MB Serial Init.vi
Initializes the serial port specified by VISA resource name to the specified settings. Wire data to the VISA resource name input to determine the polymorphic instance to use or manually select the instance.
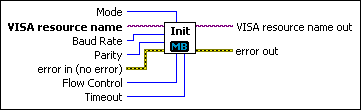
 | Mode is used to select which type of MODBUS frame to use. For MB Serial Init.vi, this affects the number of data bits the serial port uses.
RTU Data is represented in binary format (8 data bits). ASCII | ||||||||||||
 | VISA resource name specifies the resource to be opened. This control also specifies the session and class. For more information about VISA resource names, refer to the NI-VISA Help. | ||||||||||||
 | Baud Rate is the rate of transmission. The default is 9600. | ||||||||||||
 | Parity specifies the parity used for every frame to be transmitted or received. This input accepts the following values:
| ||||||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs. The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, the VI or function runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||||||||
 | Flow Control sets the type of control the transfer mechanism uses. This input accepts the following values:
| ||||||||||||
 | Timeout specifies the maximum time period, in milliseconds, that the VI waits for the slave's response before throwing an error. | ||||||||||||
 | VISA resource name out is the resource to which a VISA session is opened and its class. The class matches that of the VISA resource name input. For more information about VISA resource names, refer to the NI-VISA Help. | ||||||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces. Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|