SI Save System Model to File VI
Owning Palette: Model Management VIs
Installed With: System Identification Toolkit
Saves a system model to a .sim file. A .sim file is a system identification model file that saves all model coefficients regardless of the model type. Use the SI Load System Model from File VI to load a system model from a .sim file.

 Place on the block diagram Place on the block diagram |  Find on the Functions palette Find on the Functions palette |
 | system model contains information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. | ||||||
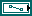 | file path is the path to the file to which you want to save the system model. If you specify a valid path in file path, this VI saves the model to the file whose path is file path. If file path is empty (default) or is <Not A Path>, this VI displays a dialog box from which you can select a file. You receive an error if you do not specify file path. | ||||||
 | start path is the path to the initially displayed directory or folder in the Select a file to save system identification model dialog box. If you do not specify a valid path in file path, the Select a file to save system identification model dialog box opens. You can select the file to which you want to save the system model from this dialog box. The default value is <Not A Path>, which is the path to the last directory or folder shown in the Select a file to save system identification model dialog box. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
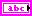 | default name is the name you want to appear as the initial file or directory name in the Select a file to save system identification model dialog box. The default is an empty string. | ||||||
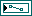 | new file path returns the path of the file to which this VI saves the system model. You can use this output to determine the path of the file that you saved using the Select a file to save system identification model dialog box. new file path returns <Not A Path> if you click the Cancel button in the dialog box. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
Example
Refer to the Save Model to File VI in the labview\examples\System Identification\Getting Started\General.llb for an example of using the SI Save System Model to File VI.