Retrieving and Writing XML Data
You can execute SQL queries to return results as XML rather than standard rowsets. These queries can be executed directly or from within stored procedures. To retrieve results directly, you use the FOR XML clause of the SELECT statement, and within the FOR XML clause you specify an XML mode: RAW, AUTO, or EXPLICIT.
For example, this SELECT statement retrieves information from Customers and Orders table in the Northwind database. This query specifies the AUTO mode in the FOR XML clause:
SELECT Customers.CustomerID, ContactName, CompanyName,
Orders.CustomerID, OrderDate
FROM Customers, Orders
WHERE Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID
AND (Customers.CustomerID = N'ALFKI'
OR Customers.CustomerID = N'XYZAA')
ORDER BY Customers.CustomerID
FOR XML AUTO
Whereas you can use the FOR XML clause to retrieve data as an XML document, you can use the Transact-SQL OPENXML function to insert data represented as an XML document. OPENXML is a rowset provider similar to a table or a view, providing a rowset over in-memory XML documents. OPENXML allows access to XML data as if it is a relational rowset by providing a rowset view of the internal representation of an XML document. The records in the rowset can be stored in database tables. OPENXML can be used in SELECT, and SELECT INTO statements where a source table or view can be specified.
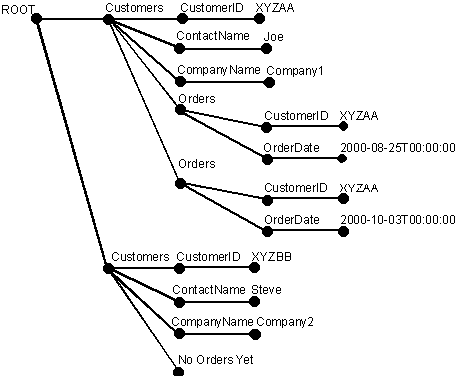
The following example shows the use of OPENXML in an INSERT statement and a SELECT statement. The sample XML document consists of <Customers> and <Orders> elements. First, the sp_xml_preparedocument stored procedure parses the XML document. The parsed document is a tree representation of the nodes (elements, attributes, text, comments, and so on) in the XML document. OPENXML then refers to this parsed XML document and provides a rowset view of all or parts of this XML document. An INSERT statement using OPENXML can insert data from such a rowset into a database table. Several OPENXML calls can be used to provide rowset view of various parts of the XML document and process them, for example, inserting them into different tables (this process is also referred to as "Shredding XML into tables"). In the following example, an XML document is shredded in a way that <Customers> elements are stored in the Customers table and <Orders> elements are stored in the Orders table using two INSERT statements.
The example also shows a SELECT statement with OPENXML that retrieves CustomerID and OrderDate from the XML document.
DECLARE @hDoc int
EXEC sp_xml_preparedocument @hDoc OUTPUT,
N'<ROOT>
<Customers CustomerID="XYZAA" ContactName="Joe"
CompanyName="Company1">
<Orders CustomerID="XYZAA"
OrderDate="2000-08-25T00:00:00"/>
<Orders CustomerID="XYZAA"
OrderDate="2000-10-03T00:00:00"/>
</Customers>
<Customers CustomerID="XYZBB" ContactName="Steve"
CompanyName="Company2">No Orders yet!
</Customers>
</ROOT>'
-- Use OPENXML to provide rowset consisting of customer data.
INSERT Customers
SELECT *
FROM OPENXML(@hDoc, N'/ROOT/Customers')
WITH Customers
-- Use OPENXML to provide rowset consisting of order data.
INSERT Orders
SELECT *
FROM OPENXML(@hDoc, N'//Orders')
WITH Orders
-- Using OPENXML in a SELECT statement.
SELECT * FROM OPENXML(@hDoc, N'/ROOT/Customers/Orders') with (CustomerID nchar(5) '../@CustomerID', OrderDate datetime)
-- Remove the internal representation of the XML document.
EXEC sp_xml_removedocument @hDoc
This illustration shows the parsed XML tree of the preceding XML document that was created by sp_xml_pareparedocument.