Owning Palette: FPGA Interface Functions
Installed With: FPGA Interface
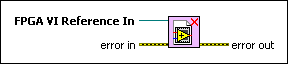
Closes the reference to the FPGA VI and, optionally, resets or aborts execution of the VI.
The Close FPGA VI Reference function also stops all DMA FIFOs on the FPGA.
 Place on the block diagram Place on the block diagram |  Find on the Functions palette Find on the Functions palette |
 | FPGA VI Reference In is the reference to the FPGA VI running on the FPGA target. You must open a reference to the FPGA VI to use this parameter. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally even if an error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code.
Use exception control to treat what is normally an error as no error or to treat a warning as an error.
Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
Close FPGA VI Reference Details
The Close FPGA VI Reference function always closes the reference to the FPGA VI. To configure this function to only close the reference, right-click the function and select Close from the shortcut menu.
When the FPGA target is set to Execute VI on FPGA Target, you also can right-click the Close FPGA VI Reference function and select Close and Reset if Last Reference from the shortcut menu to stop and reset the FPGA VI running on the FPGA target if the function is invoked for the last reference to the VI.
When the FPGA target is set to Execute VI on Development Computer, you also can right-click the Close FPGA VI Reference function and select Close and Abort without Reference Counting from the shortcut menu to abort the FPGA VI. Reference counting is not available in this case, so the function always aborts the FPGA VI.
When you change the target configuration from execution on the FPGA target to execution on the development computer, the FPGA Module translates Close and Reset if Last Reference as Close and Abort without Reference Counting. When you change the target configuration from execution on the development computer to execution on the FPGA target, the FPGA Module translates Close and Abort without Reference Counting as Close and Reset if Last Reference.
There are differences in behavior between resetting the VI executing on the FPGA target and aborting the VI executing on the development computer. Resetting the VI on an FPGA target sets VI controls and indicators to their default states, sets uninitialized shift registers to their default values, clears FIFOs, and sets global variables to their default values. Aborting the VI on the development computer does not reset the default values in the FPGA VI. The behavior of aborting the VI on the development computer depends on whether that VI remains in memory after a reference to the VI is closed. If the VI is not in memory, the next time you open a reference to that VI, the VI behaves as if it was just loaded from disk, with all of the relevant values set to defaults. If the VI is in memory, the next time you open a reference to the VI, the VI is in with whatever internal state it happens to be in. The VI remains in memory if the front panel is open, the VI is a subVI of another VI, or there are other references to the VI.