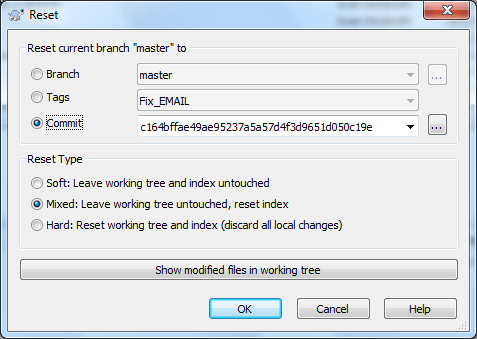
The reset dialog can be used to reset the current HEAD to the specified state and optionally also the index and the working tree. This can also be used to abort a merge.
On the Reset dialog, you can click to browse the log and choose a specific version. In Abort merge dialog, you can only reset to HEAD.
Soft: Leave working tree and index untouched Does not touch the index file nor the working tree at all (but resets the head to the selected commit, just like all modes do). This leaves all your changed files "Changes to be committed" as before. This option is not available in Abort Merge dialog.
Mixed: Leave working tree untouched, reset index Resets the index but not the working tree (i.e., the changed files are preserved but not marked for commit) and reports what has not been updated. This is the git default action. This option can abort a merge.
Hard: Reset working tree and index (discard all local changes) Resets the index and working tree. Any changes to tracked files in the working tree since the selected commit are discarded. This option can abort a merge, and it is the default action in Abort Merge dialog.
![[Caution]](caution.png)
|
Git hard reset does not use the Windows recycle bin |
|---|---|
|
Unlike the revert or clean functions of TortoiseGit, the hard reset does not make use of the Windows recycle bin, i.e., uncommitted changes might get lost! |
You can find more information at Section G.3.111, “git-reset(1)”.