provide developer access to the property set data stored by MAX. A MAX user can enter this data via the File Properties dialog. There are three tabs to this dialog which correspond to the options which may be specified for the PropertySet parameter used in the methods below. The PROPSPEC and PROPVARIANT structures used below are part of the Windows API. Developers can find sample code using these methods in \MAXSDK\SAMPLES\UTILITIES\PROPERTYTEST\PROPERTYTEST.CPP.
Prototype:
virtual int GetNumProperties(int PropertySet)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns the number of properties of the specified property set. See the note at the start of this group of methods above for info on property sets.
Parameters:
int PropertySet
See List of PropertySet Options.
Prototype:
virtual int FindProperty(int PropertySet, const PROPSPEC* propspec)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Return the index of the specified property or -1 if it is not found. See the note at the start of this group of methods above for info on property sets.
Parameters:
int PropertySet
See List of PropertySet Options.
const PROPSPEC* propspec
Points to a PROPSPEC structure of the property to find. The Windows API PROPSPEC structure is used by many of the methods of IPropertyStorage to specify a property either by its property identifier or the associated string name. See the Windows API for details on this structure.
Return Value:
The zero based index of the specified property or -1 if not found.
Prototype:
virtual const PROPVARIANT* GetPropertyVariant(int PropertySet, int idx)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Return the value of the property at this index, in PROPVARIANT form. See the note at the start of this group of methods above for info on property sets.
Parameters:
int PropertySet
See List of PropertySet Options.
int idx
The zero based index of the property variant to get.
Return Value:
Points to a PROPVARIANT structure. This Windows API structure is used in most of the methods of IPropertyStorage to define the type tag and the value of a property in a property set. See the Windows API for details on this structure.
Prototype:
virtual const PROPSPEC* GetPropertySpec(int PropertySet, int idx)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Return the name of the property at this index, in PROPSPEC form. See the note at the start of this group of methods above for info on property sets.
Parameters:
int PropertySet
See List of PropertySet Options.
int idx
The zero based index of the property name to get.
Return Value:
Points to a PROPSPEC structure. The Windows API PROPSPEC structure is used by many of the methods of IPropertyStorage to specify a property either by its property identifier or the associated string name. See the Windows API for details on this structure.
Prototype:
virtual void AddProperty(int PropertySet, const PROPSPEC* propspec, const PROPVARIANT* propvar)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method adds a property to the specified property set. See the sample code in \MAXSDK\SAMPLES\UTILITIES\PROPERTYTEST\PROPERTYTEST.CPP.
See the note at the start of this group of methods above for info on property sets.
Parameters:
int PropertySet
See List of PropertySet Options.
const PROPSPEC* propspec
Points to a PROPSPEC structure.
const PROPVARIANT* propvar
Points to a PROPVARIANT structure.
Prototype:
virtual void DeleteProperty(int PropertySet, const PROPSPEC* propspec)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Deletes the specified property. The property will be removed and the memory freed. See the note at the start of this group of methods above for info on property sets.
Parameters:
int PropertySet
See List of PropertySet Options.
const PROPSPEC* propspec
Points to a PROPSPEC structure to delete.
Prototype:
virtual void SetIncludeXRefsInHierarchy(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This method allows a plug-in to specify whether scene XRef objects are hidden from the hierarchy when it is traversed. Normally this parameter is set to FALSE except during rendering. If a plug-in wants access to XRef scene objects then it should set this to TRUE and traverse the scene and then set it back to FALSE when it's done.
Most of the time the XRef trees (whose root node is a child of the client scene's root node) are skipped when traversing the hierarchy. When this option is turned on, all root nodes will include child XRef scene root nodes in any traversal related functions such as NumberOfChildren() and GetChildNode(i).
This option is turned on automatically before rendering and turned off after so that scene XRefs appear in the production renderer. Note: This option should not be left on if it is turned on since it would cause scene XRef objects to be accessible to the user in the client scene.
Note that plug-ins can also access XRef objects using the Class INode XRef methods.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE to include XRefs in the hierarchy; FALSE to not include them.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL GetIncludeXRefsInHierarchy()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if XRefs are included in the traversal of the scene hierarchy; otherwise FALSE. See the method above for details.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL IsXRefAutoUpdateSuspended()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the automatic updating of XRefs is suspended; otherwise FALSE. When an XRef file is changed and that causes an XRef object to update, the old XRef object gets deleted from memory which can cause problems for some plug-ins. For example, the Dynamics system would have a problem if an update occured while a solution was solving. This method is used to disable the automatic updating to prevent the problem.
Prototype:
virtual void SetXRefAutoUpdateSuspended(BOOL onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Sets if the automatic updating of XRefs is suspended or not. See the note in IsXRefAutoUpdateSuspended() for details.
Parameters:
BOOL onOff
TRUE to suspend; FALSE to restore automatic updating.
Prototype:
virtual BOOL IsSceneXRefNode(INode *node)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the specified node is part of a scene XRef or FALSE if the node is a regular modifiable node in the current scene.
Parameters:
INode *node
The node to check.
Prototype:
virtual bool IsTrialLicense()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
Returns TRUE if the application is running under a trial license, as opposed to a full, authorized license; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual bool IsNetworkLicense()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
As of R4 this method will always return false as R4 does not have network licencing.
Prototype:
virtual bool IsEmergencyLicense()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
As of R4 this method is no longer supported and always returns false.
Returns TRUE if the application is running under an emergency license, while the full license is exported; otherwise FALSE.
Prototype:
virtual int GetProductVersion()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns the product version which is one of the following values:
PRODUCT_VERSION_DEVEL -- A debug build, or licensed in-house.
PRODUCT_VERSION_TRIAL -- A trial license.
PRODUCT_VERSION_ORDINARY -- A commercial license.
PRODUCT_VERSION_NFR -- Not for resale.
PRODUCT_VERSION_EDU -- Educational or student license.
Prototype:
virtual int GetLicenseBehavior()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns one of the following values which indicates the liscence behaviour:
LICENSE_BEHAVIOR_PERMANENT -- A permanent license, or hardware lock.
LICENSE_BEHAVIOR_EXTENDABLE -- A term license which can be extended.
LICENSE_BEHAVIOR_NONEXTENDABLE -- A term license which cannot be extended.
Prototype:
virtual int GetLicenseDaysLeft()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
Returns an integer indicating the number of full days left in the term of the license. A value of 0 means that today is the last day of validity. For permanent licenses, a fixed value is returned indicating greater than 10 years are left.
Prototype:
virtual bool IsFeatureLicensed(int subNum)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 4.0 and later only.
This method is not currently supported and always returns false. In the future it will be used for returning true or false as the license subgroup designated by the argument is or is not enabled.
Return Value:
TRUE if licensed; FALSE if not licensed.
Deferred Loading Related Methods
Prototype:
virtual void EnableDeferredPluginLoading(bool onOff)=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
In the Preferences dialog / General Tab / Plug-In Loading section there is a Checkbox labelled 'Load Plug-Ins when Used'. This method sets the state of this toggle. See the Advanced Topics section Deferred Loading of Plug-Ins.
Parameters:
bool onOff
TRUE for on; FALSE for off.
Prototype:
virtual bool DeferredPluginLoadingEnabled()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
In the Preferences dialog / General Tab / Plug-In Loading section there is a Checkbox labelled 'Load Plug-Ins when Used'. This method returns the state of this toggle.. See the Advanced Topics section Deferred Loading of Plug-Ins.
Return Value:
TRUE if on; FALSE if off.
Prototype:
virtual void FlushUndoBuffer()=0;
Remarks:
This method is available in release 3.0 and later only.
This function will flush the undo buffer. See the Advanced Topics section Undo / Redo.