|
|
FORECAST
Calculates, or predicts, a future value by using existing values. The predicted value is a y-value for a given x-value. The known values are existing x-values and y-values, and the new value is predicted by using linear regression. You can use this function to predict future sales, inventory requirements, or consumer trends.
Syntax
FORECAST(x,known_y's,known_x's)
X is the data point for which you want to predict a value.
Known_y's is the dependent array or range of data.
Known_x's is the independent array or range of data.
Remarks
- If x is nonnumeric, FORECAST returns the #VALUE! error value.
- If known_y's and known_x's are empty or contain a different number of data points, FORECAST returns the #N/A error value.
- If the variance of known_x's equals zero, then FORECAST returns the #DIV/0! error value.
- The equation for FORECAST is a+bx, where:
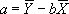
and:
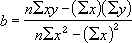
Example
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank spreadsheet.
- Create a blank spreadsheet.
- Select the example in the Help topic.

Selecting an example from Help
- Press CTRL+C.
- In the spreadsheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
- To switch between viewing the formula that returns the result and the result in the cell, select the cell and press F2 and then ENTER, or click Commands and Options on the spreadsheet toolbar, click the Formula tab, and look in the Formula in active cell (active cell) box.
| Known Y | Known X |
|---|---|
| 6 | 20 |
| 7 | 28 |
| 9 | 31 |
| 15 | 38 |
| 21 | 40 |
| Formula | Description (Result) |
| =FORECAST(30,A2:A6,B2:B6) | Predicts a value for y given an x value of 30 (10.60725) |
 How?
How?