The Control Panel
Using the Serial/IP Control Panel
There are three ways to get to the Control Panel: In the Serial/IP program group in the Windows Start Menu, click the Control Panel shortcut; or in the Windows System Tray, right-click the Serial/IP icon and click the Configure command; or in the Windows Control Panel, open the Serial/IP applet.
If the Serial/IP Redirector has been installed with the Administrator Only Mode feature, then the Serial/IP Control Panel will only be available to users with Administrator privileges.
To configure a virtual COM port, select a virtual COM port in the list at the left, and then change the settings on the right. Changes will be recorded within two seconds, with no further action. To apply the settings of the current virtual COM port to other ports, click Copy Settings To, and then select the ports to receive the settings.
Advanced Options
To configure Advanced Options for all COM ports, open the Serial/IP Control Panel, and Click Advanced. In the Advanced Settings window, select the Options tab, and then change the settings.
Changed settings will not affect the operation of currently active virtual COM ports. See the Advanced Options section for further details.
Select Ports
The Select Ports command will display a window that allows selection of the Serial/IP COM ports.
To add or remove virtual COM ports in the Serial/IP Control Panel, click Select Ports. Change the installed virtual COM ports by selecting and clearing checkboxes. The corresponding COM port ranges will appear in the lower panel.
Alternatively, the COM port ranges may be edited directly. Use individual COM port numbers (such as 4, 5, 7) and/or ranges (such as 11-18, 30-53), separated by commas. When editing the COM port ranges, the checkboxes in the upper panel will change accordingly. Click OK when finished.
When the redirector is first installed, at least one virtual COM port must be selected. Virtual COM ports may be added and removed, but at least one port must remain.
The list of available COM ports will neither include COM ports for local hardware, nor any virtual COM ports created by other applications (such as printers and Bluetooth devices).
If a virtual COM port is removed and later recreated, then the settings of the previously removed COM port will be applied.
IP Address and Port Number
The IP Address of the Server and Port Number will inform the redirector of the location of the server on the network, and the TCP port number at which the server will provide the device for this virtual COM port. As noted below, up to four servers may be specified.
In the Serial/IP Control Panel, select a virtual COM port. In the IP Address field, type in either an IP address in the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx (e.g., 192.9.200.1.), or a hostname (e.g., devserver or devserver.xyz.com).
In Port Number, type in the TCP port number at which the server provides the serial device.
If the Serial/IP Redirector is unable to connect to a server, then the failover feature will attempt to connect to backup servers, if they are specified in IP Address.
To use the failover feature, enter up to four IP addresses or hostnames into IP Address, separated by space characters or commas. Examples: 192.9.200.1 192.9.200.2 or devserver1.xyz.com, devserver2.xyz.com, deserver3.xyz.com
If the redirector is unable to establish a connection to a server, then it will attempt to connect to the next server in the list. Each connection attempt will use the same TCP port number.
By default, the length of time for each connection attempt will be governed by the Windows TCP/IP stack. The duration of the attempt may be limited with the Advanced Option, End Connection Attempt after.
Accept Connections
Serial/IP is able to accept incoming TCP connections from remote devices by selecting the Accept Connections checkbox. For the associated Port Number, type in a TCP port number that is available on the local computer.
Each virtual COM port can be configured for outbound connections, inbound connections, or both.
If Restore Failed Connections is enabled, then it will only function for outbound connections. A failed inbound connection must be re-initiated by the remote device.
User Credentials
If the serial device server requires a login, then the Use Credentials From checkbox must be selected.
When Use Credentials From is selected, the redirector will wait for the server to prompt for a username and password. The virtual COM port can not be used by the application until the login sequence has successfully completed.
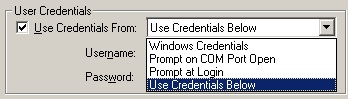
The Use Credentials checkbox and drop-down list
To set User Credentials, in the Serial/IP Control Panel, choose a virtual COM port and select the Use Credentials From checkbox. In the drop-down list, select one of the four sources for the credentials:
| · | Use Credentials Below - The redirector will take the credentials from the Username and Password fields. |
| · | Windows Credentials - The redirector will obtain values for the username and password every time a Windows login occurs. The redirector will have no username or password until the next Windows login. By default, the Advanced Option, Include Domain in Windows Credentials will be enabled, in which the redirector will send the Windows domain name along with the credentials to the server. |
| · | Prompt at Login - Every time a user logs into Windows, the redirector will display a window prompting for a username and password. To change the credentials, click Prompt Now. This option will not be available on multi-user operating systems such as Microsoft Terminal Services and Citrix MetaFrame Access Suite. If a user is not logged in at the time a COM port is opened, then the redirector will proceed as if the Use Credentials From checkbox was not selected. |
| · | Prompt on COM Port Open - Every time an application opens this virtual COM port, the redirector will display a window prompting for a username and password. These credentials will only be applied for this specific use of the virtual COM port. If a user is not logged in at the time a COM port is opened, then the redirector will proceed as if the Use Credentials From checkbox was not selected. If the user clicks Cancel, or does not click OK within 60 seconds, then the redirector will proceed as if credentials were not required for this connection. This option is not available on multi-user operating systems such as Microsoft Terminal Services and Citrix MetaFrame Access Suite. |
Connection Protocol
The setting for Connection Protocol defines the TCP/IP network protocol that the redirector will use when connecting to the serial device server.
Auto Configure will reliably detect the correct setting for Connection Protocol. It is important to use the setting that the Auto Configure recommends.
To set the Connection Protocol, in the Serial/IP Control Panel, select a virtual COM port. Then select either Telnet or Raw TCP under Connection Protocols. However, the preferred method is to run Auto Configure and click the Use Settings button after it has completed.
The Raw TCP Connection is the default setting in which the redirector uses a TCP/IP socket connection, with no additional protocol.
When the redirector is set to use the Telnet protocol to connect to the server, additional telnet information can be sent. The COM Port Control protocol is a subset of the Telnet protocol that will be used by the redirector, if it is supported by the server.
Using the Telnet protocol does not mean that the connection will be made on the standard TCP port for Telnet (port 23). The TCP port that is being used will be specified in the Port Number field for the virtual COM port.
DSR / DCD / CTS Emulation
Serial/IP can emulate the behavior of the DSR, DCD, and CTS signals. To set DSR / DCD / CTS Emulation in the Serial/IP Control Panel, select a checkbox. Then in the drop-down list, select an emulation method.
When this setting is not selected, the redirector will not emulate the control signals. If the server supports the COM Port Control protocol, then the signal will track the real-time condition of the signal, as reported by the server. If the server does not support the COM Port Control protocol, then the signal will always indicate as low.
When a setting is Enabled and set to Always High, the corresponding signal will always indicate as high. When it is Enabled and set to Always Low, the signal will always indicate as low. Setting it to Enabled and Track Connection causes the signal to indicate as high when there is a network connection to the server, and as low otherwise.
There is seldom a reason to use DSR / DCD / CTS Emulation. Only check this setting if the application will need a different pattern of signals, other than those being relayed by the redirector from the server, or to compensate for the lack of COM Port Control protocol support in the server.
If Auto Configure detects server support for the COM Port Control protocol, then it will recommend disabling the settings for the signal emulations. If any signal emulation is enabled, then it will override the effects of the COM Port Control protocol.
DTR is Modem Escape
The Serial/IP Redirector can simulate DTR signal transitions.
To set DTR is Modem Escape, in the Serial/IP Control Panel, select the DTR is Modem Escape checkbox.
This feature is primarily used when a modem application (notably Windows Dial-up Networking) requires that the DTR signal be used as a method of telling the modem to enter command mode.
If the Auto Configure detects server support for the COM Port Control protocol, then this option will have no effect.
Restore Failed Connections
This option will make the Serial/IP Redirector attempt to restore failed network connections to the server.
To set Restore Failed Connections, in the Serial/IP Control Panel, select the Restore Failed Connections checkbox.
When this setting is enabled and the redirector notices that the TCP connection is broken, it will immediately attempt to reconnect to the server. The reconnection attempt will fail if the Windows TCP/IP stack indicates a failure, or the interval specified in End Connection Attempt after expires. If a reconnection attempt fails, then the redirector will keep trying at increasing intervals until the connection is restored, or the application closes the virtual COM port.
The Restore Failed Connections option should only be used if the application can continue normal operation after a failed connection becomes restored.