Distributed Queries
Distributed queries access data from multiple heterogeneous data sources, which can be stored on either the same or different computers. Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2000 supports distributed queries by using OLE DB, the Microsoft specification of an application programming interface (API) for universal data access.
This Distributed Queries section discusses general distributed query concepts and describes how to use Transact-SQL statements in distributed queries to access data on separate instances of SQL Server, or non-SQL Server data sources. Other sections of SQL Server Books Online contain additional related information.
| For this information | See |
|---|---|
| Configuring OLE DB providers and linked servers | Configuring Linked Servers |
| Distributed queries in distributed transactions | Distributed Queries and Distributed Transactions |
| Linked servers | Accessing External Data |
| ODBC and distributed queries | Schema Functions Supporting Distributed Queries |
| Information about specific OLE DB Providers | OLE DB Providers Tested with SQL Server |
| Performance issues | Optimizing Distributed Queries |
| Reference for OLE DB Provider developers | OLE DB Provider Reference for Distributed Queries |
| Transact-SQL language in distributed queries | External Data and Transact-SQL |
| Troubleshooting distributed queries | Distributed Queries Error Messages |
Distributed queries provide SQL Server users with access to:
- Distributed data stored in multiple instances of SQL Server.
- Heterogeneous data stored in various relational and non-relational data sources accessed using an OLE DB provider.
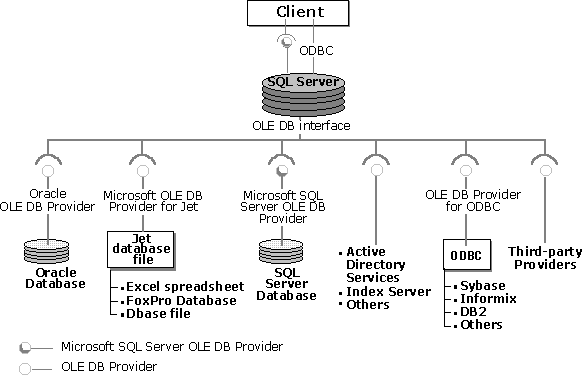
OLE DB providers expose data in tabular objects called rowsets. SQL Server 2000 allows rowsets from OLE DB providers to be referenced in Transact-SQL statements as if they were a SQL Server table.
Tables and views in external data sources can be referenced directly in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE Transact-SQL statements. Because distributed queries use OLE DB as the underlying interface, distributed queries can access traditional relational DBMS systems with SQL query processors, as well as data managed by data sources of varying capabilities and sophistication. As long as the software owning the data exposes it in a tabular rowset through an OLE DB provider, the data can be used in distributed queries.
Note Using distributed queries in SQL Server is similar to the linked table functionality through ODBC, which was supported previously by Microsoft Access. This functionality is now built into SQL Server with OLE DB as the interface to external data.