SI Model Residual Analysis VI
Owning Palette: Model Validation VIs
Installed With: System Identification Toolkit
Computes and analyzes the prediction error for the response output of a model system. Wire data to the stimulus signal and response signal inputs to determine the polymorphic instance to use or manually select the instance.
 | Note This VI does not support the transfer function or zero-pole-gain models. For AR models, this VI ignores stimulus signal. |
Use the pull-down menu to select an instance of this VI.
 Place on the block diagram Place on the block diagram |  Find on the Functions palette Find on the Functions palette |
SI Model Residual Analysis (SISO Waveform)

 | system model contains information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model contains.
| ||||||
 | stimulus signal specifies the input waveform of the stimulus signal. | ||||||
 | response signal specifies the input waveform of the response signal. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | confidence level of autocorrelation returns the confidence level of autocorrelation. The values of autocorrelation between plus and minus confidence level of autocorrelation are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. | ||||||
 | prediction error returns the waveform of the one-step-ahead prediction error of the system response. | ||||||
 | autocorrelation returns the autocorrelation of prediction error. autocorrelation and cross correlation provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
 | cross correlation returns the cross correlation of prediction error and stimulus signal. autocorrelation and cross correlation provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
| ||||||
 | confidence level of cross correlation returns the confidence level of cross correlation. The values of cross correlation between plus and minus confidence level of cross correlation are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. |
SI Model Residual Analysis (SISO Array)

 | system model contains information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model contains.
| ||||||
 | stimulus signal specifies the input array of the stimulus signal. | ||||||
 | response signal specifies the input array of the response signal. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | sampling rate specifies the sampling rate of the input signals. sampling rate must equal the sampling rate used to estimate the system model. | ||||||
 | confidence level of autocorrelation returns the confidence level of autocorrelation. The values of autocorrelation between plus and minus confidence level of autocorrelation are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. | ||||||
 | prediction error returns the one-step-ahead prediction error of the system response. | ||||||
 | autocorrelation returns the autocorrelation of prediction error. autocorrelation and cross correlation provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
 | cross correlation returns the cross correlation of prediction error and stimulus signal. autocorrelation and cross correlation provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
| ||||||
 | confidence level of cross correlation returns the confidence level of cross correlation. The values of cross correlation between plus and minus confidence level of cross correlation are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. |
SI Model Residual Analysis (MISO Waveform)

 | system model contains information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model contains.
| ||||||
 | stimulus signals specifies the input waveform array of the stimulus signals. Each element of the array is the waveform of one stimulus signal. | ||||||
 | response signal specifies the input waveform of the response signal. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | confidence level of autocorrelation returns the confidence level of autocorrelation. The values of autocorrelation between plus and minus confidence level of autocorrelation are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. | ||||||
 | prediction error returns the waveform of the one-step-ahead prediction error of the system response. | ||||||
 | autocorrelation returns the autocorrelation of prediction error. autocorrelation and cross correlations provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
 | cross correlations returns the cross correlations of prediction error and stimulus signals. Each element of the waveform array is the cross correlation between one input and the prediction error of the output. autocorrelation and cross correlations provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
| ||||||
 | confidence levels of cross correlations returns the confidence levels of cross correlations. The values of cross correlations between plus and minus confidence levels of cross correlations are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. |
SI Model Residual Analysis (MISO Array)

 | system model contains information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model contains.
| ||||||
 | stimulus signals specifies the input array of the stimulus signals. Each row in the array is one stimulus signal. | ||||||
 | response signal specifies the input array of the response signal. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | sampling rate specifies the sampling rate of the input signals. sampling rate must equal the sampling rate used to estimate the system model. | ||||||
 | confidence level of autocorrelation returns the confidence level of autocorrelation. The values of autocorrelation between plus and minus confidence level of autocorrelation are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. | ||||||
 | prediction error returns the one-step-ahead prediction error of the system response. | ||||||
 | autocorrelation returns the autocorrelation of prediction error. autocorrelation and cross correlations provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
 | cross correlations returns the cross correlations of prediction error and stimulus signals. Each row in the array is the cross correlation between one input and the prediction error of the output. autocorrelation and cross correlations provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
| ||||||
 | confidence levels of cross correlations returns the confidence levels of cross correlations. The values of cross correlations between plus and minus confidence levels of cross correlations are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. |
SI Model Residual Analysis (MIMO Waveform)

 | system model contains information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model contains.
| ||||||
 | stimulus signals specifies the input waveform array of the stimulus signals. Each element of the array is the waveform of one stimulus signal. | ||||||
 | response signals specifies the input waveform array of the response signals. Each element of the array is the waveform of one response signal. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | confidence levels of autocorrelations returns the confidence levels of autocorrelations. Each element of the array is the confidence level of one autocorrelation. The values of autocorrelations between plus and minus confidence levels of autocorrelations are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. | ||||||
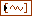 | prediction errors returns the one-step-ahead prediction errors of the system response. Each element of the waveform array is the prediction error of one response. | ||||||
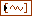 | autocorrelations returns the autocorrelations of prediction errors. Each element of the array is the autocorrelation of the prediction error for one output. autocorrelations and cross correlations provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
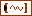 | cross correlations returns the cross correlations of prediction errors and stimulus signals. autocorrelations and cross correlations provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. The element of the ith row and jth column in the array is the cross correlation between the jth input and the prediction error of the ith output. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
| ||||||
 | confidence levels of cross correlations returns the confidence levels of cross correlations. Each element of the array is the confidence level of one cross correlation. The element in the ith row and jth column of confidence levels of cross correlations is the confidence level of the cross correlation between the jth input and the prediction error of the ith output. The values of cross correlations between plus and minus confidence levels of cross correlations are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. |
SI Model Residual Analysis (MIMO Array)

 | system model contains information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model contains.
| ||||||
 | stimulus signals specifies the input array of the stimulus signals. Each row in the array is one stimulus signal. | ||||||
 | response signals specifies the input array of the response signals. Each row in the array is one response signal. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | sampling rate specifies the sampling rate of the input signals. sampling rate must equal the sampling rate used to estimate the system model. | ||||||
 | confidence levels of autocorrelations returns the confidence levels of autocorrelations. Each element of the array is the confidence level of one autocorrelation. The values of autocorrelations between plus and minus confidence levels of autocorrelations are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. | ||||||
 | prediction errors returns the one-step-ahead prediction errors of the system response. Each row in the array is the prediction error for one output. | ||||||
 | autocorrelations returns the autocorrelations of prediction errors. Each row in the array is the autocorrelation of the prediction error for one output. autocorrelations and cross correlations provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. | ||||||
 | cross correlations returns the cross correlations of prediction errors and stimulus signals. autocorrelations and cross correlations provide the measure of the quality of the estimated model. The 1D subarray of cross correlations with the ith first index and jth second index is the cross correlation between the jth input and the prediction error of the ith output. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
| ||||||
 | confidence levels of cross correlations returns the confidence levels of cross correlations. Each element of the array is the confidence level of one cross correlation. The element in the ith row and jth column of confidence levels of cross correlations is the confidence level of the cross correlation between the jth input and the prediction error of the ith output. The values of cross correlations between plus and minus confidence levels of cross correlations are insignificant, and you can consider them to be equal to 0. |
Examples
Refer to the following VIs for examples of using the SI Model Residual Analysis VI: