Digital Upconverter
A digital upconverter (DUC) accepts a complex IQ waveform as its input. The DUC then converts this complex waveform to a real waveform with the same frequency content but centered at a higher IF center frequency. In other words, the baseband signal is "upconverted" to IF. This upconversion is done digitally in DUC firmware.
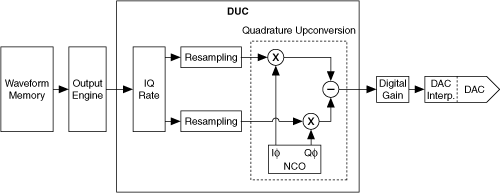
The DUC is a set of algorithms implemented in an FPGA. Two main operations are performed by these algorithms: resampling and upconversion. The FPGA resamples the baseband IQ waveform from the given IQ rate to the digital-to-analog converter (DAC) sample rate (100 MS/s). The DUC then multiplies the resampled IQ waveform by an internally-generated complex IF carrier. This multiplication produces a waveform with a center frequency that matches the IF carrier frequency and frequency content that matches the baseband IQ waveform. This upconverted waveform is then fed into the DAC.
The NI PXI-5671 uses the DUC in the NI 5441 AWG module when the IQ rate is set to 8.33 MS/s or less. The DUC on the NI PXI-5672 is always enabled. The DUC offers the following benefits:
- Lower IQ rates configurable in smaller intervals:
- Reduces the onboard memory required for a given waveform. For example, for a 1 MHz wide signal, you can set the IQ rate using the IQ Rate (S/s) property or the NIRFSG_ATTR_IQ_RATE attribute to 1.25 MS/s, meaning that each second of the waveform duration uses 1.25 million samples of onboard memory. If you set the IQ rate to 100 MS/s, each second of the waveform duration uses 100 million samples of onboard memory.
- Increases the maximum duration of a waveform; the smaller the IQ rate, the longer a waveform can be generated without repetition. For example, using an NI PXIe-5672 with 256 MB of memory running at an IQ rate of 6.1 kS/s, the maximum waveform duration is over three hours. In contrast, the maximum waveform duration for a signal at an IQ rate of 100 MS/s is approximately 1.34 seconds.
- Guarantees that a phase-continuous input waveform remains phase continuous upon generation, regardless of the setting of the Phase Continuity Enabled property or the NIRFSG_ATTR_PHASE_CONTINUITY_ENABLED attribute.
- Frequency accuracy is not constrained by the Frequency Tolerance (Hz) property or the NIRFSG_ATTR_FREQUENCY_TOLERANCE attribute. The Frequency Tolerance (Hz) property or the NIRFSG_ATTR_FREQUENCY_TOLERANCE attribute is ignored, and NI-RFSG sets the frequency as accurately as possible for the hardware.
- Changing the RF frequency does not cause the arbitrary waveform to be rewritten to the AWG module. This capability can dramatically speed up applications that generate the same signal at multiple RF frequencies.