| Home | All Classes | Main Classes | Annotated | Grouped Classes | Functions |  |
QRegion Class Reference
The QRegion class specifies a clip region for a painter. More...
#include <qregion.h>
Public Members
- enum RegionType { Rectangle, Ellipse }
- QRegion ()
- QRegion ( int x, int y, int w, int h, RegionType t = Rectangle )
- QRegion ( const QRect & r, RegionType t = Rectangle )
- QRegion ( const QPointArray & a, bool winding = FALSE )
- QRegion ( const QRegion & r )
- QRegion ( const QBitmap & bm )
- ~QRegion ()
- QRegion & operator= ( const QRegion & r )
- bool isNull () const
- bool isEmpty () const
- bool contains ( const QPoint & p ) const
- bool contains ( const QRect & r ) const
- void translate ( int dx, int dy )
- QRegion unite ( const QRegion & r ) const
- QRegion intersect ( const QRegion & r ) const
- QRegion subtract ( const QRegion & r ) const
- QRegion eor ( const QRegion & r ) const
- QRect boundingRect () const
- QMemArray<QRect> rects () const
- const QRegion operator| ( const QRegion & r ) const
- const QRegion operator+ ( const QRegion & r ) const
- const QRegion operator& ( const QRegion & r ) const
- const QRegion operator- ( const QRegion & r ) const
- const QRegion operator^ ( const QRegion & r ) const
- QRegion & operator|= ( const QRegion & r )
- QRegion & operator+= ( const QRegion & r )
- QRegion & operator&= ( const QRegion & r )
- QRegion & operator-= ( const QRegion & r )
- QRegion & operator^= ( const QRegion & r )
- bool operator== ( const QRegion & r ) const
- bool operator!= ( const QRegion & r ) const
- HRGN handle () const
Related Functions
- QDataStream & operator<< ( QDataStream & s, const QRegion & r )
- QDataStream & operator>> ( QDataStream & s, QRegion & r )
Detailed Description
The QRegion class specifies a clip region for a painter.
QRegion is used with QPainter::setClipRegion() to limit the paint area to what needs to be painted. There is also a QWidget::repaint() that takes a QRegion parameter. QRegion is the best tool for reducing flicker.
A region can be created from a rectangle, an ellipse, a polygon or a bitmap. Complex regions may be created by combining simple regions using unite(), intersect(), subtract() or eor() (exclusive or). You can move a region using translate().
You can test whether a region isNull(), isEmpty() or if it contains() a QPoint or QRect. The bounding rectangle is given by boundingRect().
The function rects() gives a decomposition of the region into rectangles.
Example of using complex regions:
void MyWidget::paintEvent( QPaintEvent * )
{
QPainter p; // our painter
QRegion r1( QRect(100,100,200,80), // r1 = elliptic region
QRegion::Ellipse );
QRegion r2( QRect(100,120,90,30) ); // r2 = rectangular region
QRegion r3 = r1.intersect( r2 ); // r3 = intersection
p.begin( this ); // start painting widget
p.setClipRegion( r3 ); // set clip region
... // paint clipped graphics
p.end(); // painting done
}
QRegion is an implicitly shared class.
Due to window system limitations, the width and height of a region is limited to 65535 on Unix/X11.
See also QPainter::setClipRegion(), QPainter::setClipRect(), Graphics Classes and Image Processing Classes.
Member Type Documentation
QRegion::RegionType
Specifies the shape of the region to be created.
- QRegion::Rectangle - the region covers the entire rectangle.
- QRegion::Ellipse - the region is an ellipse inside the rectangle.
Member Function Documentation
QRegion::QRegion ()
Constructs a null region.
See also isNull().
QRegion::QRegion ( int x, int y, int w, int h, RegionType t = Rectangle )
Constructs a rectangular or elliptic region.If t is Rectangle, the region is the filled rectangle (x, y, w, h). If t is Ellipse, the region is the filled ellipse with center at (x + w / 2, y + h / 2) and size (w ,h ).
QRegion::QRegion ( const QRect & r, RegionType t = Rectangle )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It behaves essentially like the above function.Create a region based on the rectange r with region type t.
If the rectangle is invalid a null region will be created.
See also QRegion::RegionType.
QRegion::QRegion ( const QPointArray & a, bool winding = FALSE )
Constructs a polygon region from the point array a.If winding is TRUE, the polygon region is filled using the winding algorithm, otherwise the default even-odd fill algorithm is used.
This constructor may create complex regions that will slow down painting when used.
QRegion::QRegion ( const QRegion & r )
Constructs a new region which is equal to region r.QRegion::QRegion ( const QBitmap & bm )
Constructs a region from the bitmap bm.The resulting region consists of the pixels in bitmap bm that are color1, as if each pixel was a 1 by 1 rectangle.
This constructor may create complex regions that will slow down painting when used. Note that drawing masked pixmaps can be done much faster using QPixmap::setMask().
QRegion::~QRegion ()
Destroys the region.QRect QRegion::boundingRect () const
Returns the bounding rectangle of this region. An empty region gives a rectangle that is QRect::isNull().bool QRegion::contains ( const QPoint & p ) const
Returns TRUE if the region contains the point p; otherwise returns FALSE.bool QRegion::contains ( const QRect & r ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It behaves essentially like the above function.Returns TRUE if the region overlaps the rectangle r; otherwise returns FALSE.
QRegion QRegion::eor ( const QRegion & r ) const
Returns a region which is the exclusive or (XOR) of this region and r.
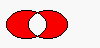
The figure shows the exclusive or of two elliptical regions.
HRGN QRegion::handle () const
Returns the region's handle.
QRegion QRegion::intersect ( const QRegion & r ) const
Returns a region which is the intersection of this region and r.
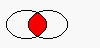
The figure shows the intersection of two elliptical regions.
bool QRegion::isEmpty () const
Returns TRUE if the region is empty; otherwise returns FALSE. An empty region is a region that contains no points.Example:
QRegion r1( 10, 10, 20, 20 );
QRegion r2( 40, 40, 20, 20 );
QRegion r3;
r1.isNull(); // FALSE
r1.isEmpty(); // FALSE
r3.isNull(); // TRUE
r3.isEmpty(); // TRUE
r3 = r1.intersect( r2 ); // r3 = intersection of r1 and r2
r3.isNull(); // FALSE
r3.isEmpty(); // TRUE
r3 = r1.unite( r2 ); // r3 = union of r1 and r2
r3.isNull(); // FALSE
r3.isEmpty(); // FALSE
See also isNull().
bool QRegion::isNull () const
Returns TRUE if the region is a null region; otherwise returns FALSE.A null region is a region that has not been initialized. A null region is always empty.
See also isEmpty().
bool QRegion::operator!= ( const QRegion & r ) const
Returns TRUE if the region is different from r; otherwise returns FALSE.
const QRegion QRegion::operator& ( const QRegion & r ) const
Applies the intersect() function to this region and r. r1&r2 is equivalent to r1.intersect(r2)
See also intersect().
QRegion & QRegion::operator&= ( const QRegion & r )
Applies the intersect() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1&=r2 is equivalent to r1=r1.intersect(r2)
See also intersect().
const QRegion QRegion::operator+ ( const QRegion & r ) const
Applies the unite() function to this region and r. r1+r2 is equivalent to r1.unite(r2)
See also unite() and operator|().
QRegion & QRegion::operator+= ( const QRegion & r )
Applies the unite() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1+=r2 is equivalent to r1=r1.unite(r2)
See also intersect().
const QRegion QRegion::operator- ( const QRegion & r ) const
Applies the subtract() function to this region and r. r1-r2 is equivalent to r1.subtract(r2)
See also subtract().
QRegion & QRegion::operator-= ( const QRegion & r )
Applies the subtract() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1-=r2 is equivalent to r1=r1.subtract(r2)
See also subtract().
QRegion & QRegion::operator= ( const QRegion & r )
Assigns r to this region and returns a reference to the region.bool QRegion::operator== ( const QRegion & r ) const
Returns TRUE if the region is equal to r; otherwise returns FALSE.const QRegion QRegion::operator^ ( const QRegion & r ) const
Applies the eor() function to this region and r. r1^r2 is equivalent to r1.eor(r2)
See also eor().
QRegion & QRegion::operator^= ( const QRegion & r )
Applies the eor() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1^=r2 is equivalent to r1=r1.eor(r2)
See also eor().
const QRegion QRegion::operator| ( const QRegion & r ) const
Applies the unite() function to this region and r. r1|r2 is equivalent to r1.unite(r2)
See also unite() and operator+().
QRegion & QRegion::operator|= ( const QRegion & r )
Applies the unite() function to this region and r and assigns the result to this region. r1|=r2 is equivalent to r1=r1.unite(r2)
See also unite().
QMemArray<QRect> QRegion::rects () const
Returns an array of non-overlapping rectangles that make up the region.The union of all the rectangles is equal to the original region.
QRegion QRegion::subtract ( const QRegion & r ) const
Returns a region which is r subtracted from this region.
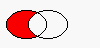
The figure shows the result when the ellipse on the right is subtracted from the ellipse on the left. (left-right )
void QRegion::translate ( int dx, int dy )
Translates (moves) the region dx along the X axis and dy along the Y axis.QRegion QRegion::unite ( const QRegion & r ) const
Returns a region which is the union of this region and r.
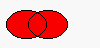
The figure shows the union of two elliptical regions.
Related Functions
QDataStream & operator<< ( QDataStream & s, const QRegion & r )
Writes the region r to the stream s and returns a reference to the stream.
See also Format of the QDataStream operators.
QDataStream & operator>> ( QDataStream & s, QRegion & r )
Reads a region from the stream s into r and returns a reference to the stream.
See also Format of the QDataStream operators.
This file is part of the Qt toolkit. Copyright © 1995-2002 Trolltech. All Rights Reserved.
| Copyright © 2002 Trolltech | Trademarks | Qt version 3.0.5
|