Recover My Files Data Recovery Software | English
V4
___________________________________________________
Understanding Search Results
Recover Drive
A Recover Drive search is targeted at the recovery of partitions from a formatted, corrupt, raw or unallocated hard drive. A successful recovery should locate and display the full file and folder structure in the search results screen.
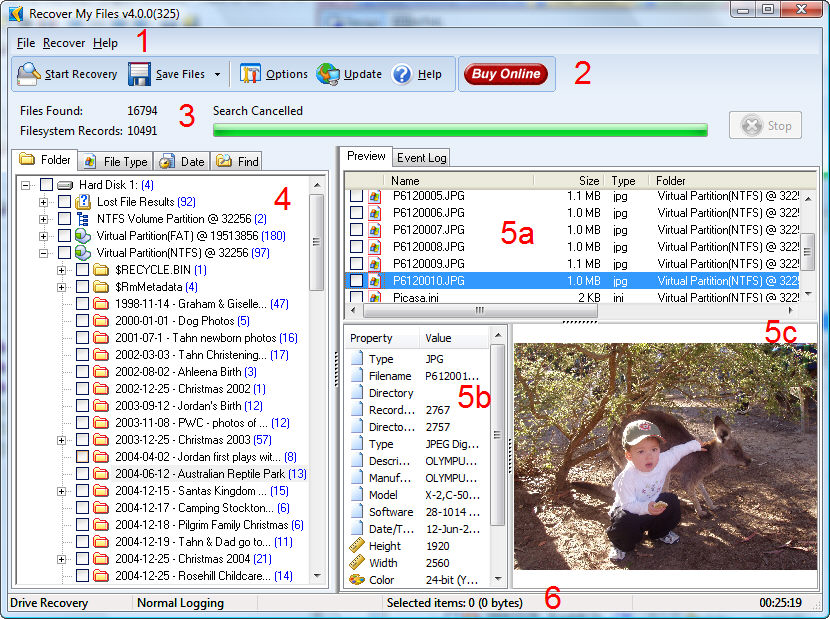
In a "Recover Drive", it usually the "Folder" view which has most relevance, as it displays the file and folder structure of the recovered files (shown as area 4 in this screen-shot). Drive recovery results fall into three categories:
Drive Recover Search Results Screen
|
Recovered Partitions
When a valid existing partition is located on a drive it is represented in Folder view as follows:

The description of this partition is:
"@ 32256" represents the sector on the drive where the partition was located
"[NAME]" (if present) represents the volume name of the partition
"(2)" represents the number of sub folders that it contains.
Click on the + sign to expand the partition to view the sub folders that it contains. Click on individual files to display the properties for the selected file and a preview of the file.
Recovered Virtual Partitions
A virtual partition is essentially the old underlying partition on a drive. For example, when a hard disk is formatted and Windows is reinstalled, the existing new installation of Windows will be recovered as the active partition (described above) with the old underlying partition recovered as the virtual partition. A virtual partition is represented in Folder view as follows:

Virtual Partition(FAT) - represents the type of partition located
"@ 19513856" represents the sector on the drive where the partition was located
"[NAME]" - (if a name exists) represents the volume name of the partition
"(180)" represents the number of sub folders that it contains.
Click on the + sign to expand the partition to view the sub folders that it contains.
 Sometimes incomplete or 'ghost' partitions can be located. Each partition
shown in "Folder" view should be checked to see if it contains
valid data. The primary test is whether individual files contained in
the recovered partition is whether individual files can be displayed in
the preview window.
Sometimes incomplete or 'ghost' partitions can be located. Each partition
shown in "Folder" view should be checked to see if it contains
valid data. The primary test is whether individual files contained in
the recovered partition is whether individual files can be displayed in
the preview window.
Lost File Results
In Drive Recover mode, 'Lost Files' are the file types that were selected (either pre-selected in automatic mode, or manually selected) to aid in the identification of the file system. They are represented in Folder view as:

"(92)" represents the number of files that it contains.
Click on the + sign to expand the partition to view the files that it contains.
If the recovery of partitions was NOT successful (or only partially successful), Lost Files can be important as they will still give access to your lost data (but without original file names or folder structure). Learn more about Lost Files here.
Searching for Lost Files Recover My Files has the capability to perform a sequential search of the disk to identify "Lost Files" by their internal file structure, (i.e. their header, content and footer). This is often referred to as a "file header search" or "data carving". Shown below is the content of a JPEG picture, the way a computer sees it. A JPEG can be identified by the "y0ya..JFIF" header, and contains further information about the camera used to create the image:
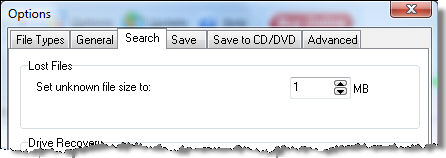
Once the header of a file is identified, Recover My Files will travel a pre-defined distance down the drive to analyze the file structure and locate the end of the file. If the file end is not found, but sufficient information is found within the file to suggest it will at minimum be partially recovered, it is assigned a default file size according to that file type. The global default size of lost files can be set in the OPTIONS > SEARCH window:
Limitations of a Lost File search are:
|
If partition recovery was not successful, it is suggest that you run a second drive recovery, using selected file types, to find your important files.
General Information about the Search Results Screen
The Recover My Files search results screen is broken down into 8 areas, as shown in this screen-shot.
Drive Recover Search Results Screen
|
1. Text Menu
The text menu is where basic functions are performed, including:
Displaying the software version information
What version number do I have installed?
To find this information, at the top of the main program screen in text menu items "File | Recover | Help", click on "Help > About". This will open the program About Box which contains the information.
2. Toolbar buttons

The text menu is where basic functions are performed, including:
"Start Recovery" starts the search process
"Save Files" is used to save the search results
"Options" enables the setting of program options
"Update" checks for available updates (internet access required)
"Help" opens this help file.
3. Search Progress
The search progress area (shown in the screen-shot as area 3) contains important information about the search.
Drive Recover Search Results Screen
|
Files Found
In a File recovery, the 'Files Found' number represents each Deleted File and each Lost File found.
What is a Lost File? A Lost File is one that has been deleted, but which no longer has a Windows Operating System record in the FAT or MFT. Windows no longer knows about this file, but content of the file remains on the disk and can be recovered. Lost files are located using a technique referred to as "data carving". Data carving is the technique of recovering files based on content. Recover My Files examines the header, content and footer of a file to determine if it matches a known structure, e.g. JPEG, TIF, XLS, DOC etc. The limitation of data carving is that;
|
What is a "Deleted File" On a computer storage device, the term 'Filesystem' is used to describe the schema by which electronic files are stored. A common characteristic of a Filesystem is that they use a table on the drive to track every file on the disk, including user deleted files. Each record in the table holds all information about a file, including its size, time and date stamps, permissions, etc., (required for file and folder name recovery), and tells the computer which storage sectors on the drive hold the file data. The first version of this table in Microsoft was called the "File Allocation Table" (FAT), but more recently released a new table format called the XFAT, and for NTFS formatted drives, the "Master File Table" (MFT). When a file on the drive is deleted, the FAT or MFT record is marked as such and can be used to find the location of the deleted file and recover it, including the original file name and folder location. |
In Drive recover mode, the 'Files Found' number represents each Lost File found and each file found in a recovered partition.
What is a Lost File? A Lost File is one that has been deleted, but which no longer has a Windows Operating System record in the FAT or MFT. Windows no longer knows about this file, but content of the file remains on the disk and can be recovered. Lost files are located using a technique referred to as "data carving". Data carving is the technique of recovering files based on content. Recover My Files examines the header, content and footer of a file to determine if it matches a known structure, e.g. JPEG, TIF, XLS, DOC etc. The limitation of data carving is that;
|
Filesystem records
Filesystem records indicate where a missing
Filesystem has been found. Each Filesystem record represents a file with
its full file and folder name.
The Filesystem records number can be used as a guide to identify when a
Drive Recovery can be stopped (without the need to let the search run
to the end). Learn
more about Filesystem records here.
Search Phase 2 - Searching for File System records (FAT/XFAT/MFT) using selected file types
Once Phase 1 of the search is complete, Phase 2 of the search will automatically commence. Phase 2 uses the selected file types to help locate file system records on the drive.
On a computer storage device, the term 'File System' is used to describe the schema by which electronic files are stored. The most common File Systems are;
Microsoft's FAT (File Allocation Table), usually used for external media and camera cards;
Microsoft's XFAT, an enhanced version of FAT for improved performance on external media and camera cards;
Microsoft NTFS (Maser File Table, [MFT]), primarily used for PC hard drives;
Apple Macintosh HPFS (High Performance File System); and
Linux EXT2/3.
A common characteristic of a File System is that they use a table on the drive to track every file on the disk. Each record in the table holds all information about a file, including its size, time and date stamps, permissions, etc., (required for file and folder name recovery), and tells the computer which storage sectors on the drive hold the file data.
The number of file system records found is
displayed in the progress bar. Each Filesystem Record represents a file
with its full file and folder name:

 If you are
in a hurry to recovery your data:
If you are
in a hurry to recovery your data:
When the number of "Filesystem Records:" found reaches a high number (an average home computer has between 50,000 and 150,000 Filesystem records), stops increasing, and remains constant, it means the file system records located have been read. On your average home PC you should reach this point within 2 hours of searching. You can press the STOP button (note down the 'block' number that the search is up to in case you wish to recommence the search at a later time);
or, if time is not a concern to you, let the search run to the end.
Once you have stopped the search, or the search finishes, the search results will build and display in "Folder" view of the results screen as a "Virtual Partition". A virtual partition is displayed in the results screen as:

Expand the search results (using the '+') to determine if your missing files have been located.
Learn more about the Drive Recover search results screen here.
4. View Search Results
Recover My Files makes search results available under four different views, access by clicking on the following tabs (as shown in area 2 of this screen-shot):
Drive Recover Search Results Screen
|
Folder view
The "Folder Tab" is used to display the file and folder structure
of the search results and is similar to how Windows displays the files
and folders in Windows Explorer. Learn more about the Folder
tab here.
"Folder" Tab The "Folder Tab" is used to display the file and folder structure of the search results and is similar to how Windows displays the files and folders in Windows Explorer. In File Recover mode, it displays the file and folder structure of Deleted Files. In Disk Recover mode, it displays the files and folder structure of recovered partitions. When files are selected and save from Folder view, the folder structure of the saved files will replicate what is displayed here. |
File Type view
File Type view lists files according to their extension. This can be used
as a fast way to locate a file when the type is know but the original
folder location is not. The "Other
Extensions" folder contains all other file extensions not specifically
selected in the search.
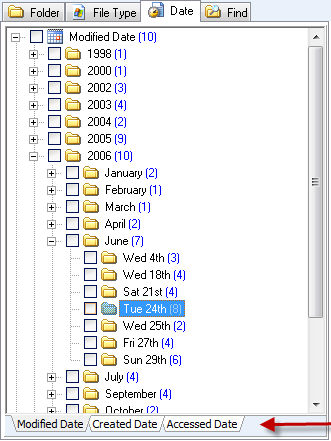
Date view
The "Date" view sorts files by date. Learn more
about the Date tab here
Date Tab The Date tab sorts search results file date. This can be useful to quickly locate digital camera pictures and other files that were known to be created at a specific point in time. The date used in the sort is changed by selecting one of the following tabs at the bottom of the window:
|
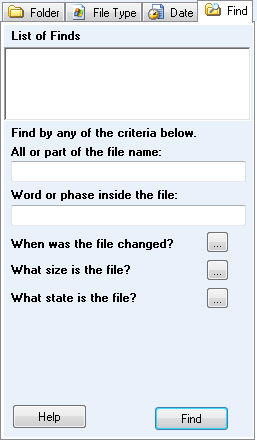
Find
The Find tab is used to search through the existing search results
for relevant files based on your selected search criteria. Learn more
about the Find tab Learn more about the Find Tab here.
"Find" Tab The Find tab is used to search through the existing search results for relevant files. A find can only be run once a search is completed.
|
5. Preview (and Event Log)
The file preview are is in three windows: 5a, select the individual file; 5b, view the file properties; and 5c, preview the file (see screen-shot). The preview windows may display the following messages:
Drive Recover Search Results Screen
|
"A preview is not available for this file type": Recover My Files has examined the file header and determined that the file types does not support a preview;
"Corrupt file, preview not available": Recover My Files has examined the file header and determined that it is a file type that can be previewed, however the data inside the file is damaged and a preview of the file cannot be displayed. It is unlikely that when a file that displays this message is saved that it will open properly.
6. Information Bar
Type of search
The bottom left hand corner of the search results screen identifies if "Files Recovery" or "Drive Recovery" mode was selected.
Type of logging
Displays the logging mode that is currently being used. Logging is displayed in the Event Log tab in section 5a (as shown in this screen-shot).
Drive Recover Search Results Screen
|
Normal Logging: Normal logging provides information about the recovery process.
Debug Logging: Debug logging gives additional information about the recovery process. Debug logging is resource intensive and will slow down a search. It is recommended that you only use debug logging mode when instructed to do so by GetData support staff. Right click on the log screen to copy the information to the windows clipboard.
Selected items to be saved
This shows the number of files selected to be saved and the total size of the files selected, e.g. "Selected items 25 (22.3mb)". In this example, a minimum of 23 megabytes is required on an external drive to save the files. Learn about saving files here.
Search duration
The duration of the search is displayed in the bottom right hand corner of the main program screen.
Troubleshooting
+ Search Progress: The
search is very slow - how do I speed it up?
|
|
+ Search
Results: Lost
Files are all the same size (e.g. 1024kb)
|
|
| + Search Results:
The recovered
file does not contain valid data
Does the saved file contain data? Open the file and view the raw data inside the file. You can do this by:
No, the file does not contain any data In some instances a storage device may have powered down (or gone flat) during the save process. This may cause Recover My Files to save blank files, as the data can no longer be read. If the saved file is blank, you need to change your drive power settings in the control panel: Control Panel > Power Options > and make sure that the hard drives are not set to power down after a specific period of time (in XP the setting should be "Never"). After you run the search and before you save the files, check that the drive is running by:
Yes, the file does contain data but it will not open If the save file contains data, but does not open, it is corrupt. Try an alternate method to open the file. E.g. Explorer View: Explorer View for Windows Explorer is a file viewing program that can view over 300 file types. In many situations it can read corrupt files that will onto open in their creating application. Photos: Irfanview (www.irfanview.com) is a free graphics viewer which is good at opening corrupt image files; Word Files: Word Repair is a free Microsoft Word repair utility that can extract text from damaged .doc files PST Files: Recover My Email (www.recover-my-email.com) is a tool for reading corrupt Microsoft Outlook .PST files
What causes corrupt files? Files with their original file name When a file has been found with its original file name, it has been found by locating a File System record for that file which points to the location of the file data on the disk. In a successful recovery, it should be possible to click on the file found in the results window and preview its content, or save the file and open it normally. If the recovered file does not contain valid data, the possible reasons are:
LostFiles Lost files are located by searching for the header, structure and footer of the file data. Recover My Files performs a series of tests on each Lost File type, to determine the possibility of recovery. Partially corrupt files will be returned as there is the possibility that the files can be accessed using the methods described above.
|
|
| See the full troubleshooting guide here |