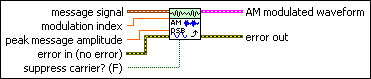
MT Modulate AM VI
Performs amplitude modulation (AM) on an RF carrier wave, with optional suppression of the carrier wave, according to a baseband information signal specified by the message signal parameter. The complex envelope of the amplitude-modulated signal is returned in the AM modulated waveform indicator.
This VI performs signal processing on data and operates independently of hardware settings. This VI can be used in simulated as well as hardware-equipped applications.
Use the pull-down menu to select an instance of this VI.
MT Modulate AM (DSB)
This polymorphic instance performs double sideband (DSB) amplitude modulation.
 |
message signal specifies the message signal used to modulate the carrier wave.
|
||||||
 |
modulation index specifies the desired modulation index of the AM modulated waveform parameter. A value of 0.7, for example, corresponds to a modulation index of 70%. A value greater than unity (1) may cause overmodulation and distortion. This parameter is ignored when suppress carrier? is set to TRUE. The default is 1.0. |
||||||
 |
peak message amplitude specifies the peak message amplitude of the message signal. This value is used to scale (normalize) the input message signal prior to modulation. This value must be positive. The default is 1.0. |
||||||
 |
suppress carrier? specifies whether to suppress the carrier of the modulated signal. When suppress carrier? is set to FALSE (the default), the output amplitude-modulated baseband signal consists of a DC component corresponding to the carrier tone. |
||||||
 |
error in (no error) accepts error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error displayed.
|
||||||
 |
AM modulated waveform returns the AM-DSB-modulated complex baseband time-domain data for demodulation.
|
||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error displayed.
|
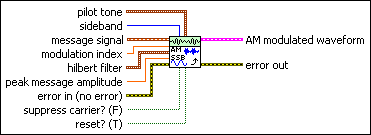
MT Modulate AM (SSB)
This polymorphic instance performs single sideband (SSB) amplitude modulation.
 |
message signal specifies the message signal used to modulate the carrier wave.
|
||||||||||
 |
modulation index specifies the desired modulation index of the AM modulated waveform parameter. A value of 0.7, for example, corresponds to a modulation index of 70%. A value greater than unity (1) may cause overmodulation and distortion. This parameter is ignored when suppress carrier? is set to TRUE. The default is 1.0. |
||||||||||
 |
hilbert filter specifies the complex-valued Hilbert filter used for sideband cancellation during generation of the AM-SSB baseband complex signal. This filter is internally applied to the message signal to generate the baseband complex analytic signal.
|
||||||||||
 |
peak message amplitude specifies the peak message amplitude of the message signal. This value is used to scale (normalize) the input message signal prior to modulation. This value must be positive. The default is 1.0. |
||||||||||
 |
pilot tone specifies the parameters for specifying pilot tone generation. The pilot tone is added to the Hilbert-filtered complex baseband signal to generate the AM-SSB modulated waveform. The pilot tone provides a coherent phase reference during AM-SSB demodulation for performing carrier phase and carrier frequency offset correction. Set amplitude to 0 to disable addition of the pilot tone.
|
||||||||||
 |
sideband specifies whether the AM-SSB modulator retains the lower or upper sideband of the message spectrum to generate the AM-SSB baseband complex analytic signal.
|
||||||||||
 |
suppress carrier? specifies whether to suppress the carrier of the modulated signal. When suppress carrier? is set to FALSE (the default), the output amplitude-modulated baseband signal consists of a DC component corresponding to the carrier tone. |
||||||||||
 |
reset? specifies whether the VI continues AM-SSB modulation using internal states from previous iterations.
|
||||||||||
 |
error in (no error) accepts error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error displayed.
|
||||||||||
 |
AM modulated waveform returns the AM-SSB-modulated complex baseband time-domain data for demodulation.
|
||||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error displayed.
|
MT Modulate AM (SSB) Details
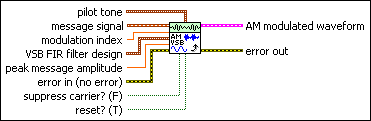
MT Modulate AM (VSB)
This polymorphic instance performs vestigial sideband (VSB) amplitude modulation.
 |
message signal specifies the message signal used to modulate the carrier wave.
|
||||||||||||||
 |
modulation index specifies the desired modulation index of the AM modulated waveform parameter. A value of 0.7, for example, corresponds to a modulation index of 70%. A value greater than unity (1) may cause overmodulation and distortion. This parameter is ignored when suppress carrier? is set to TRUE. The default is 1.0. |
||||||||||||||
 |
VSB FIR filter design specifies the vestigial filter design parameters corresponding to the desired VSB spectrum. The vestigial filter is generated when reset? is set to TRUE, and the filter is applied to the input message signal. Default values in this cluster correspond to NTSC analog picture carrier specifications.
|
||||||||||||||
 |
peak message amplitude specifies the peak message amplitude of the message signal. This value is used to scale (normalize) the input message signal prior to modulation. This value must be positive. The default is 1.0. |
||||||||||||||
 |
suppress carrier? specifies whether to suppress the carrier of the modulated signal. When suppress carrier? is set to FALSE (the default), the output amplitude-modulated baseband signal consists of a DC component corresponding to the carrier tone. |
||||||||||||||
 |
reset? specifies whether the VI continues AM-VSB modulation using internal states from previous iterations.
|
||||||||||||||
 |
pilot tone specifies the parameters for specifying pilot tone generation. The pilot tone is added to the Hilbert-filtered complex baseband signal to generate the AM-VSB modulated waveform. The pilot tone provides a coherent phase reference during AM-VSB demodulation for performing carrier phase and carrier frequency offset correction. Set amplitude to 0 to disable addition of the pilot tone.
|
||||||||||||||
 |
error in (no error) accepts error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error displayed.
|
||||||||||||||
 |
AM modulated waveform returns the baseband AM vestigial sideband modulated signal data and its complex envelope.
|
||||||||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error displayed.
|
MT Modulate AM (VSB) Details
Details
 |
Tip To adjust the carrier phase, use the initial phase parameter of the MT Upconvert Baseband VI. |
 |
Note To avoid distortion, amplitude normalize the message signal to ±1.0. This VI prescales the message signal by the scalar peak amplitude prior to modulation. The default value of 1.0 indicates that no prescaling occurs. |
Double Sideband (DSB) Amplitude Modulation
The output amplitude-modulated signal is represented by the following equations:
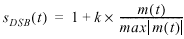
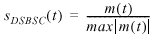
where
m(t) represents the message signal data
S DSB (t) and S DSBSC (t) represent the AM modulated signal
k represents the modulation index
Single Sideband (SSB) Amplitude Modulation
AM-SSB modulation ensures bandwidth reduction by only retaining either the upper or lower sideband in the message spectrum after the modulation process. The following figure illustrates the series of algorithms applied to the incoming signal m(t). The VI applies the AM-DSB algorithms and then applies the Hilbert filter to remove the signal.
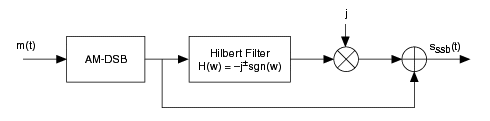
When suppress carrier? is set to FALSE, the output amplitude-modulated signal is represented by the following formula:
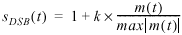
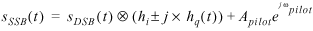
where
m(t)represents the message signal data
S DSB (t) represents the double sideband AM modulated signal (unsuppressed carrier)
S SSB (t) represents the single sideband AM modulated signal (unsuppressed carrier)
k represents the modulation index
A pilot represents the amplitude of the pilot tone
ω pilot represents the frequency of the pilot tone
h i represents the real component of the Hilbert filter
h q represents the imaginary component of the Hilbert filter
When suppress carrier? is set to TRUE,
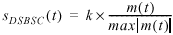
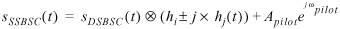
where
m(t)represents the message signal data
S DSBSC (t) represents the double sideband AM modulated signal (unsuppressed carrier)
S SSBSC (t) represents the single sideband AM modulated signal (unsuppressed carrier)
k represents the modulation index
A pilot represents the amplitude of the pilot tone
ω pilot represents the frequency of the pilot tone
h i represents the real component of the Hilbert filter
h q represents the imaginary component of the Hilbert filter
In both suppressed and unsuppressed carrier cases, one of two possible Hilbert filter designs is specified using the design element in the Hilbert filter cluster. Select either a Windowed Hilbert transformer or an Equiripple Hilbert transformer.
The Windowed Hilbert transformer generates a length N Hilbert filter with an impulse response h(n) given by the following equation:
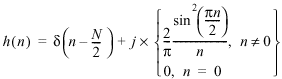
The Equiripple Hilbert transformer generates a length N Hilbert filter with an impulse response h(n) given by the following equation:

where g(n) represents an equiripple lowpass filter with a normalized cutoff frequency of 0.25 Hz.
Vestigial Sideband (VSB) Amplitude Modulation
VSB amplitude modulation involves retaining a portion of the unwanted sideband (called the vestige) in the message spectrum prior to transmission, rather than completely eliminating it as in single-sideband modulation. The following figure illustrates the series of algorithms applied to the incoming signal m(t). The VI applies the AM-DSB algorithms and then applies the Vestigial filter to remove the vestige.
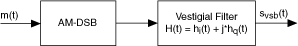
The output amplitude-modulated signal is represented by the following equation:
With suppress carrier? set to FALSE:
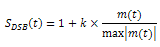
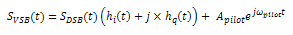
where
m(t)represents the message signal data
S DSB (t) represents the double sideband AM modulated signal (unsuppressed carrier)
S VSB (t) represents the vestigial sideband AM modulated signal (unsuppressed carrier)
k represents the modulation index
A pilot represents the amplitude of the pilot tone
ω pilot represents the frequency of the pilot tone
h i represents the real component of the vestigial filter
h q represents the imaginary component of the vestigial filter
With suppress carrier? set to TRUE:
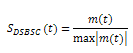
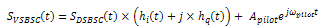
where
m(t)represents the message signal data
S DSBSC (t) represents the double sideband AM modulated signal (unsuppressed carrier)
S VSBSC (t) represents the vestigial sideband AM modulated signal (unsuppressed carrier)
k represents the modulation index
A pilot represents the amplitude of the pilot tone
ω pilot represents the frequency of the pilot tone
h i represents the real component of the Hilbert filter
h q represents the imaginary component of the Hilbert filter