Basic Authentication Process
The following figures and text describe the series of tasks required to authenticate requests to AWS using an HMAC-SHA request signature. It is assumed you have already created an AWS account and received an Access Key ID and Secret Access Key. For more information about those, see Your Product Advertising API Account and Your AWS Identifiers.
You perform the first three tasks.
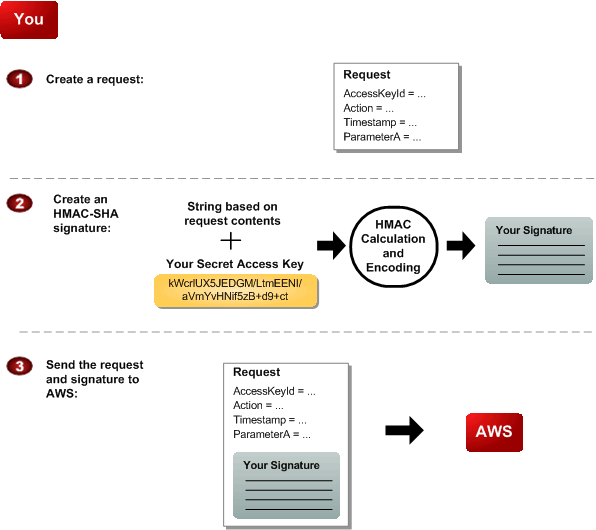
Process for Authentication: Tasks You Perform
| 1 |
You construct a request to AWS. |
| 2 |
You calculate a keyed-hash message authentication code (HMAC-SHA) signature using your Secret Access Key (for information about HMAC, go to http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc2104.html) |
| 3 |
You include the signature and your Access Key ID in the request, and then send the request to AWS. |
AWS performs the next three tasks.
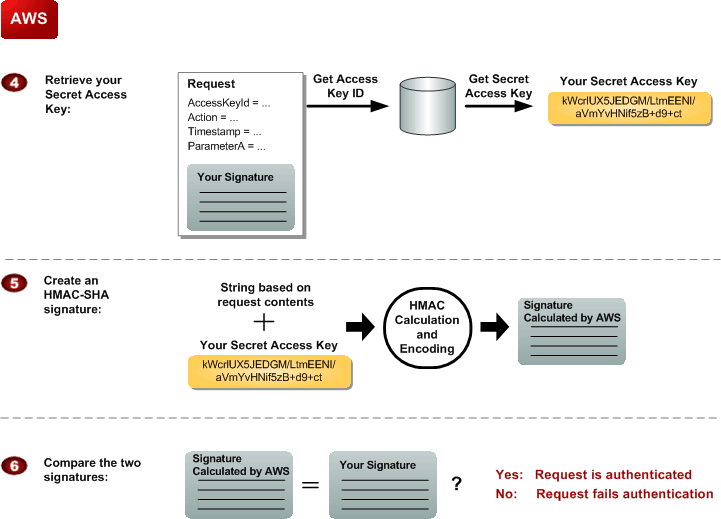
Process for Authentication: Tasks AWS Performs
 |
Product Advertising API uses the Access Key ID to look up your Secret Access Key. |
 |
Product Advertising API generates a signature from the request data and the Secret Access Key using the same algorithm you used to calculate the signature you sent in the request. |
 |
If the signature generated by AWS matches the one you sent in the request, the request is considered authentic. If the comparison fails, the request is discarded, and AWS returns an error response. |