Introduction to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud
Topics
What Is Amazon EC2?
Amazon EC2 is a web service that enables you to launch and manage server instances in Amazon's data centers using APIs or available tools and utilities. You can use Amazon EC2 server instances at any time, for as long as you need, and for any legal purpose. If you need 100 instances for a two-day research project, sure. If you need a group of instances that can be scaled up and down to meet the traffic fluctuations of your Facebook application, no problem.
Instances are available in different sizes and configurations. This allows us to provide different instance types that you can use to meet specific needs. For example, you might want to use an m1.small instance (one Amazon EC2 Compute Unit) as a web server, an m1.xlarge instance (eight Amazon EC2 Compute Units) as a database server, or an extra large High-CPU instance (twenty Amazon EC2 Compute Units) for processor intensive applications.
What makes Amazon EC2 different is that you use only the capacity that you need. This eliminates your need to make large and expensive hardware purchases, reduces the need to forecast traffic, and enables you to immediately deal with changes in requirements or spikes in popularity related to your application or service.
Service Highlights
-
Elastic—Amazon EC2 enables you to increase or decrease capacity within minutes, not hours or days. You can commission one, hundreds or even thousands of server instances simultaneously. Of course, because this is all controlled with web service APIs, your application can automatically scale itself up and down depending on its needs.
-
Completely Controlled—You have complete control of your instances. You have root access to each one, and you can interact with them as you would any machine. You can stop your instance while retaining the data on your boot partition and subsequently restart the same instance using web service APIs. You also have access to console output of your instances.
-
Flexible—You have the choice of multiple instance types, operating systems, and software packages. Amazon EC2 allows you to select a configuration of memory, CPU, and instance storage, and the boot partition size that is optimal for your choice of operating system and application. For example, your choice of operating systems includes numerous Linux distributions, Microsoft Windows Server and OpenSolaris.
-
Designed for use with other Amazon Web Services—Amazon EC2 works in conjunction with Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), Amazon SimpleDB and Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) to provide a complete solution for computing, query processing and storage across a wide range of applications.
-
Reliable—Amazon EC2 offers a highly reliable environment where replacement instances can be rapidly and predictably commissioned. The service runs within Amazon’s proven network infrastructure and data centers. The Amazon EC2 Service Level Agreement commitment is 99.95% availability for each Amazon EC2 Region.
-
Secure—Amazon EC2 provides numerous mechanisms for securing your compute resources.
-
Amazon EC2 includes web service interfaces to configure firewall settings that control network access to and between groups of instances.
-
When launching Amazon EC2 resources within Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), you can isolate your compute instances by specifying the IP range you wish to use, and connect to your existing IT infrastructure using industry-standard encrypted IPsec VPN.
-
-
Inexpensive—Amazon EC2 passes on to you the financial benefits of Amazon’s scale. You pay a very low rate for the compute capacity you actually consume.
-
On-Demand Instances—On-Demand Instances let you pay for compute capacity by the hour with no long-term commitments. This frees you from the costs and complexities of planning, purchasing, and maintaining hardware and transforms what are commonly large fixed costs into much smaller variable costs. On-Demand Instances also remove the need to buy "safety net" capacity to handle periodic traffic spikes.
-
Reserved Instances—Reserved Instances give you the option to make a low, one-time payment for each instance you want to reserve and in turn receive a significant discount on the hourly usage charge for that instance. After the one-time payment for an instance, that instance is reserved for you, and you have no further obligation; you may choose to run that instance for the discounted usage rate for the duration of your term, or when you do not use the instance, you will not pay usage charges on it.
-
Features
Amazon EC2 provides a number of powerful features for building scalable, failure resilient, enterprise class applications, including:
Features for Building Failure Resilient Applications
-
Amazon Elastic Block Store—Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) offers persistent storage for Amazon EC2 instances. Amazon EBS volumes provide off-instance storage that persists independently from the life of an instance. Amazon EBS volumes are highly available, highly reliable volumes that can be leveraged as an Amazon EC2 instance’s boot partition or attached to a running Amazon EC2 instance and are exposed as a standard block devices. When used as a boot partition, Amazon EC2 instances can be stopped and subsequently restarted, enabling you to only pay for the storage resources used while maintaining your instance’s state. Amazon EBS volumes offer greatly improved durability over local Amazon EC2 instance stores, as Amazon EBS volumes are automatically replicated on the backend (in a single Availability Zone). For those wanting even more durability, Amazon EBS provides the ability to create point-in-time consistent snapshots of your volumes that are then stored in Amazon S3, and automatically replicated across multiple Availability Zones. These snapshots can be used as the starting point for new Amazon EBS volumes, and can protect your data for long term durability. You can also easily share these snapshots with co-workers and other AWS developers.
-
Multiple Locations—Amazon EC2 provides the ability to place instances in multiple locations. Amazon EC2 locations are composed of Regions and Availability Zones. Availability Zones are distinct locations that are engineered to be insulated from failures in other Availability Zones and provide inexpensive, low latency network connectivity to other Availability Zones in the same Region. By launching instances in separate Availability Zones, you can protect your applications from failure of a single location. Regions consist of one or more Availability Zones, are geographically dispersed, and will be in separate geographic areas or countries. The Amazon EC2 Service Level Agreement commitment is 99.95% availability for each Amazon EC2 Region. Amazon EC2 is currently available in two three Regions: the US-East (Northern Virginia) Region and the US-West (Northern California) Region in the United States, and the EU (Ireland) Region in Europe.
-
Elastic IP Addresses—Elastic IP addresses are static IP addresses designed for dynamic cloud computing. An Elastic IP address is associated with your account not a particular instance, and you control that address until you choose to explicitly release it. Unlike traditional static IP addresses, however, Elastic IP addresses allow you to mask instance or Availability Zone failures by programmatically remapping your public IP addresses to any instance in your account. Rather than waiting on a data technician to reconfigure or replace your host, or waiting for DNS to propagate to all of your customers, Amazon EC2 enables you to engineer around problems with your instance or software by quickly remapping your Elastic IP address to a replacement instance.
-
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud—Amazon VPC is a secure and seamless bridge between a company’s existing IT infrastructure and the AWS cloud. Amazon VPC enables enterprises to connect their existing infrastructure to a set of isolated AWS compute resources via a Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection, and to extend their existing management capabilities such as security services, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to include their AWS resources.
-
Amazon CloudWatch—Amazon CloudWatch is a web service that provides monitoring for AWS cloud resources, starting with Amazon EC2. It provides you with visibility into resource utilization, operational performance, and overall demand patterns—including metrics such as CPU utilization, disk reads and writes, and network traffic. To use Amazon CloudWatch, simply select the Amazon EC2 instances that you’d like to monitor; within minutes, Amazon CloudWatch will begin aggregating and storing monitoring data that can be accessed using web service APIs or Command Line Tools.
-
Auto Scaling—Auto Scaling allows you to automatically scale your Amazon EC2 capacity up or down according to conditions you define. With Auto Scaling, you can ensure that the number of Amazon EC2 instances you’re using scales up seamlessly during demand spikes to maintain performance, and scales down automatically during demand lulls to minimize costs. Auto Scaling is particularly well suited for applications that experience hourly, daily, or weekly variability in usage. Auto Scaling is enabled by Amazon CloudWatch and available at no additional charge beyond Amazon CloudWatch fees.
-
Elastic Load Balancing—Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple Amazon EC2 instances. It enables you to achieve even greater fault tolerance in your applications, seamlessly providing the amount of load balancing capacity needed in response to incoming application traffic. Elastic Load Balancing detects unhealthy instances within a pool and automatically reroutes traffic to healthy instances until the unhealthy instances have been restored. You can enable Elastic Load Balancing within a single Availability Zone or across multiple zones for even more consistent application performance. Amazon CloudWatch can be used to capture a specific Elastic Load Balancer’s operational metrics, such as request count and request latency, at no additional cost beyond Elastic Load Balancing fees.
Popular Uses for Amazon EC2
Although the applications for Amazon EC2 are only limited by your ingenuity, the following is a list of popular uses for Amazon EC2:
-
Scalable Applications—You can build a scalable application that shrinks or expands to meet your current demands.
This can help you use only the compute resources that you need and can help you respond to events where a mention on a popular news site can result in a dramatic spike in traffic.
-
Temporary Events—You can use Amazon EC2 for temporary solutions and one-off events that would require you to maintain compute resources that are normally idle.
This includes hosting conferences in virtual worlds, live blogging, distribution of newly released media, and short-term promotional web sites.
-
Batch Processing—You can use Amazon EC2 for projects that require massive compute resources which would be expensive to build on your own.
This includes video and image processing, financial data processing, and science and research applications.
-
Fault Resilient Applications—You can build an application across multiple availability zones which will be protected against the loss of an entire physical location.
Amazon EC2 Charges
With Amazon EC2, you don’t have to pay upfront fees, you don’t have to commit to a fixed amount of bandwidth, and you don’t have to meet any minimum usage requirements. As with other AWS services, you only pay for what you use.
The following figure summarizes how you are charged for using Amazon EC2.
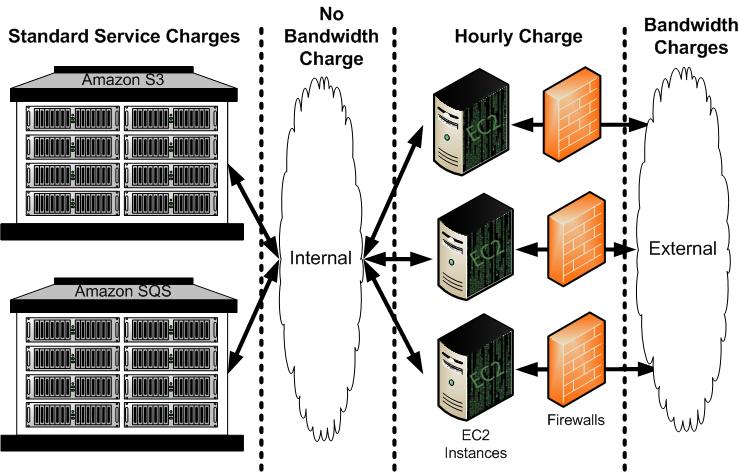
For detailed information on Amazon EC2 charges, go to the Amazon EC2 Product Page.