Versioning Overview
Versioning provides a way to define and redefine objects at specific points in time. This topic uses an example to explain versioning behavior in Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2000 Meta Data Services.
How Versioning Works in Meta Data Services
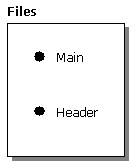
Objects in a Meta Data Services repository conform to classes. The following figure shows two objects that conform to the File class.
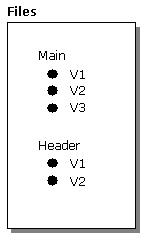
An individual object can change whenever any of its property values or collections change. Sometimes the new property values or collections simply replace the preceding ones. Other times, you may want to retain both the old values and the new values. The repository engine can retain the old property values and collections with an old version of the object. The following figure shows three versions of the Main file and two versions of the Header file.
The different versions of an object can have different property values. The following figure includes property values for the properties X, Y, and Z, properties that the File class exposes through its various interfaces. In the figure, individual versions have different values for the properties. The picture shows the property values as ordered X-Y-Z triplets. "(22,3,4)" means X=22, Y=3, and Z=4.
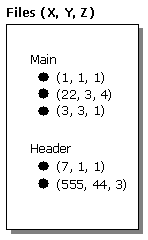
Note how this works: the repository engine does not store multiple values for a particular property of an object. Instead, it stores multiple versions of an object such that each individual version can contain its own individual property values.
The different versions of an object can also have different collections. The following figure shows one collection (of the Persons-of-File collection type) for each of the five object versions of the File class. (To save space, the X-Y-Z triplets are not shown.)
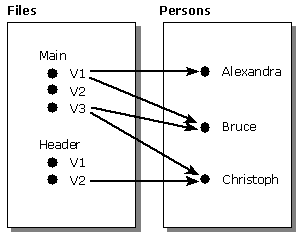
Here are the collections of the five object versions of the File class:
- Persons-of-Version 1-of-Main: {Alexandra, Bruce}
- Persons-of-Version 2-of-Main: { } (The empty set)
- Persons-of-Version 3-of-Main: {Bruce, Christoph}
- Persons-of-Version 1-of-Header: { } (The empty set)
- Persons-of-Version 2-of-Header: {Christoph}
Although the preceding figure shows that the three different versions of Main have three different values for the collection type Persons-of-File, things are much simpler at run time. At run time, when your program manipulates an object, it manipulates a particular version of that object. In other words, whenever you secure a reference to an object, the repository engine actually gives you a reference to a specific version of an object. No matter how your program obtains the reference, through IRepository::get_Object, through navigation, or through any other technique, the repository engine provides you a reference to one version of that object.
For example, suppose your program has a reference to Version 3-of-Main and Version 2-of-Header. The following figure distinguishes between object versions to which your program has current references (filled-in circles) and the other object versions (blank circles).
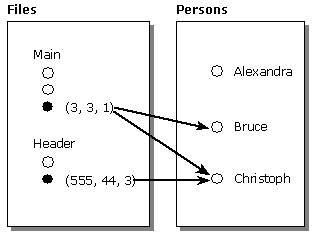
The preceding figure indicates that your program does not currently have a reference to any person. Your program merely has references to some collections that include persons. To get a reference to a specific person (for example, Bruce), your program can navigate to it.
The preceding figure is simplified; it shows only one version of each person. The following figure is more realistic.
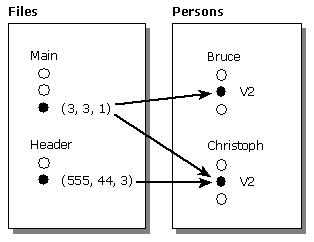
The preceding figure shows two collections. One collection is Persons-of-Version 3-of-Main, which contains Version 2-of-Bruce and Version 2-of-Christoph. The other collection is Persons-of-Version 2-of-Header; it contains Version 2-of-Christoph. The figure also shows that your program already has references to Version 2-of-Bruce and Version 2-of-Christoph (because the corresponding dots are filled in).
The preceding figure reflects that when you navigate along a relationship to a target object, you navigate to a specific version of that object. The figure reflects this by showing each arrow pointing to a specific version of an object to which you have already navigated (a filled-in circle in the set of versions of persons).
In most situations, this view is adequate. For example, you can think of a target object collection as containing a particular version of each target object. A more detailed view, shown in the following figure, is sometimes useful.
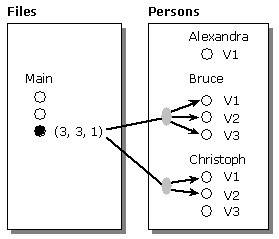
The preceding figure shows a single collection, Persons-of-Version 3-Of-Main. It contains two items: Bruce and Christoph. The figure does not indicate which particular version of Bruce is in the collection, because your program has not yet navigated from Version 3-of-Main to Bruce. But it does indicate that when you do navigate to Bruce, the repository engine can return a reference to any of the three versions. Similarly, the picture does not indicate which version of Christoph is in the collection, but it does indicate that when you navigate to Christoph, the repository engine returns a reference to Version 1 or to Version 2, but not to Version 3.