Windows® 2000 Driver Software: Broadcom NetXtreme™ Gigabit Ethernet Adapter User's Guide
This chapter provides the following information:
 Installing
the Driver Software
Installing
the Driver Software
 Modifying
Configuration Parameters
Modifying
Configuration Parameters
 Installing
Broadcom Advanced Server Program
Installing
Broadcom Advanced Server Program
 Uninstalling
Broadcom Advanced Server Program
Uninstalling
Broadcom Advanced Server Program
 Save
and Restore Configuration
Save
and Restore Configuration
 |
NOTE The Broadcom NetXtreme™ Gigabit Ethernet Adapter must be physically installed in your system prior to installing the driver software. See Installing the Hardware for details. |
When the Windows 2000 system first boots up after installing a new hardware device, such as a Gigabit Ethernet Adapter, the system automatically detects the new hardware and prompts you to install the driver software for that device.
A network device driver must be installed before the Gigabit Ethernet Adapter can be used with your Windows 2000 system.
Installing the Adapter Software
To install the adapter software for Windows 2000, do the following
 |
NOTE Before beginning this procedure, verify that the Windows 2000 system has been upgraded to the latest version with the latest service pack applied. |
- Start your Windows 2000 system
and log in. You must have System Administrator privileges to install the driver
software.
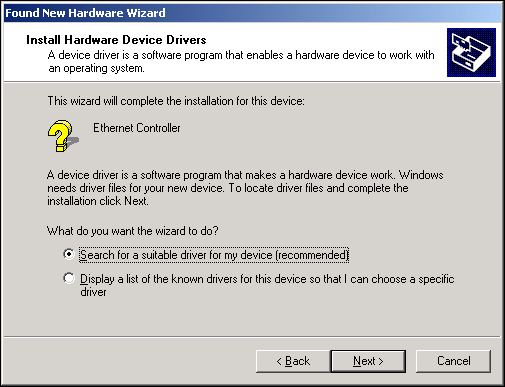
When you boot up the Windows 2000 system after installing the adapter card, a series of Found New Hardware Wizard windows are displayed.
- In the Install Hardware Device Drivers window, click Search for a suitable driver for my device (recommended), then click Next.
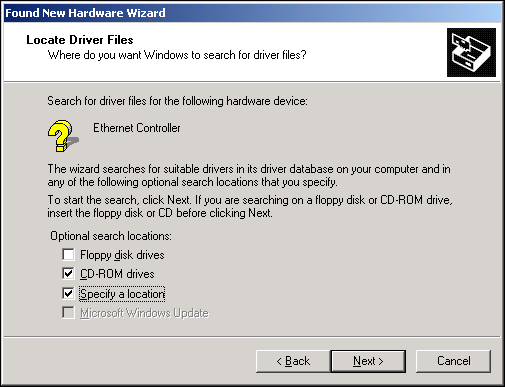
- In the Locate Driver Files window, select the applicable
search location check boxes.
- When prompted, insert the media to be searched into your
CD-ROM drive, type the path to the driver, and select OK.
Example: e:\
Where "e:" is the designation of the CD-ROM drive on your system.
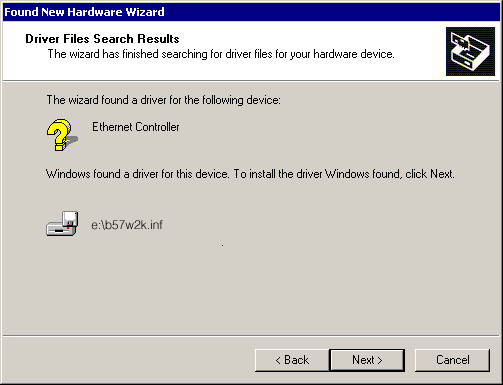
- In the Driver Files Search Results window, verify that
the correct path to the driver software is shown, then click Next.
 |
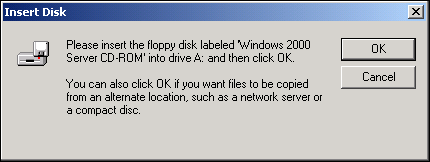
NOTE If the Insert Disk window appears, do not insert the Windows 2000 disk: |
Some early versions of Windows 2000 may display a spurious message requesting you to insert the Windows 2000 disk. If this occurs, leave the driver installation media in the drive and click OK. If asked to specify the location of the Windows 2000 CD-ROM instead, click Browse (dont use the text entry field) and locate the path to the Gigabit Ethernet drivers that was specified above.
Once installation of the driver software is complete, you are ready to modify configuration parameters.
Modifying Configuration Parameters
Although the default values should be appropriate in most cases, you may change any of the available options to meet the requirements of your specific system. Once the adapter driver software has been installed, you can use this procedure to verify or change the following adapter properties:
- 802.1p QOS
- Checksum Offload
- Ethernet@WireSpeed™
- Flow Control
- Jumbo Mtu
- Speed & Duplex
- Wake Up Capabilities
- WOL Speed
Driver Properties Advanced Tab
To configure the adapter parameters, bring up the Driver Properties Advanced tab as follows:
- On the Desktop, right-click the My Computer icon and select the Properties option from the pop-up menu. The System Properties window displays.
- Click the Hardware tab and then click Device Manager. The Device Manager window displays.
- Scroll down the list of hardware devices to Network Adapters. Click the plus (+) to the left of the icon to display the list of adapters currently configured.
- Double-click the Gigabit Ethernet Adapter you want to
configure. The Gigabit Ethernet Properties window displays, showing the General
tab.
- Click the Advanced tab. A window showing the list
of configurable properties (and default values) for the adapter displays.
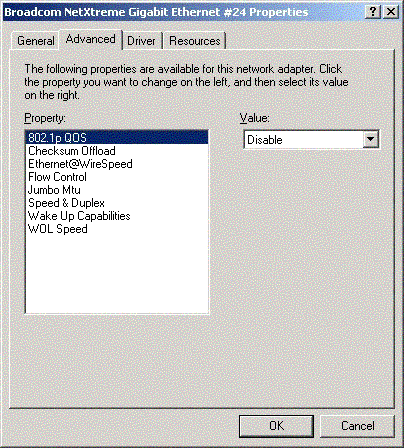
- Change the operating parameters as desired. To change adapter operating parameters listed under the Advanced tab, click on the options listed under Properties and then use the pull-down window under Value to change the default or assigned value.
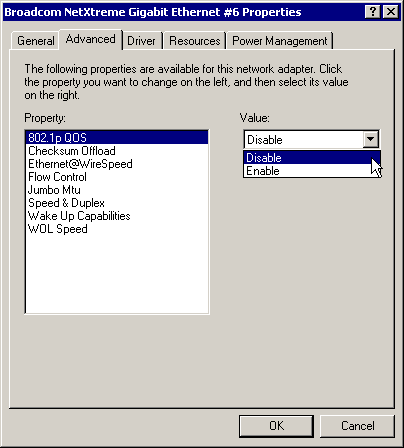
802.1p QOS Parameter
The 802.1p QOS parameter is a standard that enables Quality of Service. Disabled by default, select Enable from the Value drop-down menu to enable this parameter. Once enabled, select Disable from the Advanced tab "Value" drop-down menu to disable this parameter.
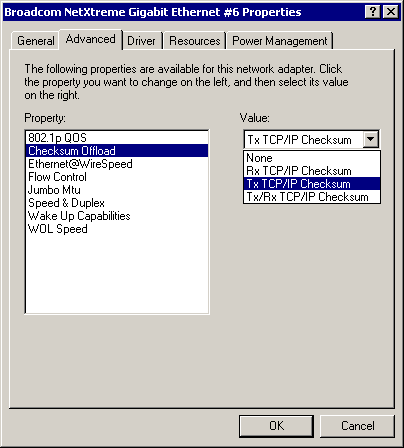
Checksum Offload Parameter
Normally the Checksum Offload function is computed by the protocol stack. By selecting one of the Checksum Offload parameters, the checksum can be computed by the Gigabit Ethernet Adapter. To enable one of the Checksum Offload parameters, select the parameter from the Advanced tab "Value" drop-down menu. These parameters described and shown below:
- Rx TCP/IP Checksum - Enables receive TCP, IP, and UDP checksum offloading
- Tx TCP/IP Checksum (default) - Enables transmit TCP, IP, and UDP checksum offloading
- Tx/Rx TCP/IP Checksum -
Enables transmit and receive TCP, IP, and UDP checksum offloading
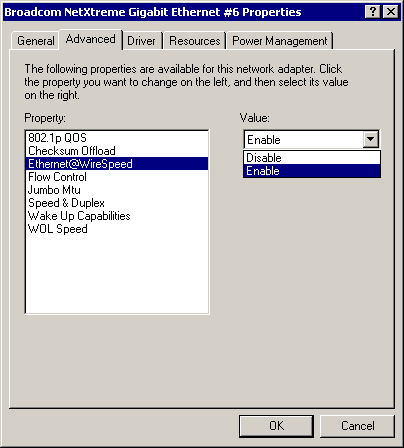
Ethernet@WireSpeed™ Parameter
The Ethernet@WireSpeed parameter enables a 1000BASE-T Ethernet adapter to establish a link at a lower speed when only 2 pairs of wires are available in the cable plant. By default, the adapter is set to Enable. To disable the Ethernet@WireSpeed™ parameter, select Disable from the "Value" drop-down menu as shown below:
- Disable - Disables Ethernet@WireSpeed
- Enable (default) - Enables
Ethernet@WireSpeed
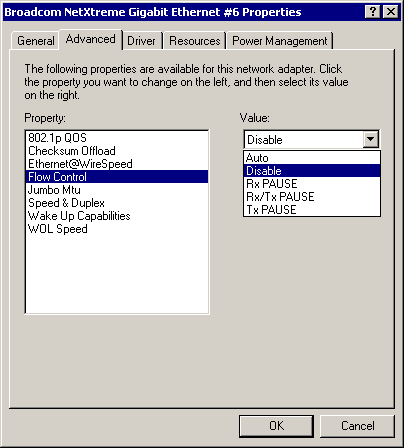
Flow Control Parameter
The Flow Control parameter allows the user to enable or disable the receipt or transmission of PAUSE frames. PAUSE frames enable the adapter and the switch to control the transmit rate. The side that is receiving the PAUSE frame will momentarily stop transmitting. The recommended selection is Disable, which will configure the adapter to ignore PAUSE frames. Disabled by default, to enable Flow Control to receive, transmit, or receive and transmit PAUSE frames, select the appropriate parameter from the Advanced tab "Value" drop-down menu described and shown below.
- Auto - PAUSE frame receipt and transmission is optimized
- Disable - (default) PAUSE frame receipt and transmission is disabled (recommended)
- Rx PAUSE - PAUSE frame receipt is enabled
- Rx/Tx PAUSE - PAUSE frame receipt and transmission is enabled
- Tx PAUSE - PAUSE frame transmission is enabled
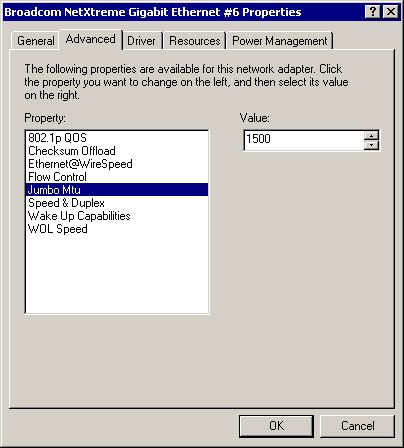
Jumbo Mtu Parameter
The Jumbo Mtu parameter allows the adapter to transmit and receive oversized Ethernet frames that are greater than 1514 but less than 9000 bytes in length. Note that this parameter will require a switch that is able to process large frames.
Set at 1500 bytes by default, to increase the size of the received frames, increment the byte quantity in 500-byte increments from the Advanced tab "Value" counter, shown below.
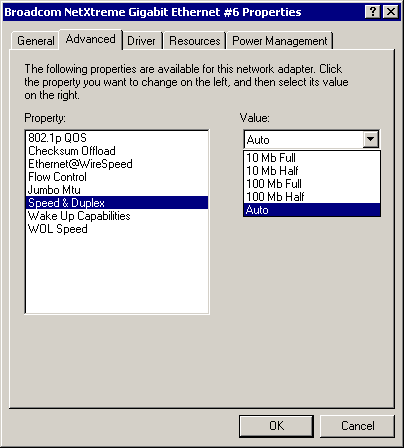
Speed & Duplex Parameter
The Speed & Duplex parameter allows the user to set the connection speed and duplex mode of the network. Note that Duplex Mode allows the adapter to transmit and receive network data simultaneously. The adapter is set to Auto (optimum connection) by default. Set the speed and mode as described and shown below:
- 10 Mb Full - Sets the speed at 10Mbps and mode to Full Duplex
- 10 Mb Half - Sets the speed at 10Mbps and mode to Half Duplex
- 100 Mb Full - Sets the speed at 100Mbps and mode to Full Duplex
- 100 Mb Half - Sets the speed at 100Mbps and mode to Half Duplex
- Auto - (Default) Sets the speed and mode for optimum network connection (recommended)
|
|
NOTE 1Gbps speed is enabled by selecting Auto. |
 |
NOTES Auto is the recommended selection. This selection allows the adapter to dynamically detect the line speed and duplex mode of the network. Whenever the network capability changes, the adapter will automatically detect and adjust to the new line speed and duplex mode. You must ensure that the link partner is also set to Auto. |
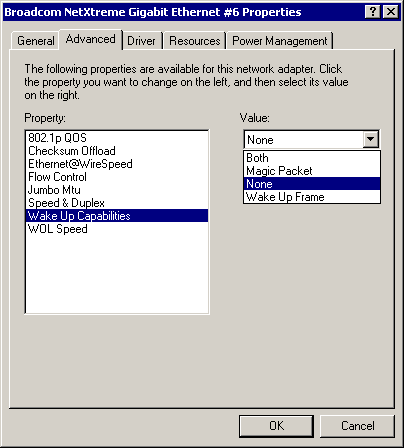
Wake Up Capabilities Parameter
The Wake Up Capabilities parameter allows the user to set the adapter to wake up from a low power mode when it receives a network wake up frame. Two wake up frames are possible: Magic Packet and Wake Up Frame. By default, the adapter is set to Both. To choose the type of frame the adapter will wake up from, select the appropriate Advanced tab parameter from the "Value" drop-down menu as described and shown below:
- Both (both) - Selects both Magic Packet and Wake Up Frame as wake up frames
- Magic Packet - Select Magic Packet as the wake up frame
- None - Selects no wake up frame
- Wake Up Frame
- Selects Wake Up Frame as the wake up frame
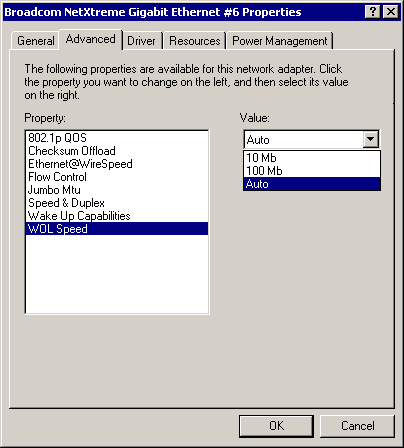
WOL Speed Parameter
The WOL Speed parameter allows the user to select the speed at which the adapter connects to the network during Wake-on-LAN mode. By default, the adapter is set to Auto. Set the speed as described and shown below:
 |
NOTE WOL Speed at 100 Mb is only supported on the 5701 and 5703. |
- 10 Mb - Sets the speed at 10 Mb
- 100 Mb - Sets the speed at 100 Mb
- Auto (default) - Sets the
speed for optimum network connection
Save Settings
- When the adapter parameter configuration is complete, click OK at the Gigabit Ethernet Controller Properties screen to accept the settings.
- If prompted to restart your computer, click Yes. Note that, while it is not necessary to reboot the system for new adapter properties to take effect, rebooting is recommended to reinitialize all registers.
- Verify that the adapter port LEDs operate as described in Table 1 in the Introduction.
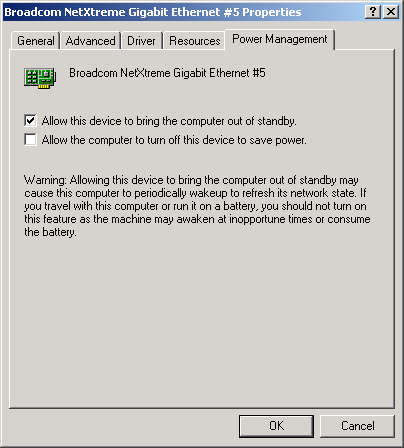
Power Management
Power management specifies whether the operating system turns off the selected device if that device is able to be turned off. If the device is busy doing something, however, (servicing a call, for example), the operating system will not shut down the device. The operating system will try to shut down every possible device only when it is hibernating. Some devices must stay on at all times. If you need the device to stay on at all times, do not check this box.
 |
NOTE To enable the Wake-on LAN in standby mode for the Broadcom NetXtreme™ Gigabit Ethernet adapter you must select the "Allow the device to bring the computer out of standby" checkbox. |
Before physically removing an adapter from your system, first remove the adapter driver software.
- Start your Windows 2000 system and log in. You must have System Administrator privileges to remove the driver software.
- Open the Control Panel and double-click the System icon.
- At the System Properties screen, click the Hardware
tab.
-
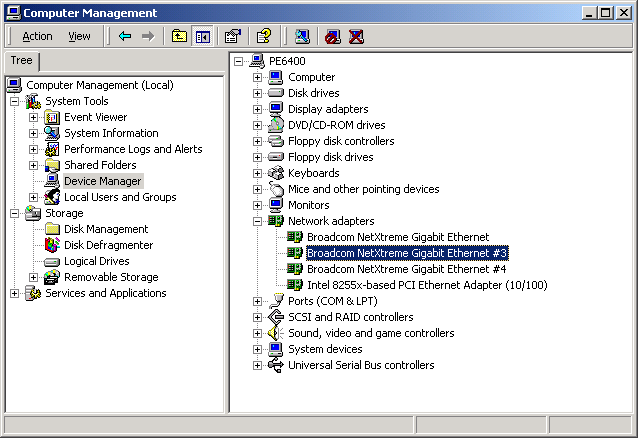
Click Device Manager to display the Computer Management window.
- Expand Network adapters
(click the + sign). All network adapters will display.
- Right-click on the adapter to be removed and select Uninstall.
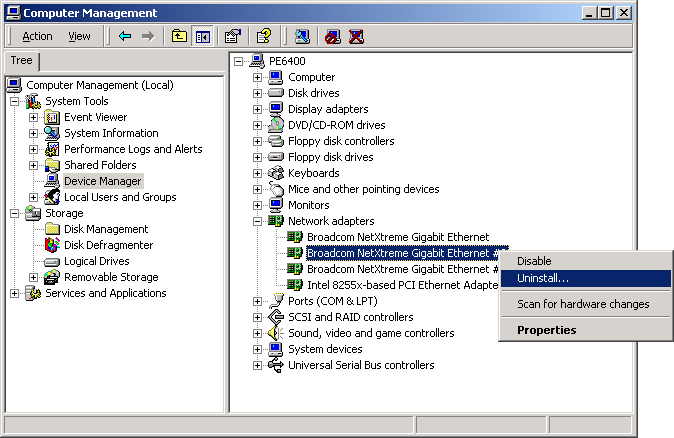
 |
NOTE Not all driver files are removed as part of this procedure. Note that the driver and adapter can be removed via Hot Plug, if supported. |
 |
NOTE The following procedure only applies if BASP was not installed during the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite installation. BASP is typically loaded when you install the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite (BASC). |
To install the Broadcom Advanced Server Program Driver Properties (BASP), do the following:
 |
NOTE Before installing BASP on Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Terminal Services, the command "change user /install" must be issued, otherwise a "User Mode" error will occur. By default, Terminal Services is set to "User Mode" from which applications can not be installed.This command changes the terminal from "User Mode" to "Installation Mode" from which applications can be installed. |
-
Insert the Broadcom CD into the computer's CD-ROM drive.
- Browse the CD to this path: Windows2000\BcmServ,
and double-click on baspinst.exe.
This will install the BASP software and display the following window.
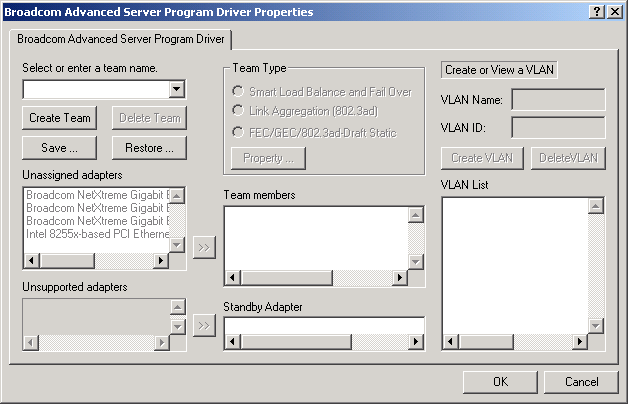
From this menu, you can create a team, see "Creating a Team and Assigning Adapters", or click OK to complete the installation.
To uninstall the Broadcom Advanced Server Program Driver Properties (BASP), do the following:
- Select Start>Settings>Network
and Dial-up Connections. The following screen appears.
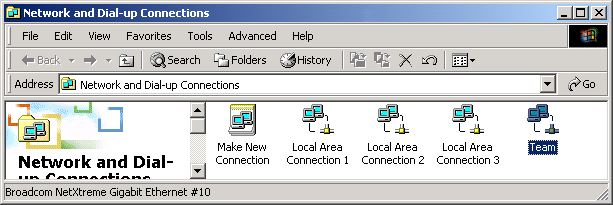
- When the Network and Dial-up Connections window opens,
right-click on any network adapter. This displays the Local Area Connection
Properties window.
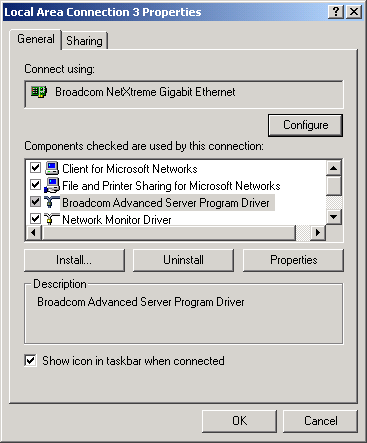
- Highlight the Broadcom Advanced
Server Program Driver, and select Uninstall. The following screen appears.
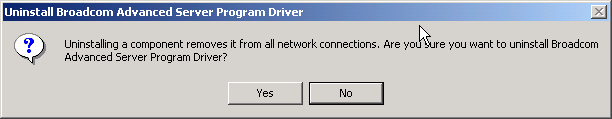
- Select Yes. The following
screen appears.
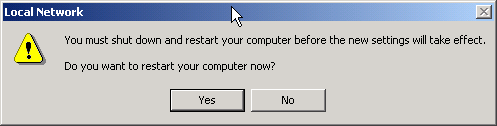
- Select Yes to restart your computer. This completes the uninstall procedure.
Configuring Teaming
 |
NOTE All teaming configurations are performed using the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite (BACS). Refer to "Broadcom Advanced Control Suite" for additional information. |
 |
NOTE To avoid failover problems when using BASP, make sure that the spanning tree protocol is disabled on the switch to which the network adapter is connected. |
Any available adapter can be configured as part of a team. Teaming is a method of grouping multiple adapters to a virtual adapter (bundling multiple adapters to look like a single adapter). The benefit of this approach is load balancing and redundancy, see the "Teaming Overview".
A team is created by selecting the desired adapter(s) from the Unassigned adapters window and moving it to the Team members window. To the outside world this appears to be one adapter. Each member in the Load Balance Member list shares the traffic burden of all members.
The Standby Adapter field is used to permit the selection of one of the team members to handle traffic, should all members in the Team Member list fail. The selected Standby Member will not handle any traffic unless all Load Balance Members fail. When one Team Member (or more) is restored (fail-back), traffic will then be handled by the restored team member(s).
- Configuring Teaming consists of the following tasks:
- Accessing the Broadcom Advanced Server Program Driver Properties (BASP) interface
- Creating teams
- Adding adapters to the teams
- Assigning an IP address to the teams
Each of these tasks are described below, along with procedures on how to delete adapters from a team and to delete a teams.
Accessing the BASP Driver Interface
Use this procedure to access the adapter properties for Teaming Configuration:
- Right-click on the My Network Places icon and
select Properties.

- When the Network and Dial-up Connections window opens,
right-click on any network adapter. This displays the Local Area Connection
Properties window.

- Select Broadcom Advanced Server Program Driver and click
the Properties button. The BASP window is displayed.
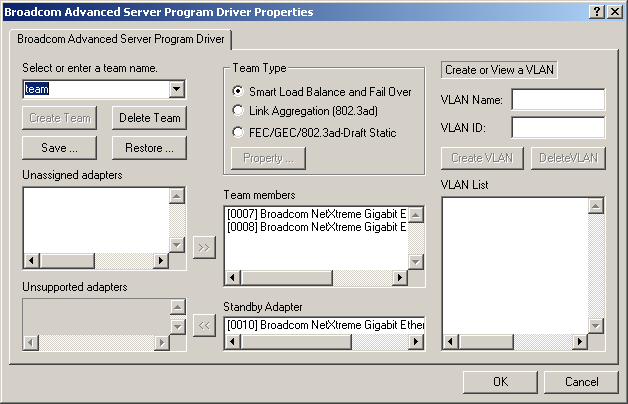
Interface components of the BASP driver properties window are described below:
- Select or enter a team name - This entry field is used to select or enter a team name.
- Unassigned adapters - This list displays all of the Ethernet adapters that are available to be added to a team. Since each adapter can be added to only one team, the adapter is removed from this list once it has been assigned to a team.
- Team Type - Smart Load Balance and Failover: This specifies
a switched independent team for Load balancing and Failover.
FEC/GEC: Also known as general trunking. No standby adapter is allowed when this option is selected.
- Team members - This list displays
all adapters that belong to a selected team.
- Standby Adapter - This
list displays the standby adapter selected for belonging to a selected team.
- VLAN List - This list displays all the VLANs that have been created for the selected team.
Creating a Team and Assigning Adapters
A team is comprised of at least one primary adapter (a standby adapter is optional). Each adapter can belong to only one team. To configure a new team, access the Broadcom Advanced Server Program Driver Properties window and perform the following steps:
- Enter a team name in the "Select or enter a team name" entry field.
- Click Create Team.
- Place an adapter into the team.
- In the Unassigned adapters list, select the adapter(s) that you want to add to the team created in the previous step. Move the selected adapters to the Team members list box using the double arrows.
- When you are finished configuring teams, click OK to accept the changes.
 |
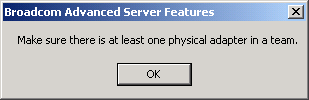
NOTE At least one adapter must be displayed in the Team Members list box. |
- If a team has no adapters assigned, you will be prompted to add an adapter or delete the team.
- Click OK. When team configuration has been correctly performed, one Virtual Team adapter instance will be created for each configured team and will appear along with the other adapters in the Network and Dial-up Connections window.
- Configure the Team IP address if necessary. If other adapters in your system use TCP/IP bindings, the TCP/IP Properties window will open. Configure the IP address and any other necessary TCP/IP configuration for the team.
- Click OK when finished.
Removing Adapters from a Team
To remove an adapter from its assigned team, select the adapter in the Team Members list and press the Delete key or the double-left arrow. The adapter will be removed from the team list and will reappear in the Unassigned adapters list.
Deleting a Team
To delete a configured team and release its assigned adapters, select the team in the team list and click the Delete Team button. The team and all its assigned adapters will be removed from the team list. The released adapters will reappear in the Unassigned adapters list.
 |
NOTE Adapters that are part of a team inherit all the basic configuration properties of the team, including VLANs associated with the team. If you delete a Team, any VLANs configured for that team will also be deleted. |
Configuring VLANs
VLAN Configuration is optional. Before configuring VLANs,
see the "VLAN Overview."
 |
NOTE Adapters that are members of a Team can also be configured to support VLANs. However, VLANs cannot be configured for a team that includes non-Broadcom adapters. |
By default, Ethernet adapters are configured with VLAN support disabled. Up to 64 VLANs can be defined for each team on your server. Configuring VLANs consists of the following tasks:
- Accessing the VLAN configuration interface.
- Adding VLAN(s) to the team(s). This includes assigning a unique identifier and name to each new VLAN.
 |
NOTE When adding 64 VLANs, the
64th VLAN must have a VLAN ID of 0 (63 VLANs are tagged and 1 VLAN is
untagged).
|
Each of these tasks is described below, along with procedures describing how to delete VLANs or modify the properties of a configured VLAN.
Accessing the Adapter VLAN Configuration Interface
Use this procedure to access the adapter properties for VLAN Configuration:
- Open the system Control Panel and double-click Network
and Dial-up Connections icon.

- Double-click any Local Area Connection icon and click
BASP properties. The BASP driver properties window
will display:
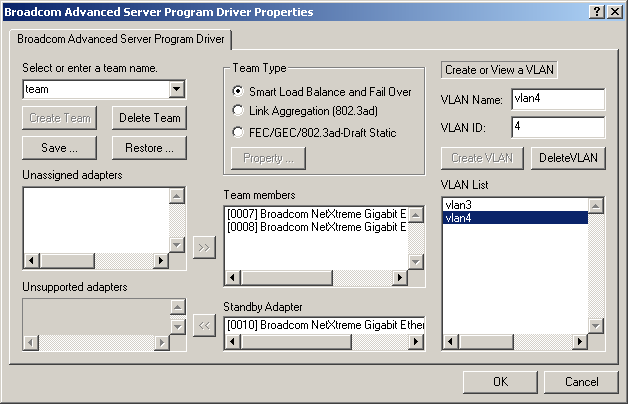
The BASP driver properties window lists the installed adapters and the VLANs configured for each Team. Each VLAN is identified with a unique identifier number and name that will only appear in this window. Interface components of the VLAN Configuration window are described in detail below:
- VLAN List - This list displays all of the VLANs that have been configured.
- Control Buttons - There are two control buttons: Create VLAN, and Delete VLAN. These buttons are used for creating and deleting VLANs.
Adding a VLAN
You can define up to 64 VLANs per team. To configure a new VLAN, perform the following steps:
- From the BASP window, select the team to which you want to add a VLAN.
- Enter a VLAN Name and VLAN ID, then click the Create VLAN button.
- When you are finished adding VLANs to this team, click OK. A new virtual adapter is created for each VLAN.
 |
NOTE To maintain optimum adapter
performance, your system should have 64 MB of system memory for each
eight VLANs created per adapter. When adding VLANs to a single adapter,
a one-adapter team must be created.
|
Deleting a VLAN
 |
NOTE Adapters that are part of a team inherit all the basic configuration properties of the team, including VLANs associated with the team. If you delete a team, any VLANs configured for that team will also be deleted. |
To delete a configured VLAN, perform the following steps:
- From the BASP window, select the VLAN you want to delete and click the Delete VLAN button. The selected VLAN will be deleted from the VLAN list window.
- When you are finished deleting VLANs, click the OK button to accept the changes.
Save and Restore Configuration
This feature is used to save the current configuration in case of a system crash. The restore feature allows the user to apply the previous configuration. Save and restore VLAN and Adapter configurations as shown below:
Save a VLAN Configuration
To save a configuration:
- Click Save at the Broadcom
Advanced Server Program Driver Properties screen.

- At the Save Configuration screen, enter the path and
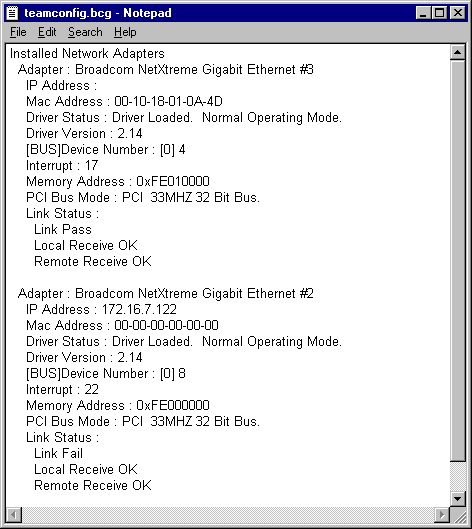
filename of the configuration to be saved (e.g., C:\temp\teamconfig.bcg).
The resulting file will be a text file that can be viewed with a text editor as shown below. Note that only the team configuration information is shown.
Restore a VLAN Configuration
- To restore a configuration, click
Restore at the Broadcom Advanced Server Program Driver Properties screen.

- At the information screen, click
Yes to erase the current configuration and replace it with a saved
configuration. Note that if the current configuration has not been saved,
it will be lost.
- At the Restore Configuration screen,
enter the path and filename of the configuration to be restored in the "Restore
the configuration file window" and click OK.

The saved configuration will be restored.