Accessing and Changing Relational Data
Dynamic Locking
Although row level locks increase concurrency, it is at the cost of system overhead. Table or page locks lower overhead, but at the expense of lowering concurrency.
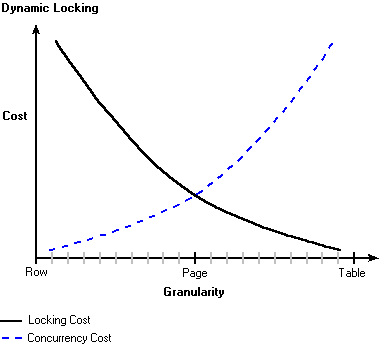
Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2000 uses a dynamic locking strategy to determine the most cost-effective locks. SQL Server automatically determines what locks are most appropriate when the query is executed, based on the characteristics of the schema and query. For example, to reduce the overhead of locking, the optimizer may choose page-level locks in an index when performing an index scan.
Dynamic locking has the following advantages:
- Simplified database administration. Database administrators no longer have to be concerned with adjusting lock escalation thresholds.
- Increased performance. SQL Server minimizes system overhead by using locks appropriate to the task.
- Application developers can concentrate on development. SQL Server adjusts locking automatically.