This chapter provides the following information:
 Broadcom
Advanced Server Program Overview
Broadcom
Advanced Server Program Overview
 Broadcom
Advanced Server Program for Windows .NET
Broadcom
Advanced Server Program for Windows .NET
 Broadcom
Advanced Server Program for Windows 2000
Broadcom
Advanced Server Program for Windows 2000
 Broadcom
Advanced Server Program for Windows NT
Broadcom
Advanced Server Program for Windows NT
 Broadcom
Advanced Server Program for Novell NetWare
Broadcom
Advanced Server Program for Novell NetWare
 Broadcom
Advanced Control Suite
Broadcom
Advanced Control Suite
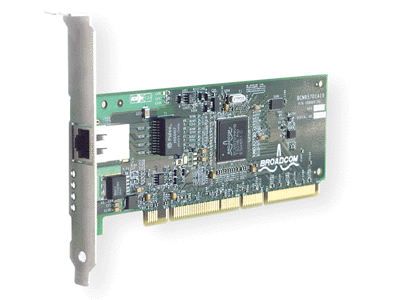
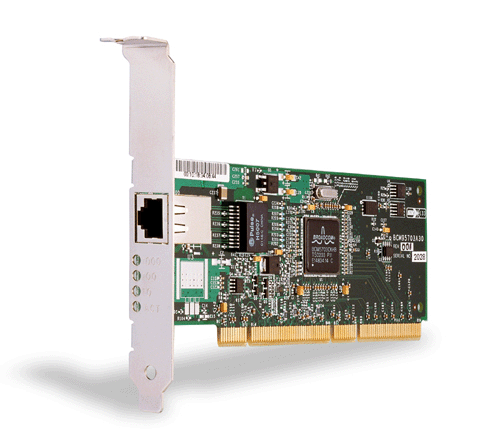
The Broadcom NetXtreme™ Gigabit Ethernet Adapter connects a PCI or PCI-X (5701, 5702, 5703) compliant server or workstation to a Gigabit Ethernet network. This adapter incorporates a technology that transfers data at a maximum rate of one gigabit per second�10 times the rate of Fast Ethernet adapters.
The Gigabit Ethernet Adapter targets the increased congestion experienced at the backbone and server in today�s networks, and provides a future upgrade path for high-end workstations that require more bandwidth than Fast Ethernet can provide.
Figure 1. The Broadcom NetXtreme™ Gigabit Ethernet Adapter (5701 shown)
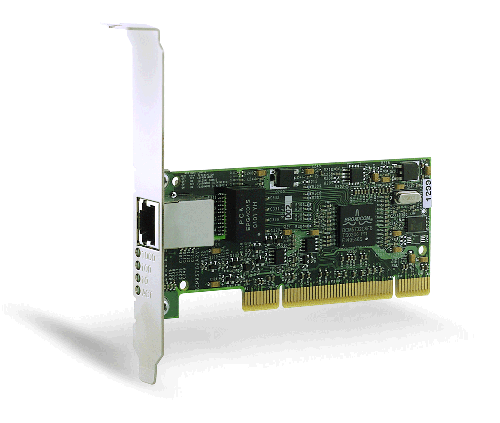
Figure 2. The Broadcom NetXtreme™ Gigabit Ethernet Adapter (5702 shown)
Figure 3. The Broadcom NetXtreme™ Gigabit Ethernet Adapter (5703C shown)
Contents of Your Shipment
Included with your adapter are the following:
- Antistatic bag (used for protecting the adapter when stored or shipped). Keep the adapter in its packaging until ready for installation.
- CD-ROM with Gigabit Ethernet driver software and documentation.
Inform your network supplier of any missing or damaged items. If you need to return the adapter, you must pack it in the original (or equivalent) packing material or the warranty will be voided.
Features
The following is a list of the Broadcom NetXtreme™ Gigabit Ethernet Adapter features for all supported operating systems:
- Gigabit Ethernet (IEEE 802.3-1999)
- Logical Link Control (IEEE 802.2)
- Flow Control (IEEE 802.3X)
- Standard Ethernet frame size (1518 bytes)
- TBI (SERDES style) Transceiver interfaces
- Jumbo frames (9KB) - Netware 5.1 does not support Jumbo Frames
- Layer 2 Priority Encoding (802.1P)
- Dual, High-Speed On-Chip RISC Processors
- Adaptive interrupt frequency
- Programmable rule checking and frame classification
- Up to 16 classes of service (CoS) (4 if no external memory)
- Up to 16 Distribution Rings (4 if no external memory)
- Integrated 96KB Frame Buffer Memory
- GMI/MII Management Interface
- 16M external SSRAM address space
- Selectable memory protection for external (on-board) memory
- Statistics for SNMP MIB II, Ethernet like MIB, and Ethernet MIB (802.3z, Clause 30)
- Four unique MAC unicast addresses
- Support for multicast addresses via 128 bits hashing hardware function
- Serial EEPROM (5703 uses Flash)
- Support for PXE available (tested against the following programs: Linux Red Hat PXE server, Windows 2000, Intel APITEST, DOS UNDI, 3Com boot server)
- JTAG support
- PCI v2.2 32/64-Bit, 33/66 MHz Bus Interface (5700, 5701, 5703)
- PCI-X v1.0 64-bit 100 MHz Bus Interface (5701, 5703)
- PCI Power Management Interface (v1.1)
- PCI Hot Plug (IBM, Compaq, Dell, and Microsoft)
- ACPI and Wake-on-LAN Support
- 64 Bit BAR support
- 3.3 V/1.8 V CMOS with 5V tolerant I/Os
Physical Description
The faceplate on the 10/100/1000BASE-T adapter provides an RJ-45 connector for connecting the adapter to another network device.

Figure 4. Broadcom NetXtreme™ Gigabit Ethernet Adapter Faceplate
The adapter has four LEDs, one for each port speed option (10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, and 1000 Mbps), and one for Activity. The three port speed LEDs indicate active links, and the ACT LED indicates data transfer status. Once the adapter is installed and the cables are connected properly, the appropriate speed LED is lit and the ACT LED is on if data traffic is present.
Once the adapter hardware has been properly installed on
your system, the LEDs indicate the following adapter states:
Table 1. Gigabit Ethernet Port LED Status
| LED | State | Description |
| 1000 | On | Good Gigabit Ethernet link. |
| Off | No 1000 Mbps link; possible link at different speed, possible bad cable, bad connector, or configuration mismatch. | |
| 100 | On | Good 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet link. |
| Off | No 100 Mbps link; possible link at different speed, possible bad cable, bad connector, or configuration mismatch. | |
| 10 | On | Good 10 Mbps Fast Ethernet link. |
| Off | No 10 Mbps link; possible link at different speed, possible bad cable, bad connector, or configuration mismatch. | |
| ACT | Blinking | Brief bursts of data detected on the port. |
| On | Streams of data detected on the port. | |
| Off | No data detected on the port. |
Broadcom Advanced Server Program (BASP) Overview
Introduction
BASP is a Broadcom intermediate software
driver for Windows .NET, Windows 2000, Windows NT, NetWare, and Linux, that
provides load-balancing, fault-tolerance, and VLAN features. These features
are provided by creating teams (virtual adapters) that consist of multiple NIC
interfaces. A team can consist of one to eight NIC interfaces and each interface
can be designated primary or standby*. All primary interfaces in a team will
participate in Load-balancing operations by sending and receiving a portion
of the total traffic. Standby interfaces will take over in the event that all
primary interfaces have lost their links. VLANs can be added to a team to allow
multiple VLANs with different VLAN IDs. A virtual adapter is created for each
VLAN added. Load-balancing and fault-tolerance features will work with any third
party's NIC adapters. VLANs only work with Broadcom NIC
adapters.
 |
NOTE - *Standby can only be used in Smart Load-Balance mode (see below). |
Limitations
Smart Load-Balance (SLB) is a protocol specific scheme and the level of support for IP, IPX, and other protocols are listed below.
Failover/Failback - All Broadcom
Failover/Failback - Multivendor
IP
IPX
NetBui
IP
IPX
NetBui
W2K
Y
Y
Y
Y
N
N
NT 4.0
Y
Y
Y
Y
N
N
NW 5.x/6.0
Y
Y
N/S
Y
N
N/S
LX 7.2/7.3
Y
N/S
N/S
Y
N/S
N/S
Load Balance - All Broadcom
Load Balance - Multivendor
IP
IPX
NetBui
IP
IPX
NetBui
W2K
Y
Y
N
Y
Y
N
NT 4.0
Y
Y
N
Y
Y
N
NW 5.x/6.0
Y
Y
N/S
Y
Y
N/S
LX 7.2/7.3
Y
N/S
N/S
Y
N/S
N/S
*Third party adapters must be NICE patched or NESL compliant to be fault tolerant and load balance in a multivendor team in Linux and Netware, respectively.
Smart Load-balance (SLB) mode works with all Ethernet switches without configuring the switch ports to any special trunking mode. Only IP traffic will be load-balanced in both inbound and outbound directions. IPX traffic will be load-balanced in outbound direction only. Other protocol packets will be sent and received through one primary NIC only. Fault-tolerance for non-IP traffic is only supported using Broadcom NICs. The Generic Trunking mode requires the Ethernet switch to support some form of port trunking mode (e.g. Cisco's Gigabit EtherChannel or other switch vendor's link aggregation mode). This mode is protocol-independent and all traffic should be load-balanced and fault-tolerant.
 |
NOTE � Broadcom recommends disabling the spanning tree protocol at the switch when using BASP. This will minimize the downtime due to spanning tree loop determination when failing over. |
Broadcom Advanced Server Program for Windows .NET
The following options are supported under Windows .NET. Refer to "Windows .NET Driver Software," for additional information.
Failover and Load Balance
- Adapter teaming for failover heterogeneous support for released 3Com® 10/100 server adapters, released Intel® 10/100 server adapters, released Intel® 1000BASE-SX server adapters, Intel® Pro 1000/T server adapters, and Intel® 82559 and 82544 LAN on Motherboards (LOMs)
- Smart Load Balance™
- Generic Link Aggregation (GEC/FEC, Open trunk)
- Link aggregation (IEEE 802.3ad)
Virtual LAN (VLANs)
- Up to 64 VLANs (63 tagged and 1 untagged) per adapter using IEEE 802.1Q-1988 tagging. VLANs only work with Broadcom NIC adapters.
Offloading
- IP,TCP/UDP checksum
- Support for segmentation of large TCP packets
Power Management
- Wake on LAN (magic packet, specific pattern) at 10/100 Mbps only
 |
NOTE � Adapter speed connection when the system is down waiting for a wake up signal is either 10Mbs or 100Mbs, but can return to 1000 when the system is up and running if connected to a 1000 Mbs capable switch. Systems intending to use WOL should be connected to a switch capable of both 1000 and 10 or 100 speeds. |
PCI Hot plug
- Support Microsoft
Broadcom Advanced Server Program for Windows 2000
The following options are supported under Windows 2000. Refer to "Windows 2000 Driver Software," for additional information.
Failover and Load Balance
- Adapter teaming for failover (heterogeneous support for released 3Com® 10/100 server adapters, released Intel® 10/100 server adapters, Intel® Pro 1000/T server adapters, and Intel® 82559 and 82544 LAN on Motherboards (LOMs)
- Smart Load Balance™
- Generic Link Aggregation (GEC/FEC, Open trunk)
- Link aggregation (IEEE 802.3ad)
Virtual LAN (VLANs)
- Up to 64 VLANs (63 tagged and 1 untagged) per adapter using IEEE 802.1Q-1988 tagging. VLANs only work with Broadcom NIC adapters.
Offloading
- IP,TCP/UDP checksum
- Support for segmentation of large TCP packets
Power Management
- Wake on LAN (magic packet, specific pattern) at 10/100 Mbps only
 |
NOTE � Adapter speed connection when the system is down waiting for a wake up signal is either 10Mbs or 100Mbs, but can return to 1000 when the system is up and running if connected to a 1000 Mbs capable switch. Systems intending to use WOL should be connected to a switch capable of both 1000 and 10 or 100 speeds. |
PCI Hot plug
- Support Microsoft
Broadcom Advanced Server Program for Windows NT 4.0
The following options are supported under Windows NT. Refer to "Windows NT 4.0 Driver Software" for additional information.
Failover and Load Balance
- Adapter teaming for failover (heterogeneous support for released 3Com® 10/100 server adapters, released Intel® 10/100 server adapters, and Intel® 82559 and 82544 LAN on Motherboards (LOMs)
- Smart Load Balance™
- Generic Link Aggregation (GEC/FEC, Open trunk)
- Link aggregation (IEEE 802.3ad)
Virtual LAN (VLANs)
- Up to 64 VLANs (63 tagged and 1 untagged) per adapter using IEEE 802.1Q-1988 tagging. VLANs only work with Broadcom NIC adapters.
Power Management
- Wake on LAN (magic packet, specific pattern) at 10/100 Mbps only (5701, 5703)
 |
NOTE � Adapter speed connection when the system is down waiting for a wake up signal is either 10Mbs or 100Mbs, but can return to 1000 when the system is up and running if connected to a 1000 Mbs capable switch. Systems intending to use WOL should be connected to a switch capable of both 1000 and 10 or 100 speeds. |
PCI Hot plug
- Support Compaq, Dell, and IBM
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite
The Broadcom Advanced Control Suite is a graphics user interface with the following functions. Refer to "Broadcom Advanced Control Suite " for additional information.
- Vital Sign
� The Vital Sign screen allows
you to view vital adapter information, network status, and network connectivity.
Active Adapters are listed.
- Diagnostics
� The Diagnostics screen
allows you to view information for Broadcom-only adapters. This function is
used to test the Broadcom network interface card or Broadcom LOM.
- Cable Analysis
� From the Cable Analysis
screen the user can monitor conditions of an Ethernet CAT5 cable connection
within a cable plant in an Ethernet network. The software detects various
cable conditions such as cable lengths between two given nodes, cable pair
breakage, cable pair polarity, and data skew between cable pairs.
- Load Balance/Virtual LAN
� The Load Balance/Virtual
LANs screen allows you to configure advanced features. Any available adapter
can be configured as part of a team.
- Statistics � The Statistics screen allows you to view traffic statistics for both Broadcom and non-Broadcom adapters. Statistical values and coverage is more comprehensive for Broadcom than for non-Broadcom adapters.
Broadcom Advanced Server Program for Novell NetWare
The following options are supported under Novell NetWare. Refer to "NetWare Driver Software," for additional information.
Failover and Load Balance
- Adapter teaming for failover (heterogeneous support for released 3Com® 10/100 server adapters, Intel® 10/100 server adapters, and Intel® 82559 and 82544 LAN on Motherboards (LOMs)
- Smart Load Balance™
- Generic Link Aggregation (GEC/FEC, Open trunk)
- Link aggregation (IEEE 802.3ad)
NESL Compliance
For optimum fault tolerance and recovery operations, BASP.LAN relies on the NIC drivers to generate NESL (NetWare Event Service Layer) events during link changes and other failure events. NESL is an optional feature in the ODI driver specification and not all drivers support it. For NESL events to propagate properly to BASP.LAN, ODINEB.NLM must be loaded before the NESL compliant ODI drivers.
Do the following to check if a NIC driver supports NESL events. Load BASP.LAN and create a team by binding the NIC adapter to the virtual slot (See instructions and examples below). In the "Virtual Adapter X Team Members" screen of the BASP.LAN's menu interface, the Link status of all bound NIC adapters are shown. Disconnect or connect the NIC adapter's cable and the link status shown on the screen should change immediately if the NIC driver supports NESL events.
Virtual LAN (VLANs)
- Up to 64 VLANs (63 tagged and 1 untagged) per adapter using IEEE 802.1Q-1988 tagging (64 is the maximum configurable, although 32 is the maximum operable). VLANs only work with Broadcom or Alteon® NIC adapters.
Offloading
- IP, TCP/UDP checksum � NetWare 5.0 or greater only
Power Management
- Wake on LAN (magic packet, specific pattern) at 10/100 Mbps only (5701, 5703)
PCI Hot plug
- Support Dell
Broadcom Advanced Server Program for Linux
The following options are supported under Linux. Refer to "Linux Driver Software" for additional information.
Failover and Load Balance
-
SLB mode works with all Ethernet switches without configuring the switch ports to any special trunking mode. Only IP traffic will be load-balanced in both inbound and outbound directions.
-
Generic trunking mode does not require NICE and can work with any NIC, however, it requires the Ethernet switch to support the technology and be properly configured. This mode is protocol-independent and all traffic should be load-balanced and fault-tolerant.
-
802.3ad mode requires NICE drivers and Ethernet switches supporting IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation. This mode is protocol-independent and all traffic should be load-balanced and fault-tolerant. All the physical interfaces in the 802.3ad teams are defaulted to be LACP active. A 802.3ad team requires all the member NICs support NICE. All the member NICs, once in the 802.3ad team, will be set with the same MAC address.
Virtual LAN (VLAN)
- VLANs can be added to a team to allow multiple VLANs with different VLAN IDs. A virtual device is created for each VLAN added.
Power Management
- Wake on LAN (magic packet, specific pattern) at 10/100 Mbps only (5701, 5703)
 |
NOTE � Adapter speed connection when the system is down waiting for a wake up signal is either 10Mbs or 100Mbs, but can return to 1000 when the system is up and running if connected to a 1000 Mbs capable switch. Systems intending to use WOL should be connected to a switch capable of both 1000 and 10 or 100 speeds. |
Creating a Driver Disk
Create driver disks using the Broadcom MakeDisk utility (setup.exe file). This utility runs under Windows, and allows you to create disks with the following drivers:
- Windows NT
- Windows 2000
- Windows .NET 32 Bit
- Window .NET 64 Bit
- Netware
- DOS ODI
- Windows NT BASP
- Windows 2000 BASP
- Netware BASP
To create a driver disk, perform the following:
- Insert a 3.5" disk into floppy drive A (default) or B.
- Insert the Dell CD-ROM into your system's CD-ROM drive.
- If the CD-ROM does not autorun, then run the makedisk file (\MakeDisk\setup.exe).
- Follow the
menu commands to the Driver Selection screen.
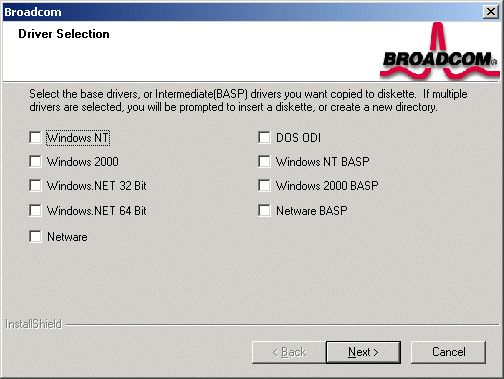
-
Select (check) the driver or drivers of choice. Note that selecting multiple drivers will result in creating multiple disks.
-
Click Next. The Setup Needs the Next Disk screen will appear.
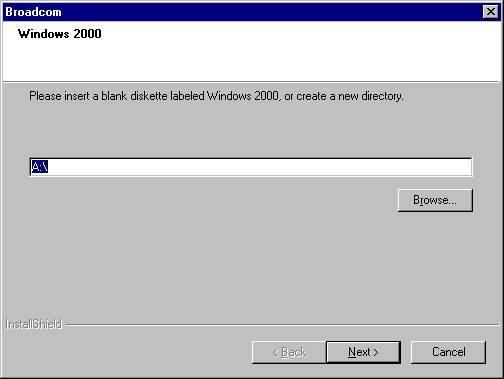
- Ensure that a diskette
is in the disk drive and click OK. The selected driver will be installed.
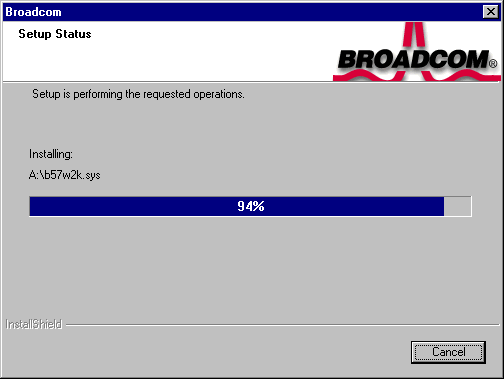
-
If more than one driver was selected, the Setup Needs the Next Disk screen will appear again. Insert another diskette and click OK.

- When all driver diskettes
have been created, an information screen will appear confirming that the diskettes
were successfully created. Click OK.