Using the Strain Gage Calibration Wizard
When you configure a strain measurement task, you can use the Strain Gage Calibration Wizard to calibrate your strain gage. Complete the following steps to calibrate the strain gage:
- Click Calibrate to launch the Strain Gage Calibration Wizard.
- Follow the steps on the Setup Hardware window. You can configure the following settings:
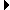 Enable Offset Nulling
Enable Offset NullingSelect Enable Offset Nulling to perform an offset nulling calibration procedure.
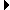 Enable Shunt Calibration
Enable Shunt CalibrationSelect Enable Shunt Calibration to perform a shunt calibration procedure. If you select this option, configure the following settings:
Shunt Resistor Value—Specify the exact resistor value of the shunt resistor. The default value is the resistance of the shunt resistor that is the factory shipping default for your hardware. For the greatest accuracy, use a 6-1/2 digit DMM to measure the resistance of your entire shunt calibration circuit with the shunt switch engaged and leads connected. This will increase the accuracy of your measurements by compensating for the shunt enable switch resistance and any lead resistance caused by long lead wires. However, since the shunt resistor value is very large, these do not greatly impact the measurement accuracy.
Shunt Resistor Location—Specify the location on the Wheatstone bridge to which the shunt resistor is connected. Refer to the figure on the Setup Hardware window for the relative positions of R1, R2, R3 and R4.
- Click Next.
- Use the Measure and Calibrate window to measure and calibrate your strain gage. The software automatically takes the first measurement, and the table displays the results. The table shows the following information:
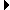 Channel Information
Channel Information- Channel Name—The name of the virtual channel on which strain calibration is performed.
- Physical Chan—The physical channel to which the strain gage is connected.
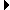 Offset Adjustment—This section shows information about the offset error to help you determine if you should perform an offset null calibration. Perform an offset null calibration if you perform a shunt calibration.
Offset Adjustment—This section shows information about the offset error to help you determine if you should perform an offset null calibration. Perform an offset null calibration if you perform a shunt calibration.- Meas Val (strain)—The measured offset value with units of strain. Normally, this value should be close to zero.
- Err (%)—Percentage offset error, determined by the equation:
Err (%) = [(offset value * 100) / (Max Range Limit – Min Range Limit)]
where Max Range Limit and Min Range Limit are the maximum and minimum strain range values specified for the given virtual channel.
 Gain Adjustment—This section shows values related to gain error and the shunt calibration procedure:
Gain Adjustment—This section shows values related to gain error and the shunt calibration procedure:- Sim Val (strain)—The simulated strain value based on the hardware setup and the shunt resistor value.
- Meas Val (strain)—The measured strain value. Normally, this value should be close to the simulated strain value.
- Gain Adj Val—The gain adjust value. This value is the end result of the shunt calibration and is used to scale strain measurements on this channel. Normally, this value is close to 1, which implies that the measured value and simulated value are equal. Your strain channel stores the gain adjust value as the AI.Bridge.ShuntCal.GainAdjust attribute.
- Err (%)—Percentage gain error, determined by the equation:
Err (%) = (measured value – simulated value) * 100 / (Max – Min)
where Max and Min are the maximum and minimum strain values specified for the given virtual channel.
- Perform your measurement and calibration with the following buttons:
- Click Measure to make a preliminary measurement using the offset and shunt calibration data from a previously run strain gage procedure.
- Click Reset Data to reset the offset and shunt calibration data and make a measurement using their default values.
- Click Calibrate to perform the offset and/or shunt calibration. The table shows the resulting measurements.
- Click Finish when you are done. The calibration data is saved as part of your virtual channel. On successful completion, the software automatically uses the calibration data when scaling voltage to strains on this virtual channel.
 |
Note If you are using an SCXI-1520 with an SCXI-1314 terminal block, PXI-4220, SCXI-1121 with an SCXI-1321 terminal block, or an SCXI-1122 with an SCXI-1322 terminal block, refer to Device-Specific Strain Gage Information for more information about device-specific settings. |
Related Topics
Signal Conditioning Requirements for Strain Gages