2.6 WDTM settings...
The Windows Desktop Heap Management (WDTM) settings control the efficiency of your Windows server's operation and can be used to fine-tune server system behavior under heavy loads. These settings affect your entire Windows system and are only available when connected to a Windows data/application server.
You should not need to amend these settings. If you do, your Windows performance or stability may be affected.
Changes should only be performed by an authorized Window's Administrator and only after the notes following have been read and understood.
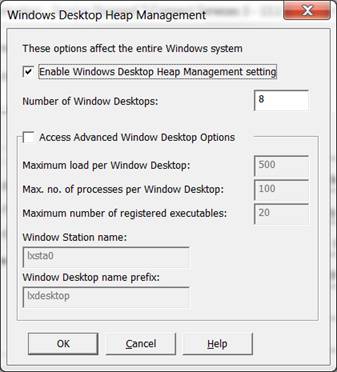
Windows Desktop Heap Management Important Notes:
Remember: The Windows Desktop Heap Management parameters affect the entire Windows system and you should not need to change them.
The shipped default values allow approximately 800 Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions (for V10.0 or later installations) to be run simultaneously on the same Windows system. In most circumstances you should not need to run more than this number of Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions. If changes are necessary, they should only be made by a Windows administrator with a logon account belonging to the Administrators group. Contact your local LANSA distributor before continuing.
These parameters do not impose any hard limit (unlike the setting in the LANSA for the Web Administrator) on the number of Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions running on the same Windows system. To limit the number of Web Jobs to less than 800, you should use the Web Administrator's setting.
The Desktop Heap parameters are designed to improve the stability of the system when the number of running Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions is below the implied limit, which, using the default values, is a Windows system running 800 Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions simultaneously. This should not seriously affect the stability of the system, assuming the Windows system is dedicated mainly to running Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions. When that number of Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions has been reached and more requests are made, Visual LANSA (version 10.0 or later) will still attempt to process the requests and create more Web Jobs (as allowed by the Maximum concurrent users setting) and/or LANSA Open sessions. This situation has the potential to cause system instability as system resources become low.
If a Windows system has the capacity to run more Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions (as determined by calculating the load limit as described below) than the default implied limit , then changing these parameters can improve the stability of the system. If the Windows system is only able to marginally handle the default 800 or less Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions, increasing the implied limit will not help the system to reliably run more Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions. Conversely, in this case, decreasing the implied limit and the Maximum concurrent users setting would improve the stability of the system.
Calculating the load limit
The actual number of Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions that can be run simultaneously is dependant on the hardware configuration and the application. Before you change the parameters, you will need to first calculate the most suitable load limit for your Windows system.
External factors also should be taken into account when determining the practical and estimated load limits. For example, if you will be running Windows batch jobs on this Windows system, these should be active when performing the limit test.
To calculate the practical load limit:
1. Change the setting to allow a large number of Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions. For example, 3000. In this case, you will need multiple Visual LANSA installations for the test, as each Visual LANSA installation supports a maximum of 1500 Web Jobs.
2. Stress the system to load more and more Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions until the system starts to display signs of instability such as slow response times, hanging jobs, etc. Take a note the number of running Web Jobs and/or LANSA Open sessions. This number becomes the practical load limit of the Windows system.
3. Estimate the suitable load limit based on (and under) the practical load limit.
4. Change the Advanced Window Desktop Options parameters according to your estimated limit.
Important notes:- These parameters are used and shared by all Visual LANSA systems (version 10.0 or later) running simultaneously on the same Windows system.
- These parameters are also used and shared by all LANSA Open sessions (version 10.0 or later) running simultaneously on the same Windows system. For your convenience, when using LANSA Open, these settings can be accessed from within the LANSA for the Web Administrator.
- If there is any LANSA system process or listener service (version 10.0 or later), for example, W3_P1200 or LCOTP, running on the Windows system, these parameters will NOT be effective for the Windows system until all system processes and listener services are cleaned up and restarted. You must clean up ALL system processes and stop ALL listener services before restarting any one of these processes or services.
Procedure for Activating the Changed Parameters
1. Use LANSA for the Web Administrator to clean up all LANSA Web Jobs for all LANSA systems (version 10.0 or later) running simultaneously on the same Windows system.
2. Close down all LANSA Open sessions (version 10.0 or later) running simultaneously on the same Windows system. Note that LANSA for the Web Administrator, LANSA Web Function Editor, IIS Plug-in use LANSA Open sessions so you need to close LANSA for the Web Administrator and Web Function Editor applications that are running and stop all Web Servers using IIS Plug-in which are connected to the same Windows system.
3. Stop all Web Servers which are connecting to the same Windows system.
4. Stop all listener services (version 10.0 or later) running on the same Windows system.
5. Restart all listener services (version 10.0 or later) running on the same Windows system.
6. Restart all Web Servers which connect to the same Windows system.
7. Restart Web Jobs or LANSA Open sessions required by end users.