Editing JPEG and TIFF Images
With DPP, you can adjust JPEG and TIFF images in the same way as RAW images using the [RGB] and [NR/ALO] tool palettes. Because adjustment made with the tool palette (recipe) only changes the image processing conditions, the "original image data itself" remains unaffected. Therefore, there are no problems with image deterioration that arise with editing and you can readjust your images any number of times.
-
Double-click a thumbnail image in the main window.
-
The edit window appears.
-
-
Select the [View] menu → [Tool palette].
-
The tool palette appears.
-
-
Select the [RGB] tab sheet on the tool palette, and edit the image.
Automatically Adjusting Brightness and Color (Tone Curve Assist)
Adjusting Brightness and Contrast
Adjusting Color Tone Using Click White Balance
Adjusting Hue, Saturation and Sharpness
Tone Curve Adjustment
Adjusting Dynamic Range -
Select the [NR/ALO] tab sheet on the tool palette, and edit the image.
Contents adjusted using the tool palette can be handled individually as a recipe file (extension ".vrd").
In DPP all the adjustments (image processing conditions information) made with the tool palette can be saved in the image as data called a "recipe", or can be saved, downloaded and applied to other images as a separate recipe file (extension ".vrd") (Utilizing Adjustment Contents (Recipe), Applying Editing Contents to Another Image).
About the RGB Tool Palette
With the functions in the [RGB] tool palette, you can adjust JPEG and TIFF images with the same functions as ordinary image editing software. However, because the adjustment width of the functions in the [RGB] tool palette is wider than the [RAW] tool palette, the image color may be saturated, or the image quality may deteriorate if you adjust too much. Therefore, take care not to adjust your images to an excessive degree. You can adjust RAW images with the functions in the [RGB] tool palette. However, for functions other than tone curve adjustment and automatic adjustment, we recommend adjusting RAW images using the same functions available in the [RAW] tool palette.
RGB Tool Palette
| [Tone curve assist] | Automatic adjustment (tone curve assist) |
| [Tone curve adjustment] | Tone curve adjustment |
| Click white balance | |
 |
Dynamic range adjustment |
| [Brightness] | Brightness and contrast adjustment |
| [Contrast] | |
| [Hue] | Hue and Saturation adjustment |
| [Saturation] | |
| [Sharpness] | Sharpness adjustment |
 |
Enlargement display position* |
*If an image is displayed enlarged, the enlargement display position can be moved by dragging. The enlargement display position appears when [Docking display] has been set and the edit image window has been enlarged. (Tool Palette)
Editing with the Tool Palette in the Main Window
By clicking the [Tool] button in the toolbar on the main window, the same tool palette that appears in the edit window is displayed and you can edit images.
Automatically Adjusting Brightness and Color (Tone Curve Assist)
In order to make the image a desirable standard image, automatically adjust the image tone curve. You can select the degree of automatic adjustment from "Standard" and "High".
Click the desired automatic adjustment button.
-
The tone curve changes as adjusted.
-
-
[
] (Standard)
- Standard automatic adjustment. Suitable for most images.
-
[
] (High)
- Use when the effect achieved in standard automatic adjustment is not strong enough.
-
[
]
- Reverts the tone curve to the original settings.
The result of automatic adjustment (tone curve assist) may not be as expected with the following images:
- Images which have been shot with the proper exposure
- Images where the brightness is unbalanced
- Images which are too dark
- Images which have extreme backlighting
Adjusting Brightness and Contrast
The brightness and contrast of an image can be adjusted.
Adjust an image while viewing it.
Enter a value or drag the slider left or right to adjust the brightness and contrast.
-
[Brightness]
- Move the slider to the right to make an image brighter and to the left to make an image darker.
-
[Contrast]
- Used to adjust modulation and degree of contrast of color. Move the slider to the right to make contrast of an image stronger and to the left to make contrast weaker.
Adjusting Color Tone Using Click White Balance
You can adjust white balance using a selected part of an image as the standard for white to make the image appear natural. Using click white balance is effective when using it in parts of an image where white color tone has changed under the influence of a light source.
-
Click the [
 ] button.
] button.-
When you move the cursor over the image, the cursor [
 ] changes to [
] changes to [  ].
].
-
Click on a point that is to be the standard for white.
-
The color of the image is adjusted with the point you selected as the standard for white.
-
If you click on another point in the image, the white balance is adjusted again.
-
To finish click white balance, right-click with the mouse or click the [
 ] button again.
] button again.
-
When there are no white areas in your image, you can adjust the white balance by clicking on a grey point of the image in step 2. This has the same adjustment result as selecting a white point.
The coordinates of the cursor position and the RGB values (8-bit conversion) of the image are displayed in the lower-left of the window.
The image is adjusted based on the average value of 5 x 5 pixel range from the clicked point.
The histogram display changes according to adjustment. You can also fix the histogram display to the display before any adjustments. (Tool Palette)
Adjusting Hue, Saturation and Sharpness
You can adjust hue (tone) and saturation and make the overall atmosphere of an image harder or softer.
Adjust an image while viewing it.
Enter a value or drag the slider left or right to adjust the hue, saturation and sharpness.
-
[Hue]
- Move the slider to the right to make color tones more yellow, and to the left to make color tones redder.
-
[Saturation]
- Move the slider to the right to make the color deeper, and to the left to make the color weaker.
-
[Sharpness]
- Move the slider to the right to make an image harder, and to the left to make an image softer.
Adjust sharpness with the window view set to [100% view], [50% view] or [200% view]. If the view is set to [Fit to window] (full view), the sharpness will seem unnatural.
Tone Curve Adjustment
You can adjust the brightness, contrast and color of a specific area by changing the tone curve.
-
Select the tone curve mode and interpolation method.
-
Right-click with the mouse inside the graph to display the menu.
-
Make adjustments.
-
Clicking the tone curve shows [
 ] on the tone curve. Drag [
] on the tone curve. Drag [  ] to your desired location.
] to your desired location. -
The horizontal axis shows the input level and the vertical axis shows the output level.
-
The maximum number of [
 ] is 8.
] is 8. -
To delete a [
 ], either press the <Del> key or double-click on the [
], either press the <Del> key or double-click on the [  ].
].
-
-
[RGB]
- Batch adjusts RGB.
-
[R]/[G]/[B]
- Adjusts each channel.
-
The histogram display changes according to adjustment. You can also fix the histogram display to the display before any adjustments. (Tool Palette)
The tone curve mode and interpolation method for a tone curve can also be changed in [Preferences]. (Tool Palette)
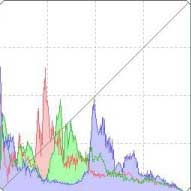
Adjusting Dynamic Range
The dynamic range (width of gradation expression) from dark points to bright points in an image can be adjusted. The more the shadow point is towards the right, the more the gradation of dark points in the image disappears and the image becomes darker. The more the highlight point is towards the left, the more the gradation of bright points in the image disappears and the image becomes brighter. The narrower the space between shadow point and highlight point becomes, the narrower the gradation from bright points to dark points of an image becomes.
Adjust an image while viewing it.
-
When you move the cursor to the left edge of the graph, the cursor [
 ] changes to [
] changes to [  ]. Drag the slider right to adjust the shadow point.
]. Drag the slider right to adjust the shadow point. -
When you move the cursor to the right edge of the graph, the cursor [
 ] changes to [
] changes to [  ]. Drag the slider left to adjust the highlight point.
]. Drag the slider left to adjust the highlight point. The horizontal axis shows the input level and the vertical axis shows the output level.
-
The setting range of shadow points is 0 to 247 (in 1-stop increments when entering a value).
The setting range of highlight points is 8 to 255 (in 1-stop increments when entering a value).
The histogram display changes according to adjustment. You can also fix the histogram display to the display before any adjustments. (Tool Palette)