<a 属性="属性值">~标签内容~</a>
| 属性 | 属性值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| ① href | URI | 指定链接指向的URI,这是期望当用户激活超链接时打开的文件(类型不限)的URI,此属性是a元素最常用的属性。URI除了可以是标准的URI,一般还可以是JavaScript为协议“javascript:”以及用于电子邮件的“mailto:” |
| ② hreflang | 语言名称 | 说明href属性定义的URI(所指向的文档)所用的基础语言 |
| ③ name | name名 | 为当前锚定位设置一个名称,以便它能够被其他链接所定位。如果在一个文档内部定位,那么就相当于在文档内设置了一个“书签”。name属性的属性值在一个文档内必须是独一无二的,而且取值必须符合id和name属性的命名规范。在XHTML中此属性被id属性取代,HTML中也可以使用id取代,但是旧的浏览器可能不支持 |
| ④ type | MIME类型 | 这个属性给出目标链接地址的内容类型。对于浏览器设置而言,如果它不支持目标类型,则可以通过该属性给出建议。不过建议设计者慎用这个属性,以避免一些意想不到的不便情况(如链接目标的内容类型与所指定的不符) |
| ⑤ charset | 字符集 | 定义链接目标的字符编码 |
| ⑥ rel | 链接类型 | 描述从当前文档到链接资源(href属性的属性值)的关系,可复数指定,属性值之间以空格隔开 |
| ⑦ rev | 链接类型 | 描述从链接资源(href属性的属性值)到当前文档的反向链接,可复数指定,属性值之间以空格隔开 |
| ⑧ shape | 预定义值 | 该属性用来定义客户端图像映射的一个区域,其值为预定义的关键字:default、rect、circle、poly。默认值是default,表示适合整张图片的形状;rect表示矩形,circle表示圆形,poly表示多边形 |
| ⑨ coords | 坐标值 | 根据shape属性定义的图像映射形状,coord属性可以定义相应的坐标值(可点击区域在整个图像中的坐标),以便浏览器能够根据这些坐标在图像范围内产生相应的形状,然后可以利用href属性设置可点击区域的超链接目标。这样,在不切割图片的情况下,把一个分为若干区域,用户点击不同的区域(这样的区域称为热点)就可以打开不同的超链接。图像图像映射的坐标从左上角(0,0)开始,越向右下角越大。这些坐标都以像素为单位度量。
|
| ⑩ target | 目标框架名 | 指定超链接打开的目标框架名,框架名可以在设置框架时指定。可能会用到的四个预定义名称:_parent表示超链接在上一级窗口中打开,_blank表示在新窗口中打开,_self表示在当前框架或窗口中打开,_top表示在浏览器整个窗口中打开,忽略任何框架 |
| ⑪ tabindex | 0~32767的整数 | 设置页面中超链接的Tab键获得焦点的顺序(按下Tab键从一个超链接移动到下一个超链接),从属性值最小的开始移动 |
| ⑫ accesskey | 任一字符 | 指定获得焦点快捷键的文字,快捷键的使用在Windows中使用Alt+快捷键,Macintosh中使用Command+快捷键。属性值应该是一个文字字符 |
⑬ 通用属性:id、class、title、style、dir、lang、xml:lang 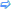 |
||
⑭ 内在事件:onfoucs、onblur 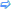 |
||
<a href="目标链接">链接</a>
建立超链接目标点识别名称:
<a name="识别名称">链接</a>
下面的例子显示了XHTML文件基础结构:
 运行
运行 打印
打印 <head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312">
<title>元素a</title>
</head>
<body>
书签:<a name="doctop">文档顶端</a><hr>
点击这个超链接将进入网站<a href="http://www.baidu.com">www.baidu.com</a><br>
点击这个超链接将进入网站<a href="http://www.google.com">google</a><br>
a元素的href属性指向的URI协议不仅可以是"http://",还可以是“ftp://”、“news://”、“telnet”、“gopher”、“email”等;现在的浏览器都支持JavaScript,所以JavaScript伪协议“javascript:”也是可以的;此外一般操作系统都带有邮件客户端软件,所以“mailto:”一般也是可以的;如果你装有QQ、MSN等即时通讯软件,那么这些软件也都有相应的伪协议。
图片也可以使用超链接,例如:<a href="http://www.w3.org" title="访问www.w3.org"><img src="src/html.gif" border="0"></a>
In the example that follows, the A element defines a link. The source anchor is the text "W3C Web site" and the destination anchor is "http://www.w3.org/":
For more information about W3C, please consult the <A href="http://www.w3.org/">W3C Web site</A>.This link designates the home page of the World Wide Web Consortium. When a user activates this link in a user agent, the user agent will retrieve the resource, in this case, an HTML document.
in such a way as to make them obvious to users (underlining, reverse video, etc.). The exact rendering depends on the user agent. Rendering may vary according to whether the user has already visited the link or not. A possible visual rendering of the previous link might be:
For more information about W3C, please consult the W3C Web site. ~~~~~~~~~~~~To tell user agents explicitly what the character encoding of the destination page is, set the charset attribute:
For more information about W3C, please consult the <A href="http://www.w3.org/" charset="ISO-8859-1">W3C Web site</A>Suppose we define an anchor named "anchor-one" in the file "one.html".
...text before the anchor... <A name="anchor-one">This is the location of anchor one.</A> ...text after the anchor...<param name="movie" value="src/bugs.swf"> <param name="quality" value="high">
<embed src="src/bugs.swf" quality="high" pluginspage="http://www.adobe.com/shockwave/download/download.cgi?P1_Prod_Version=ShockwaveFlash" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="189" height="290"></embed></object><a href="src/bugs.swf">下载</a>此动画</p>
<a href="mailto:[email protected]?subject=阅读者反馈">发邮件给我</a> <a href="#doctop">回到文档顶端</a>
</body>
</html>
(X)HTML Strict DTD不允许a元素中加入target属性,必须把target属性换成rel属性。