Owning Palette: Parametric Model Estimation VIs
Installed With: System Identification Toolkit
Estimates a user-defined model. Wire data to the stimulus signal and response signal inputs to determine the polymorphic instance to use or manually select the instance.
Use the pull-down menu to select an instance of this VI.
 Place on the block diagram Place on the block diagram |  Find on the Functions palette Find on the Functions palette |
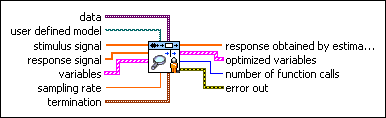
SI Estimate User-Defined Model (SISO Waveform)
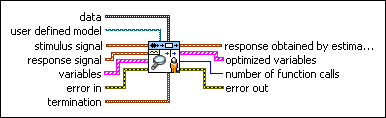
 | data specifies the static data that the user-defined function needs at run time. | ||||||||
 | user defined model is a file path to the VI that defines the model to be estimated. Use the model template in the labview\vi.lib\addons\System Identification\User-Defined Model Templates.llb to create a VI from a template. | ||||||||
 | stimulus signal specifies the input waveform of the stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 | response signal specifies the input waveform of the response signal. | ||||||||
 | variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||||
 | termination describes the stopping conditions for the model estimation.
| ||||||||
 | response obtained by estimated model returns the simulated response signal from the estimated model. | ||||||||
 | optimized variables returns the name and optimized value of each variable.
| ||||||||
 | number of function calls returns the number of times that LabVIEW calls the user-defined model VI. | ||||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
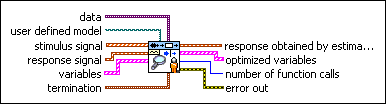
SI Estimate User-Defined Model (SISO Array)
 | data specifies the static data that the user-defined function needs at run time. | ||||||||
 | user defined model is a file path to the VI that defines the model to be estimated. Use the model template in the labview\vi.lib\addons\System Identification\User-Defined Model Templates.llb to create a VI from a template. | ||||||||
 | stimulus signal specifies the input array of the stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 | response signal specifies the input array of the response signal. | ||||||||
 | variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||||
 | sampling rate is the signal sampling rate in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. | ||||||||
 | termination describes the stopping conditions for the model estimation.
| ||||||||
 | response obtained by estimated model returns the simulated response signal from the estimated model. | ||||||||
 | optimized variables returns the name and optimized value of each variable.
| ||||||||
 | number of function calls returns the number of times that LabVIEW calls the user-defined model VI. | ||||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
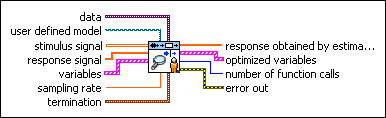
SI Estimate User-Defined Model (MISO Waveform)
 | data specifies the static data that the user-defined function needs at run time. | ||||||||
 | user defined model is a file path to the VI that defines the model to be estimated. Use the model template in the labview\vi.lib\addons\System Identification\User-Defined Model Templates.llb to create a VI from a template. | ||||||||
 | stimulus signal is the input waveform array of the stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 | response signal specifies the input waveform of the response signal. | ||||||||
 | variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||||
 | termination describes the stopping conditions for the model estimation.
| ||||||||
 | response obtained by estimated model returns the simulated response signal from the estimated model. | ||||||||
 | optimized variables returns the name and optimized value of each variable.
| ||||||||
 | number of function calls returns the number of times that LabVIEW calls the user-defined model VI. | ||||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
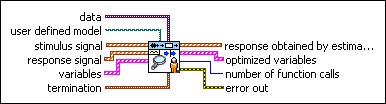
SI Estimate User-Defined Model (MISO Array)
 | data specifies the static data that the user-defined function needs at run time. | ||||||||
 | user defined model is a file path to the VI that defines the model to be estimated. Use the model template in the labview\vi.lib\addons\System Identification\User-Defined Model Templates.llb to create a VI from a template. | ||||||||
 | stimulus signal is the input array of the stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 | response signal specifies the input array of the response signal. | ||||||||
 | variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||||
 | sampling rate is the signal sampling rate in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. | ||||||||
 | termination describes the stopping conditions for the model estimation.
| ||||||||
 | response obtained by estimated model returns the simulated response signal from the estimated model. | ||||||||
 | optimized variables returns the name and optimized value of each variable.
| ||||||||
 | number of function calls returns the number of times that LabVIEW calls the user-defined model VI. | ||||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
SI Estimate User-Defined Model (MIMO Waveform)
 | data specifies the static data that the user-defined function needs at run time. | ||||||||
 | user defined model is a file path to the VI that defines the model to be estimated. Use the model template in the labview\vi.lib\addons\System Identification\User-Defined Model Templates.llb to create a VI from a template. | ||||||||
 | stimulus signal is the input waveform array of the stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 | response signal is the input waveform array of the response signal. | ||||||||
 | variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||||
 | termination describes the stopping conditions for the model estimation.
| ||||||||
 | response obtained by estimated model returns the simulated response signal from the estimated model. | ||||||||
 | optimized variables returns the name and optimized value of each variable.
| ||||||||
 | number of function calls returns the number of times that LabVIEW calls the user-defined model VI. | ||||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
SI Estimate User-Defined Model (MIMO Array)
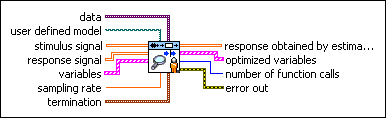
 | data specifies the static data that the user-defined function needs at run time. | ||||||||
 | user defined model is a file path to the VI that defines the model to be estimated. Use the model template in the labview\vi.lib\addons\System Identification\User-Defined Model Templates.llb to create a VI from a template. | ||||||||
 | stimulus signal is the input array of the stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 | response signal is the input array of the response signal. | ||||||||
 | variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||||
 | sampling rate is the signal sampling rate in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. | ||||||||
 | termination describes the stopping conditions for the model estimation.
| ||||||||
 | response obtained by estimated model returns the simulated response signal from the estimated model. | ||||||||
 | optimized variables returns the name and optimized value of each variable.
| ||||||||
 | number of function calls returns the number of times that LabVIEW calls the user-defined model VI. | ||||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
SI Estimate User-Defined Model Details
The SI Estimate User-Defined Model VI estimates a user-defined model using the Gauss-Newton algorithm to optimize the parameters. This VI requires a predefined model to optimize the parameters. You can use the template in the labview\vi.lib\addons\System Identification\User-Defined Model Templates.llb directory to create a predefined model. If you create a predefined model from scratch, make sure your model has exactly the same connector pane as that in the template.
The predefined model can be either a linear or nonlinear model. The LabVIEW System Identification Toolkit provides two common nonlinear models, the Weiner model and the Hammerstein model, as examples of defining nonlinear models.
Examples
Refer to the following VIs for examples of using the SI Estimate User-Defined Model VI:
- Estimate Partially Known State-Space Model VI: labview\examples\System Identification\Getting Started\User Defined Model.llb
- Parameterize Nonlinear Differential Equation VI: labview\examples\System Identification\Getting Started\User Defined Model.llb
- Estimate Hammerstein-Wiener Model VI: labview\examples\System Identification\Getting Started\User Defined Model.llb