The "Storage" category in the VM settings allows you to connect virtual hard disk, CD/DVD and floppy images and drives to your virtual machine.
In a real PC, so-called "storage controllers" connect physical disk drives to the rest of the computer. Similarly, VirtualBox presents virtual storage controllers to a virtual machine. Under each controller, the virtual devices (hard disks, CD/DVD or floppy drives) attached to the controller are shown.
Note
This section can only give you a quick introduction to the VirtualBox storage settings. Since VirtualBox gives you an enormous wealth of options in this area, we have dedicated an entire chapter of this User Manual to explaining all the details: please see Chapter 5, Virtual storage.
If you have used the "Create VM" wizard to create a machine, you will normally see something like the following:
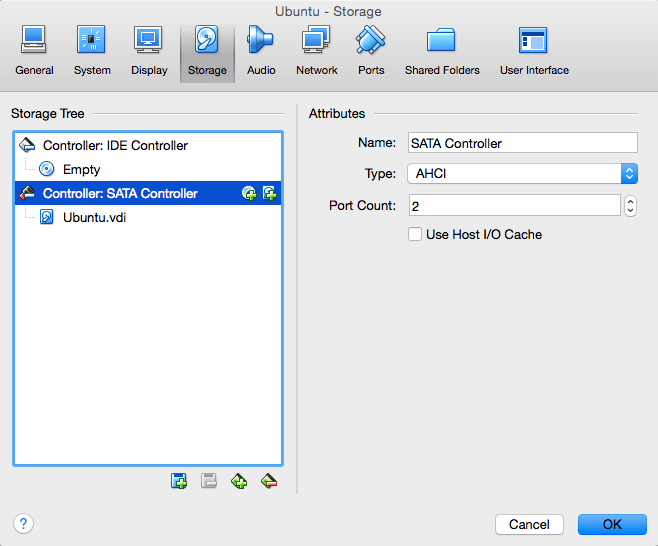
|
Depending on the guest operating system type that you selected when you created the VM, the typical layout of storage devices in a new VM is as follows:
-
You will see an IDE controller, to which a virtual CD/DVD drive has been attached (to the "secondary master" port of the IDE controller).
-
You will also see a SATA controller, which is a more modern type of storage controller for higher hard disk data throughput, to which the virtual hard disks are attached. Initially you will normally have one such virtual disk, but as you can see in the above screenshot, you can have more than one, each represented by a disk image file (VDI files, in this case).
If you created your VM with an older version of VirtualBox, the default storage layout may differ. You might then only have an IDE controller to which both the CD/DVD drive and the hard disks have been attached. This might also apply if you selected an older operating system type when you created the VM. Since older operating systems do not support SATA without additional drivers, VirtualBox will make sure that no such devices are present initially. Please see Section 5.1, “Hard disk controllers: IDE, SATA (AHCI), SCSI, SAS, USB MSD, NVMe” for additional information.
VirtualBox also provides a floppy controller, which is special: you cannot add devices other than floppy drives to it. Virtual floppy drives, like virtual CD/DVD drives, can be connected to either a host floppy drive (if you have one) or a disk image, which in this case must be in RAW format.
You can modify these media attachments freely. For example, if you wish to copy some files from another virtual disk that you created, you can connect that disk as a second hard disk, as in the above screenshot. You could also add a second virtual CD/DVD drive, or change where these items are attached. The following options are available:
-
To add another virtual hard disk, or a CD/DVD or floppy drive, select the storage controller to which it should be added (IDE, SATA, SCSI, SAS, floppy controller) and then click on the "add disk" button below the tree. You can then either select "Add CD/DVD device" or "Add Hard Disk". (If you clicked on a floppy controller, you can add a floppy drive instead.) Alternatively, right-click on the storage controller and select a menu item there.
On the right part of the window, you can then set the following:
-
You can then select to which device slot of the controller the virtual disk should be connected to. IDE controllers have four slots which have traditionally been called "primary master", "primary slave", "secondary master" and "secondary slave". By contrast, SATA and SCSI controllers offer you up to 30 slots to which virtual devices can be attached.
-
You can select which image file to use.
-
For virtual hard disks, a button with a drop-down list appears on the right, offering you to either select a virtual hard disk file using a standard file dialog or to create a new hard disk (image file), which will bring up the "Create new disk" wizard, which was described in Section 1.7, “Creating your first virtual machine”.
For details on the image file types that are supported, please see Section 5.2, “Disk image files (VDI, VMDK, VHD, HDD)”.
-
For virtual CD/DVD drives, the image files will typically be in the standard ISO format instead. Most commonly, you will select this option when installing an operating system from an ISO file that you have obtained from the Internet. For example, most Linux distributions are available in this way.
For virtual CD/DVD drives, the following additional options are available:
-
If you select "Host drive" from the list, then the physical device of the host computer is connected to the VM, so that the guest operating system can read from and write to your physical device. This is, for instance, useful if you want to install Windows from a real installation CD. In this case, select your host drive from the drop-down list presented.
If you want to write (burn) CDs or DVDs using the host drive, you need to also enable the "Passthrough" option; see Section 5.9, “CD/DVD support”.
-
If you select "Remove disk from virtual drive", VirtualBox will present an empty CD/DVD drive to the guest into which no media has been inserted.
-
-
-
-
To remove an attachment, select it and click on the "remove" icon at the bottom (or right-click on it and select the menu item).
Removable media (CD/DVDs and floppies) can be changed while the guest is running. Since the "Settings" dialog is not available at that time, you can also access these settings from the "Devices" menu of your virtual machine window.