Owning Palette: FPGA Interface Functions
Installed With: FPGA Interface
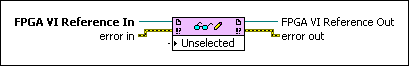
Reads a value from or writes a value to a control or indicator in the FPGA VI on the FPGA target.
 Place on the block diagram Place on the block diagram |  Find on the Functions palette Find on the Functions palette |
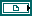 | FPGA VI Reference In is the reference to the FPGA VI running on the FPGA target. You must open a reference to the FPGA VI to use this parameter. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code.
Use exception control to treat what is normally an error as no error or to treat a warning as an error.
Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
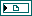 | FPGA VI Reference Out returns a reference to the FPGA VI running on the FPGA target. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
Read/Write Control Details
A host VI can control and monitor data passed through the FPGA VI front panel. You cannot access values on any wires on the FPGA VI block diagram that do not have controls or indicators unless the data is stored in a DMA FIFO.
First use the Open FPGA VI Reference function to open a reference to the FPGA target. Then wire the FPGA VI Reference Out parameter to the Read/Write Control function to access controls and indicators on the FPGA VI. You can read indicators and write controls. You also can write indicators and read controls. You can expand the Read/Write Control function to read or write multiple controls and indicators. When you run the host VI, the Read/Write Control function reads and writes controls and indicators in the order they appear in the Read/Write Control function on the block diagram.
 | Tip The Read/Write Control function supports scalar data, such as numeric and Boolean controls, and complex data, such as arrays and clusters. You can program the FPGA VI to bundle scalar data into arrays or clusters and then read or write the arrays or clusters of data as a single block with the host VI to make sure all data is read or written at the same time. You can use the Read/Write Control function to read whole clusters or an individual element of a cluster. If you need to read multiple elements of a cluster, read the whole cluster. You can write to a whole cluster, but you cannot write to individual elements of a cluster. Be careful not to overuse arrays because arrays use space on an FPGA target. |
The FPGA Module creates a register map, specific to the FPGA VI, that includes a hardware register for every control and indicator. LabVIEW uses the register map internally to communicate with the FPGA VI directly with Interactive Front Panel Communication and using the host VI with Programmatic FPGA Interface Communication.